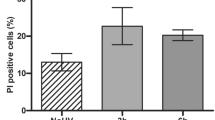
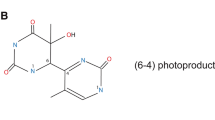
Abstract
The ultraviolet (UV) B portion of the UV light has been recognized as the most prominent risk factor for the development of skin cancer, the most common malignancy in the Caucasian population. At the cellular level, UVB signal transduction regulates replicative arrest and DNA repair, gene expression and, when damage is beyond repair, apoptotic cell death, which is induced to protect the host against the accumulation of potentially mutagenic keratinocytes. An increasing body of evidence indicates that the UVB response in skin is a complex and multifaceted biological process. The UVB signal transduction originates at multiple intracellular sites, and the cross talk between dedicated molecular mediators acting within a complex signal network, determines whether the UVB damaged cell will survive, proliferate or die. However, very little is known about the original targets or direct chromophores that put in motion the UVB response in its main target: the keratinocyte. In this review we discuss the recent identification of signalling pathways linking apical UVB mediated damaging events with the induction of apoptosis. Understanding the molecular mechanisms that underlie the process of apoptotic cell death in UVB exposed keratinocytes, is of outmost importance to reveal how defects in apoptotic pathways can contribute to skin cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Matsumura and H. N. Ananthaswamy, Toxic effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 2004, 195, 298–308.
W. A. Bruls, H. Slaper, J. C. van der Leun and L. Berrens, Transmission of human epidermis and stratum corneum as a function of thickness in the ultraviolet and visible wavelengths, Photochem. Photobiol., 1984, 40, 485–94.
R. Lavker and K. J. Kaidbey, The spectral dependence for UVA-induced cumulative damage in human skin., Invest Dermatol., 1997, 108, 17–21.
D. I. Pattison and M. J. Davies, Actions of ultraviolet light on cellular structures, EXS, 2006, 96, 131–57.
J. Krutmann, The interaction of UVA and UVB wavebands with particular emphasis on signalling, Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol., 2006, 92, 105–7.
H. S. Black, F. R. de Gruijl, P. D. Forbes, J. E. Cleaver, H. N. Ananthaswamy, E. C. de Fabo, S. E. Ullrich and R. M. Tyrrell, Photocarcinogenesis: an overview, J. Photochem. Photobiol., 1997, 40, 29–47.
F. Trautinger, Mechanisms of photodamage of the skin and its functional consequences for skin ageing, Clin. Exp. Dermatol., 2001, 26, 573–7.
J. M. Sheehan and A. R. Young, The sunburn cell revisited: an update on mechanistic aspects, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2002, 1, 365–77.
A. Van Laethem, S. Claerhout, M. Garmyn and P. Agostinis, The sunburn cell: regulation of death and survival of the keratinocyte, Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 2005, 37, 1547–53.
H. Soehnge, A. Ouhtit and O. N. Ananthaswamy, Mechanisms of induction of skin cancer by UV radiation, Front. Biosci., 1997, 1, 538–51.
R. J. Berg, H. Rebel, G. T. van der Horst, H. J. van Kranen, L. H. Mullenders, W. A. van Vloten and F. R. de Gruijl, Impact of global genome repair versus transcription-coupled repair on ultraviolet carcinogenesis in hairless mice, Cancer Res., 2000, 60, 2858–63.
C. S. Wu, C. C. Lan, M. H. Chiou and H. S. Yu, Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes melanocyte migration via increased expression of p125(FAK) on melanocytes, Acta Dermatol. Venereol., 2006, 86, 498–502.
D. Fagot, D. Asselineau and F. Bernerd, Direct role of human dermal fibroblasts and indirect participation of epidermal keratinocytes in MMP-1 production after UV-B irradiation, Arch. Dermatol. Res., 2002, 293, 576–83.
D. J. Leffell, The scientific basis of skin cancer, J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 2000, 42, 18–22.
T. M. Rünger and U. P. Kappes, Mechanisms of mutation formation with long-wave ultraviolet light (UVA), Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed., 2008, 24, 2–10.
