Abstract
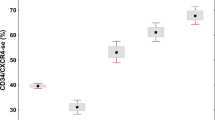
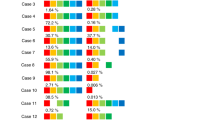
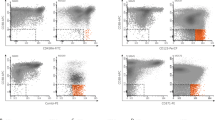
Excessive intramedullary apoptosis is central in the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Growth-inhibiting cytokines, the Fas/FasLigand pathway, and autoreactive cytotoxic T-lymphocytes have been identified to be important proapoptotic factors in MDS. In normal hematopoiesis, α4β1 and α5β1 integrin-mediated interactions between progenitors and fibronectin are critical for progenitor cell survival. In this study, we have used flow cytometry to quantify the expression levels of members of the β1 integrin family on CD34+ marrow progenitors in 27 untreated patients with MDS, three with s-AML, and 25 control subjects. In MDS, we observed that nonapoptotic progenitors significantly downregulate cell surface expression levels of α4 and β1 integrin chains compared with healthy controls. Downregulation of α4, β1, and also α5 was present in MDS patients with ≥25% apoptotic progenitors, irrespective of their French, American, British subcategory. Reduced cell surface expression levels of α4, α5, and β1 did also correlate with decreased in vitro adhesiveness to fibronectin fragments. Therefore, our observations suggest that downregulation of α4β1 and α5β1 integrins on CD34+ progenitors could be a newly identified proapoptotic mechanism in MDS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eaves CJ, Cashman JD, Sutherland HJ, Otsuka T, Humphries RK, Hogge DE et al. Molecular analysis of primitive hematopoietic cell proliferation control mechanisms. Ann NY Acad Sci 1991; 628: 298–306.
Verfaillie C, Hurley R, Bhatia R, McCarthy JB . Role of bone marrow matrix in normal and abnormal hematopoiesis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 1994; 16: 201–224.
Verfaillie CM . Adhesion receptors as regulators of the hematopoietic process. Blood 1998; 92: 2609–2612.
Chan YH, Watt SM . Adhesion receptors on haematopoietic progenitor cells. Br J Haematol 2001; 112: 541–557.
Clark EA, Brugge JS . Integrins and signal transduction pathways: the road taken. Science 1995; 268: 233–239.
Parise LV, Lee JW, Juliano RL . New aspects of integrin signaling in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 2000; 10: 407–414.
Williams DA, Rios M, Stephens C, Patel VP . Fibronectin and VLA-4 in haematopoietic stem cell–microenvironment interactions. Nature 1991; 352: 438–441.
Verfaillie CM, McCarthy JB, McGlave PB . Differentiation of primitive human multipotent hematopoietic progenitors into single lineage clonogenic progenitors is accompanied by alteration in their interaction with fibronectin. J Exp Med 1991; 174: 693–703.
Hurley RW, McCarthy JB, Verfaillie CM . Direct adhesion to bone marrow stroma via fibronectin receptors inhibits hematopoietic progenitor proliferation. J Clin Invest 1995; 96: 511–519.
Zhang Z, Vuori K, Reed JC, Ruoslahti E . The α5β1 integrin supports survival of cells on fibronectin and up-regulates Bcl-2 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 6161–6165.
Wang MW, Consoli U, Lane CM, Durett A, Lauppe MJ, Champlin R et al. Rescue from apoptosis in early (CD34-selected) versus late (non-CD34-selected) human hematopoietic cells by very late antigen 4- and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)1-dependent adhesion to bone marrow stromal cells. Cell Growth Differ 1998; 9: 105–112.
Hurley RW, McCarthy JB, Wayner EA, Verfaillie CM . Monoclonal antibody crosslinking of the α4 or β1 integrin inhibits committed clonogenic hematopoietic progenitor proliferation. Exp Hematol 1997; 25: 321–328.
Matsunaga T, Takemoto N, Sato T, Takimoto R, Tanaka I, Fujimi A et al. Interaction between leukemic-cell VLA-4 and stromal fibronectin is a decisive factor for minimal residual disease of acute myelogenous leukaemia. Nat Med 2003; 9: 1158–1165.
Bendall LJ, Makrynikola V, Hutchinson A, Bianchi AC, Bradstock KF, Gottlieb DJ . Stem cell factor enhances the adhesion of AML cells to fibronectin and augments fibronectin-mediated anti-apoptotic and proliferative signals. Leukemia 1998; 12: 1375–1382.
Mudry RE, Fortney JE, York T, Hall BM, Gibson LF . Stromal cells regulate survival of B-lineage leukemic cells during chemotherapy. Blood 2000; 96: 1926–1932.
Bhatia R, Munthe HA, Verfaillie CM . Role of abnormal integrin-cytoskeletal interaction in impaired β1 integrin function in chronic myelogenous leukemia hematopoietic progenitor cells. Exp Haematol 1999; 27: 1384–1396.
