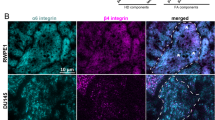
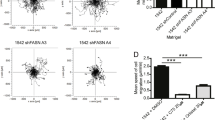
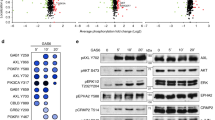
Abstract
Phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1) is activated downstream of a variety of extracellular stimuli and has previously been implicated in the regulation of motility responses central to tumour cell invasion. In this study, we used a novel RNAi vector system to achieve conditional PLCγ1 knockdown in PC3LN3 human prostate carcinoma cells for further evaluation of PLCγ1 in tumour cell biology. Using this approach, we revealed a role for PLCγ1 in the regulation of PC3LN3 cell adhesion that appears to be independent of its effects on tumour cell chemotactic migration and spreading in response to extracellular matrix. Subsequent microarray analysis of PLCγ1-knockdown cells revealed Rap GEF1 mRNA to be decreased in response to PLCγ1 loss. This translated into a decrease in Rap GEF1 protein levels and a significant loss of Rap1 activity in PLCγ1-knockdown cells. Transient knockdown of Rap GEF1 caused a reduction in PC3LN3 adhesion while overexpression of Rap GEF1 rescued the PLCγ1 knockdown-induced adhesion defect. These data highlight control of the Rap GEF1–Rap1 molecular switch as a specific requirement for PLCγ1-mediated tumour cell adhesion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JC . (2001). Cell–matrix contact structures. Cell Mol Life Sci 58: 371–392.
Arai A, Nosaka Y, Kohsaka H, Miyasaka N, Miura O . (1999). CrkL activates integrin-mediated hematopoietic cell adhesion through the guanine nucleotide exchange factor C3G. Blood 93: 3713–3722.
Aydar E, Onganer P, Perrett R, Djamgoz MB, Palmer CP . (2006). The expression and functional characterization of sigma (sigma) 1 receptors in breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett 242: 245–257.
Bernardi B, Guidetti GF, Campus F, Crittenden JR, Graybiel AM, Balduini C et al. (2006). The small GTPase Rap1b regulates the cross talk between platelet integrin alpha2beta1 and integrin alphaIIbbeta3. Blood 107: 2728–2735.
Bos JL . (2005). Linking Rap to cell adhesion. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17: 123–128.
Choi JH, Yang YR, Lee SK, Kim IS, Ha SH, Kim EK et al. (2007). Phospholipase C-gamma1 potentiates integrin-dependent cell spreading and migration through Pyk2/paxillin activation. Cell Signal 19: 1784–1796.
de Jong R, van Wijk A, Heisterkamp N, Groffen J . (1998). C3G is tyrosine-phosphorylated after integrin-mediated cell adhesion in normal but not in Bcr/Abl expressing cells. Oncogene 17: 2805–2810.
Guerrero C, Fernandez-Medarde A, Rojas JM, Font de Mora J, Esteban LM, Santos E . (1998). Transformation suppressor activity of C3G is independent of its CDC25-homology domain. Oncogene 16: 613–624.
Han J, Lim CJ, Watanabe N, Soriani A, Ratnikov B, Calderwood DA et al. (2006). Reconstructing and deconstructing agonist-induced activation of integrin alphaIIbbeta3. Curr Biol 16: 1796–1806.
Inoue O, Suzuki-Inoue K, Dean WL, Frampton J, Watson SP . (2003). Integrin alpha2beta1 mediates outside-in regulation of platelet spreading on collagen through activation of Src kinases and PLCgamma2. J Cell Biol 160: 769–780.
Jones NP, Katan M . (2007). Role of phospholipase C{gamma}1 in cell spreading requires association with a {beta}-Pix/GIT1-containing complex, leading to activation of Cdc42 and Rac1. Mol Cell Biol 27: 5790–5805.
Jones NP, Peak J, Brader S, Eccles SA, Katan M . (2005). PLCgamma1 is essential for early events in integrin signalling required for cell motility. J Cell Sci 118: 2695–2706.
Katagiri K, Shimonaka M, Kinashi T . (2004). Rap1-mediated lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 activation by the T cell antigen receptor is dependent on phospholipase C-gamma1. J Biol Chem 279: 11875–11881.
Mamoune A, Kassis J, Kharait S, Kloeker S, Manos E, Jones DA et al. (2004). DU145 human prostate carcinoma invasiveness is modulated by urokinase receptor (uPAR) downstream of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling. Exp Cell Res 299: 91–100.