D. Decraene, P. Agostinis, A. Pupe, P. de Haes and M. Garmyn, Acute response of human skin to solar radiation: regulation and function of the p53 protein, J. Photochem. Photobiol., 2001, 63, 78–83.
M. Oren, Decision making by p53: life, death and cancer, Cell Death Differ., 2003, 10, 431–42.
A. Ziegler, A. S. Jonason, D. J. Leffell, J. A. Simon, H. W. Sharma, J. Kimmelman, L. Remington, T. Jacks and D. E. Brash, Sunburn and p53 in the onset of skin cancer, Nature, 1994, 372, 773–6.
L. Latonen and M. Laiho, Cellular UV damage responses-functions of tumor suppressor p53, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2005, 1755, 71–89.
S. Jin, T. Tong, W. Fan, F. Fan, M. J. Antinore, X. Zhu, L. Mazzacurati, X. Li, K. L. Petrik, B. Rajasekaran, M. Wu and Q. Zhan, GADD45-induced cell cycle G2-M arrest associates with altered subcellular distribution of cyclin B1 and is independent of p38 kinase activity, Oncogene, 2002, 21, 8696–704.
Y. Shiloh, ATM and related protein kinases: safeguarding genome integrity, Nature Rev. Cancer, 2003, 3, 155–168.
L. D. Attardi and T. Jacks, The role of p53 in tumour suppression: lessons from mouse models, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 1999, 55, 48–63.
W. Bruins, E. Zwart, L. D. Attardi, T. Iwakuma, E. M. Hoogervorst, R. B. Beems, B. Miranda, C. T. van Oostrom, J. van den Berg, G. J. van den Aardweg, G. Lozano, H. van Steeg, T. Jacks and A. de Vries, Increased sensitivity to UV radiation in mice with a p53 point mutation at Ser389, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2004, 24, 8884–8894.
J. S. Reis-Filho, B. Torio, A. Albergaria and F. C. Schmitt, p63 expression in normal skin and usual cutaneous carcinomas, J. Cutan. Pathol., 2002, 29, 517–23.
M. Papoutsaki, F. Moretti, M. Lanza, B. Marinari, V. Sartorelli, L. Guerrini, S. Chimenti, M. Levrero and A. Costanzo, A p38-dependent pathway regulates DeltaNp63 DNA binding to p53-dependent promoters in UV-induced apoptosis of keratinocytes, Oncogene, 2005, 24, 6970–5.
G. Pellegrini, E. Dellambra, O. Golisano, E. Martinelli, I. Fantozzi, S. Bondanza, D. Ponzin, F. McKeon and M. De Luca, p63 identifies keratinocyte stem cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2001, 98, 3156–61.
J. Hildesheim, D. V. Bulavin, M. R. Anver, W. G. Alvord, M. C. Hollander, L. Vardanian and A. J. Fornace, Jr., Gadd45a protects against UV irradiation-induced skin tumors, and promotes apoptosis and stress signaling via MAPK and p53, Cancer Res., 2002, 62, 7305–7315.
N. D. Marchenko, A. Zaika and U. M. Moll, Death signal-induced localization of p53 protein to mitochondria. A potential role in apoptotic signaling, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275, 16202–12.
J. E. Chipuk, T. Kuwana, L. Bouchier-Hayes, N. M. Droin, D. D. Newmeyer, M. Schuler and D. R. Green, Direct activation of Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and apoptosis, Science, 2004, 303, 1010–4.
Z. Assefa, A. Vantieghem, M. Garmyn, W. Declercq, P. Vandenabeele, J. R. Vandenheede, R. Bouillon, W. Merlevede and P. Agostinis, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates a novel, caspase-independent pathway for the mitochondrial cytochrome c release in ultraviolet B radiation-induced apoptosis, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275, 21416–21.
K. H. Kraemer, Sunlight and skin cancer: another link revealed, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1997, 94, 11–4.
D. A. Norris, M. H. Middleton, K. Whang, M. Schleicher, T. McGovern, S. D. Bennion, K. David-Bajar, D. Davis and R. C. Duke, Human keratinocytes maintain reversible anti-apoptotic defenses in vivo and in vitro, Apoptosis, 1997, 2, 136–48.
