Abstract
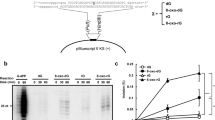
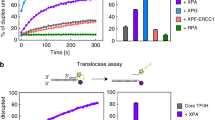
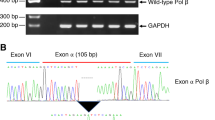
Two distinct pathways for completion of base excision repair (BER) have been discovered in eukaryotes: the DNA polymerase β (Pol β )-dependent short-patch pathway that involves the replacement of a single nucleotide and the long-patch pathway that entails the resynthesis of 2-6 nucleotides and requires PCNA. We have used cell extracts from Pol β-deleted mouse fibroblasts to separate subfractions containing either Pol δ or Pol ε. These fractions were then tested for their ability to perform both short- and long-patch BER in an in vitro repair assay, using a circular DNA template, containing a single abasic site at a defined position. Remarkably, both Pol δ and Pol ε were able to replace a single nucleotide at the lesion site, but the repair reaction is delayed compared to single nucleotide replacement by Pol β. Furthermore, our observations indicated, that either Pol δ and/or Pol ε participate in the long-patch BER. PCNA and RF-C, but not RP-A are required for this process. Our data show for the first time that Pol δ and/or Pol ε are directly involved in the long-patch BER of abasic sites and might function as back-up system for Pol β in one-gap filling reactions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stucki, M., Pascucci, B., Parlanti, E. et al. Mammalian base excision repair by DNA polymerases δ and ε. Oncogene 17, 835–843 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202001
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202001
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ROS induces NETosis by oxidizing DNA and initiating DNA repair
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
Spontaneous mutations in the single TTN gene represent high tumor mutation burden
npj Genomic Medicine (2020)
-
Nucleosomes determine their own patch size in base excision repair
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Minimizing the damage: repair pathways keep mitochondrial DNA intact
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2012)
-
OGG1 initiates age-dependent CAG trinucleotide expansion in somatic cells
Nature (2007)