Manos EJ, Kim ML, Kassis J, Chang PY, Wells A, Jones DA . (2001). Dolichol-phosphate-mannose-3 (DPM3)/prostin-1 is a novel phospholipase C-gamma regulated gene negatively associated with prostate tumor invasion. Oncogene 20: 2781–2790.
Mouneimne G, Soon L, DesMarais V, Sidani M, Song X, Yip SC et al. (2004). Phospholipase C and cofilin are required for carcinoma cell directionality in response to EGF stimulation. J Cell Biol 166: 697–708.
Nogami M, Yamazaki M, Watanabe H, Okabayashi Y, Kido Y, Kasuga M et al. (2003). Requirement of autophosphorylated tyrosine 992 of EGF receptor and its docking protein phospholipase C gamma 1 for membrane ruffle formation. FEBS Lett 536: 71–76.
Ohba Y, Ikuta K, Ogura A, Matsuda J, Mochizuki N, Nagashima K et al. (2001). Requirement for C3G-dependent Rap1 activation for cell adhesion and embryogenesis. EMBO J 20: 3333–3341.
Piechulek T, Rehlen T, Walliser C, Vatter P, Moepps B, Gierschik P . (2005). Isozyme-specific stimulation of phospholipase C-gamma2 by Rac GTPases. J Biol Chem 280: 38923–38931.
Quilliam LA, Rebhun JF, Castro AF . (2002). A growing family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors is responsible for activation of Ras-family GTPases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 71: 391–444.
Rebecchi MJ, Pentyala SN . (2000). Structure, function, and control of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Physiol Rev 80: 1291–1335.
Regunathan J, Chen Y, Kutlesa S, Dai X, Bai L, Wen R et al. (2006). Differential and nonredundant roles of phospholipase Cgamma2 and phospholipase Cgamma1 in the terminal maturation of NK cells. J Immunol 177: 5365–5376.
Sebzda E, Bracke M, Tugal T, Hogg N, Cantrell DA . (2002). Rap1A positively regulates T cells via integrin activation rather than inhibiting lymphocyte signaling. Nat Immunol 3: 251–258.
Shepard CR, Kassis J, Whaley DL, Kim HG, Wells A . (2006). PLCgamma contributes to metastasis of in situ-occurring mammary and prostate tumors. Oncogene 26: 3020–3026.
Turner T, Epps-Fung MV, Kassis J, Wells A . (1997). Molecular inhibition of phospholipase C gamma signaling abrogates DU-145 prostate tumor cell invasion. Clin Cancer Res 3: 2275–2282.
Tvorogov D, Wang XJ, Zent R, Carpenter G . (2005). Integrin-dependent PLC-gamma1 phosphorylation mediates fibronectin-dependent adhesion. J Cell Sci 118: 601–610.
Vuori K, Hirai H, Aizawa S, Ruoslahti E . (1996). Introduction of p130cas signaling complex formation upon integrin-mediated cell adhesion: a role for Src family kinases. Mol Cell Biol 16: 2606–2613.
Wang Z, Dillon TJ, Pokala V, Mishra S, Labudda K, Hunter B et al. (2006). Rap1-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by cyclic AMP is dependent on the mode of Rap1 activation. Mol Cell Biol 26: 2130–2145.
Wells A . (2000). Tumor invasion: role of growth factor-induced cell motility. Adv Cancer Res 78: 31–101.
Zhang X, Chattopadhyay A, Ji QS, Owen JD, Ruest PJ, Carpenter G et al. (1999). Focal adhesion kinase promotes phospholipase C-gamma1 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 9021–9026.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Tom Bunney for providing the bacterial lysates containing the GST-RalGDS/GST-RafRBD fusion constructs. We acknowledge Dr E Santos (IBMCC, University of Salamanca) for providing the mammalian Rap GEF1 expression vectors and Dr G Carpenter (Vanderbilt University, Nashville) for the rat PLCγ1 vector. We also thank Dr C Palmer (Imperial College, London) for assisting with the SCAMA. J Peak is funded by a Cancer Research UK PhD studentship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peak, J., Jones, N., Hobbs, S. et al. Phospholipase Cγ1 regulates the Rap GEF1-Rap1 signalling axis in the control of human prostate carcinoma cell adhesion. Oncogene 27, 2823–2832 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210954
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210954