V. Chaturvedi, J. Z. Qin, L. Stennett, D. Choubey and B. J. Nickoloff, Resistance to UV-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes during accelerated senescence is associated with functional inactivation of p53, J. Cell Physiol., 2004, 198, 100–109.
A. Mandinova, K. Lefort, A. Tommasi di Vignano, W. Stonely, P. Ostano, G. Chiorino, H. Iwaki, J. Nakanishi and G. P. Dotto, The FoxO3a gene is a key negative target of canonical Notch signalling in the keratinocyte UVB response, EMBO J., 2008, 27, 1243–54.
J. Z. Qin, P. Bacon, J. Panella, L. A. Sitailo, M. F. Denning and B. J. Nickoloff, Low-dose UV-radiation sensitizes keratinocytes to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, J. Cell Physiol., 2004, 200, 155–66.
D. Kulms and T. Schwarz, Molecular mechanisms involved in UV-induced apoptotic cell death, Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol., 2002, 15, 342–7.
B. Bang, R. Gniadecki, J. K. Larsen, O. Baadsgaard and L. Skov, In vivo UVB irradiation induces clustering of Fas (CD95) on human epidermal cells, Exp. Dermatol., 2003, 12, 791–8.
A. Gröne, Keratinocytes and cytokines, Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol., 2002, 88, 1–12.
R. L. Eckert, T. Efimova, S. R. Dashti, S. Balasubramanian, A. Deucher, J. F. Crish, M. Sturniolo and F. Bone, Keratinocyte survival, differentiation, and death: many roads lead to mitogen-activated protein kinase, J. Invest. Dermatol. Symp. Proc., 2002, 7, 36–40.
S. Kondo, D. N. Sauder, T. Kono, K. A. Galley and R. C. McKenzie, Differential modulation of interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) in human epidermal keratinocytes by UVB, Exp. Dermatol., 1994, 3, 29–39.
Y. Ogura, F. S. Sutterwala and R. A. Flavell, The inflammasome: first line of the immune response to cell stress, Cell., 2006, 126, 659–62.
F. Martinon, K. Burns and J. Tschopp, The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta, Mol. Cell, 2002, 10, 417–26.
J. A. Kummer, R. Broekhuizen, H. Everett, L. Agostini, L. Kuijk, F. Martinon, R. van Bruggen and J. Tschopp, Inflammasome components NALP 1 and 3 show distinct but separate expression profiles in human tissues suggesting a site-specific role in the inflammatory response, J. Histochem. Cytochem., 2007, 55, 443–52.
H. Watanabe, O. Gaide, V. Pétrilli, F. Martinon, E. Contassot, S. Roques, J. A. Kummer, J. Tschopp and L. E. French, Activation of the IL-1beta-processing inflammasome is involved in contact hypersensitivity, J. Invest. Dermatol., 2007, 127, 1956–63.
L. Feldmeyer, M. Keller, G. Niklaus, D. Hohl, S. Werner and H. D. Beer, The inflammasome mediates UVB-induced activation and secretion of interleukin-1beta by keratinocytes, Curr. Biol., 2007, 17, 1140–5.
D. Decraene, P. Agostinis, R. Bouillon, H. Degreef and M. Garmyn, Insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated AKT activation postpones the onset of ultraviolet B-induced apoptosis, providing more time for cyclobutane thymine dimer removal in primary human keratinocytes, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277, 32587–95.
F. Belleudi, L. Leone, L. Aimati, M. G. Stirparo, G. Cardinali, C. Marchese, L. Frati, M. Picardo and M. R. Torrisi, Endocytic pathways and biological effects induced by UVB-dependent or ligand-dependent activation of the keratinocyte growth factor receptor, FASEB J., 2006, 20, 395–7.
Y. Xu, J. J. Voorhees and G. J. Fisher, Epidermal growth factor receptor is a critical mediator of ultraviolet B irradiation-induced signal transduction in immortalized human keratinocyte HaCaT cells, Am. J. Pathol., 2006, 169, 823–30.
D. A. Lewis, S. A. Hurwitz and D. F. Spandau, UVB-induced apoptosis in normal human keratinocytes: role of the erbB receptor family, Exp. Cell Res., 2003, 284, 316–27.