De la Fuente MT, Casanova B, Garcia-Gila M, Silva A, Garcia-Pardo A . Fibronectin interaction with alpha4beta1 integrin prevents apoptosis in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlation with Bcl-2 and Bax. Leukemia 1999; 13: 266–274.
Yoshida Y . Hypothesis: apoptosis may be the mechanism responsible for the premature intramedullary cell death in the myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 1993; 7: 144–146.
Raza A, Gezer S, Mundle S, Gao XZ, Alvi S, Borok R et al. Apoptosis in bone marrow biopsy samples involving stromal and hematopoietic cells in 50 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1995; 86: 268–276.
Delforge M . Understanding the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndromes. Hematol J 2003; 4: 303–309.
Willman CL . Molecular genetic features of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Leukemia 1998; 12: S2–S6.
Kitagawa M, Saito I, Kuwata T, Yoshida S, Yamaguchi S et al. Overexpression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)- α and interferon (IFN)-γ by bone marrow cells from patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 1997; 11: 2049–2054.
Bouscary D, De Vos J, Guesnu M, Jondeau K, Viguier F, Melle J et al. Fas/Apo-1(CD95) expression and apoptosis in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 1997; 11: 839–845.
Sloand EM, Kim S, Fuhrer M, Risitano AM, Nakamura R, Maciejewski JP et al. Fas-mediated apoptosis is important in regulating cell replication and death in trisomy 8 hematopoietic cells but not in cells with other cytogenetic abnormalities. Blood 2002; 100: 4427–4432.
Watson JV . A brief history of numbers and statistics with cytometric applications. Cytometry 2001; 46: 1–22.
Parker JE, Mufti GJ, Rasool F, Mijovic A, Devereux S, Pagliuca A . The role of apoptosis, proliferation, and the Bcl-2-related proteins in the myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia secondary to MDS. Blood 2000; 96: 3932–3938.
Greenberg PL . Apoptosis and its role in the myelodysplastic syndromes: implications for disease natural history and treatment. Leukemia Res 1998; 22: 1123–1136.
Merchant SH, Gonchoroff NJ, Hutchison RE . Apoptotic index by Annexin V flow cytometry: adjunct to morphologic and cytogenetic diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndromes. Cytometry 2001; 46: 28–32.
Frish SM, Francis H . Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1994; 124: 619–626.
Raza A, Alvi S, Borok RZ, Span L, Parcharidou A, Alston D et al. Excessive proliferation matched by excessive apoptosis in myelodysplastic syndromes: the cause-effect relationship. Leukemia Lymphoma 1997; 27: 111–118.
Mazzone A, Porta C, Fossati G, Gritti D, Mazzucchelli I, Ricevuti G . Granulocyte dysplasia and dysfunction, and CD11/CD18 defects in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia Lymphoma 1996; 23: 267–275.
Maynadié M, Picard F, Husson B, Chatelain B, Cornet Y, Le Roux G et al. Groupe d'Etude Immunologique des Leucemies (GEIL). Immunophenotypic clustering of myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2002; 100: 2349–23565.
Lévesque JP, Leavesley DI, Niutta S, Vadas M, Simmons PJ . Cytokines increase human hematopoietic cell adhesiveness by activation of very late antigen (VLA)-4 and VLA-5 integrins. J Exp Med 1995; 181: 1805–1815.
Shetty V, Mundle S, Alvi S, Showel M, Broady-Robinson L, Dar S et al. Measurement of apoptosis, proliferation and three cytokines in 46 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res 1996; 20: 891–900.
Allampallam K, Shetty V, Hussaini S, Mazzoran L, Zorat F, Huang R et al. Measurement of mRNA expression for a variety of cytokines and its receptors in bone marrows of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Anticancer Res 1999; 19: 5323–5328.
Defilippi P, Truffa G, Stefanuto G, Altruda F, Silengo L, Tarone G . Tumor necrosis factor α and interferon γ modulate the expression of the vitronectin receptor (integrin β3) in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 7638–7645.
Asano H, Ohashi H, Ichihara M, Kinoshita T, Murate T, Kobayashi M et al. Evidence for nonclonal hematopoietic progenitor cell populations in bone marrow of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1994; 4: 588–594.
Delforge M, Demuynck H, Verhoef G, Vandenberghe P, Zachee P, Maertens J et al. Patients with high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome can have polyclonal or clonal haemopoiesis in complete haematological remission. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 486–494.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delforge, M., Raets, V., Van Duppen, V. et al. CD34+ marrow progenitors from MDS patients with high levels of intramedullary apoptosis have reduced expression of α4β1 and α5β1 integrins. Leukemia 19, 57–63 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403551
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403551