H. Q. Wang, T. Quan, T. T. F. He, F. Franke, J. J. Voorhees and G. J. Fisher, Epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent, NF-kappaB-independent activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway inhibits ultraviolet irradiation-induced caspases-3, -8, and −9 in human keratinocytes, J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278, 45737–45.
M. Seo, M. J. Lee, J. H. Heo, Y. I. Lee, Y. Kim, S. Y. Kim, E. S. Lee and Y. S. Juhnn, G protein beta gamma subunits augment UVB-induced apoptosis by stimulating the release of soluble heparin binding EGF-like growth factor from human keratinocytes, J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282, 24720–30.
E. Fritsche, C. Schäfer, C. Calles, T. Bernsmann, T. Bernshausen, M. Wurm, U. Hübenthal, J. E. Cline, H. Hajimiragha, P. Schroeder, L. O. Klotz, A. Rannug, P. Fürst, H. Hanenberg, J. Abel and J. Krutmann, Lightening up the UV response by identification of the arylhydrocarbon receptor as a cytoplasmatic target for ultraviolet B radiation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007, 104, 8851–6.
P. Agostinis, M. Garmyn and A. Van Laethem, The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: An illuminating effector of the UVB response, Sci STKE, 2007, 403, pe49.
D. R. Bickers and M. Athar, Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of skin disease, J. Invest. Dermatol., 2006, 126, 2565–75.
M. Ding, J. Li, S. S. Leonard, X. Shi, M. Costa, V. Castranova, V. Vallyathan and C. Huang, Differential role of hydrogen peroxide in UV-induced signal transduction, Mol. Cell. Biochem., 2002, 234–235, 81–90.
H. R. Rezvani, F. Mazurier, M. Cario-André, C. Pain, C. Ged, A. Taïeb and H. de Verneuil, Protective effects of catalase overexpression on UVB-induced apoptosis in normal human keratinocytes, J. Biol. Chem., 2006, 281, 17999–8007.
G. H. Jin, Y. Liu, S. Z. Jin, X. D. Liu and S. Z. Liu, UVB induced oxidative stress in human keratinocytes and protective effect of antioxidant agents, Radiat. Environ. Biophys., 2007, 46, 61–8.
Z. Assefa, M. Garmyn, A. Vantieghem, W. Declercq, P. Vandenabeele, J. R. Vandenheede and P. Agostinis, Ultraviolet B radiation-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes: cytosolic activation of procaspase-8 and the role of Bcl-2, FEBS Lett., 2003, 540, 125–32.
D. E. Heck, A. M. Vetrano, T. M. Mariano and J. D. Laskin, UVB light stimulates production of reactive oxygen species: unexpected role for catalase, J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278, 22432–6.
C. S. Sander, H. Chang, S. Salzmann, C. S. Müller, S. Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, P. Elsner and J. J. Thiele, Photoaging is associated with protein oxidation in human skin in vivo, J. Invest. Dermatol., 2002, 118, 618–25.
E. Kvam and R. M. Tyrrell, Induction of oxidative DNA base damage in human skin cells by UV and near visible radiation, Carcinogenesis, 1997, 18(12), 2379–84.
A. Van Laethem, K. Nys, S. Van Kelst, S. Claerhout, H. Ichijo, J. R. Vandenheede, M. Garmyn and P. Agostinis, Apoptosis signal regulating kinase-1 connects reactive oxygen species to p38 MAPK-induced mitochondrial apoptosis in UVB-irradiated human keratinocytes, Free Radical Biol. Med., 2006, 41, 1361–71.
H. Wang and I. E. Kochevar, Involvement of UVB-induced reactive oxygen species in TGF-beta biosynthesis and activation in keratinocytes, Free Radic Biol. Med., 2005, 38, 890–7.
J. D. Lambeth, NOX enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen, Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2004, 4, 181–9.
Z. Assefa, A. Van Laethem, M. Garmyn and P. Agostinis, Ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis in keratinocytes: on the role of cytosolic factors, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2005, 1755, 90–106.
D. Decraene, K. Smaers, D. Gan, T. Mammone, M. Matsui, D. Maes, L. Declercq and M. Garmyn, A synthetic superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetic (EUK-134) inhibits membrane-damage-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and reduces p53 accumulation in ultraviolet B-exposed primary human keratinocytes, J. Invest. Dermatol., 2004, 122, 484–91.
D. Peus, R. A. Vasa, A. Beyerle, A. Meves, C. Krautmacher and M. R. Pittelkow, UVB activates ERK1/2 and p38 signaling pathways via reactive oxygen species in cultured keratinocytes, J. Invest. Dermatol., 1999a, 112, 751–6.
F. Afaq, N. Ahmad and H. Mukhtar, Suppression of UVB-induced phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor kappa B by green tea polyphenol in SKH-1 hairless mice, Oncogene, 2003, 22, 9254–64.
M. Nomura, A. Kaji, W. Y. Ma, S. Zhong, G. Liu, G. T. Bowden, K. I. Miyamoto and Z. Dong, Mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1 mediates activation of Akt by ultraviolet B irradiation, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276, 25558–67.
A. M. Bode and Z. Dong, Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in UV-induced signal transduction, Sci STKE, 2003, 28.
A. Van Laethem, S. Van Kelst, S. Lippens, W. Declercq, P. Vandenabeele, S. Janssens, J. R. Vandenheede, M. Garmyn and P. Agostinis, Activation of p38 MAPK is required for Bax translocation to mitochondria, cytochrome c release and apoptosis induced by UVB irradiation in human keratinocytes, FASEB J., 2004, 18, 1946–8.
S. Gross, A. Knebel, T. Tenev, A. Neininger, M. Gaestel, P. Herrlich and F. D. Böhmer, Inactivation of protein-tyrosine phosphatases as mechanism of UV-induced signal transduction, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, 274, 26378–86.
J. Matsukawa, A. Matsuzawa, K. Takeda and H. Ichijo, The ASK1-MAP kinase cascades in mammalian stress response, J. Biochem., 2004, 136, 261–5.
H. R. Rezvani, S. Dedieu, S. North, F. Belloc, R. Rossignol, T. Letellier, H. de Verneuil, A. Taïeb and F. Mazurier, Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, a key factor in the keratinocyte response to UVB exposure, J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282, 16413–22.
C. Saliou, M. Kitazawa, L. McLaughlin, J. P. Yang, J. K. Lodge, T. Tetsuka, K. Iwasaki, J. Cillard, T. Okamoto and L. Packer, Antioxidants modulate acute solar ultraviolet radiation-induced NF-kappa-B activation in a human keratinocyte cell line, Free Radical Biol. Med., 1999, 26, 174–83.
D. A. Lewis and D. F. Spandau, UVB-induced activation of NF-kappaB is regulated by the IGF-1R and dependent on p38 MAPK, J. Invest. Dermatol., 2008, 128, 1022–9.
K. Otkjaer, K. Kragballe, C. Johansen, A. T. Funding, H. Just, U. B. Jensen, L. G. Sørensen, P. L. Nørby, J. T. Clausen and L. Iversen, IL-20 gene expression is induced by IL-1beta through mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB-dependent mechanisms, J. Invest. Dermatol., 2007, 127, 1326–36.
M. Karin and Y. Ben-Neriah, Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity, Annu. Rev. Immunol., 2000, 18, 621–63.
P. Herrlich, M. Karin and C. Weiss, Supreme EnLIGHTenment: damage recognition and signaling in the mammalian UV response, Mol. Cell, 2008, 29, 279–90.
J. Z. Qin, V. Chaturvedi, M. F. Denning, D. Choubey, M. O. Diaz and B. J. Nickoloff, Role of NF-kappaB in the apoptotic-resistant phenotype of keratinocytes, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, 274, 37957–64.
M. van Hogerlinden, B. L. Rozell, L. Ahrlund-Richter and R. Toftgård, Squamous cell carcinomas and increased apoptosis in skin with inhibited Rel/nuclear factor-kappaB signaling, Cancer Res, 1999, 59, 3299–303.
D. A. Lewis and D. F. Spandau, UVB activation of NF-kappaB in normal human keratinocytes occurs via a unique mechanism, Arch. Dermatol. Res., 2007, 299, 93–101.
S. Grundström, P. Anderson, P. Scheipers and A. Sundstedt, Bcl-3 and NFkappaB p50-p50 homodimers act as transcriptional repressors in tolerant CD4+ T cells, J. Biol. Chem., 2004, 279, 8460–8.
S. K. Mantena and S. K. Katiyar, Grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit UV-radiation-induced oxidative stress and activation of MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling in human epidermal keratinocytes, Free Radical Biol. Med., 2006, 40, 1603–14.
B. J. Nickoloff, J. Z. Qin, V. Chaturvedi, P. Bacon, J. Panella and M. F. Denning, Life and death signaling pathways contributing to skin cancer, J. Invest. Dermatol. Symp. Proc., 2002, 7, 27–35.
L. A. Sitailo, S. S. Tibudan and M. F. Denning, Activation of caspase-9 is required for UV-induced apoptosis of human keratinocytes, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277, 19346–52.
R. Takasawa and S. Tanuma, Sustained release of Smac/DIABLO from mitochondria commits to undergo UVB-induced apoptosis, Apoptosis, 2003, 8, 291–9.
L. A. Sitailo, S. S. Tibudan and M. F. Denning, Bax activation and induction of apoptosis in human keratinocytes by the protein kinase C delta catalytic domain, J. Invest. Dermatol., 2004, 123, 434–443.
M. F. Denning, Y. Wang, S. Tibudan, S. Alkan, B. J. Nickoloff and J. Z. Qin, Caspase activation and disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential during UV radiation-induced apoptosis of human keratinocytes requires activation of protein kinase C, Cell Death Differ., 2002, 9, 40–52.
D. Grossman, J. M. McNiff, F. Li and D. C. Altieri, Expression of the apoptosis inhibitor, survivin, in nonmelanoma skin cancer and gene targeting in a keratinocyte cell line, Lab Invest., 1999, 79, 1121–6.
D. Grossman, P. J. Kim, O. P. Blanc-Brude, D. E. Brash, S. Tognin, P. C. Marchisio and D. C. Altieri, Transgenic expression of survivin in keratinocytes counteracts UVB-induced apoptosis and cooperates with loss of p53, J. Clin. Invest., 2001, 108, 991–9.
D. Kulms and T. Schwarz, Independent contribution of three different pathways to ultraviolet-B-induced apoptosis, Biochem. Pharmacol., 2002, 64, 837–41.
D. V. Bulavin, S. Saito, M. C. Hollander, K. Sakaguchi, C. W. Anderson, E. Appella and A. J. Fornace, Phosphorylation of human p53 by p38 kinase coordinates N-terminal phosphorylation and apoptosis in response to UV radiation, EMBO J., 1999, 18, 6845–54.
Q. B. She, N. Chen and Z. Dong, ERKs and p38 kinase phosphorylate p53 protein at serine 15 in response to UV radiation, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275, 20444–9.
D. A. Lewis, Q. Yi, J. B. Travers and D. F. Spandau, UVB-induced Senescence in Human Keratinocytes Requires a Functional Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor and p53, Mol Biol Cell., 2008, 19, 1346–1353.
W. Englaro, B. Derijard, J. P. Ortonne and R. Ballotti, Solar ultraviolet light activates extracellular signal-regulated kinases and the ternary complex factor in human normal keratinocytes, Oncogene, 1998, 16, 661–4.
T. W. Fischer, M. A. Zmijewski, J. Wortsman and A. Slominski, Melatonin maintains mitochondrial membrane potential and attenuates activation of initiator (casp-9) and effector caspases (casp-3/casp-7) and PARP in UVR-exposed HaCaT keratinocytes, J. Pineal Res., 2008, 44, 397–407.
L. Verschooten, S. Claerhout, A. Van Laethem, P. Agostinis and M. Garmyn, New strategies of photoprotection, Photochem. Photobiol., 2006, 82, 1016–23.
C. Denicourt and S. F. Dowdy, Medicine. Targeting apoptotic pathways in cancer cells, Science, 2004, 305, 1411–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Laethem, A., Garmyn, M. & Agostinis, P. Starting and propagating apoptotic signals in UVB irradiated keratinocytes. Photochem Photobiol Sci 8, 299–308 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b813346h
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b813346h