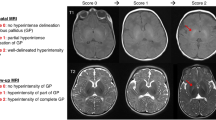
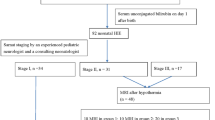
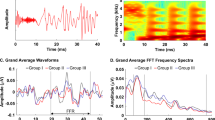
Abstract
When sedation, prematurity or other disease processes mask symptoms in the clinically ill newborn, serum bilirubin concentration is monitored as the sole indicator of kernicterus risk. This case emphasizes the value of auditory brainstem responses for the management of indirect hyperbilirubinemia complicated by prematurity, hemolytic anemia, asphyxia, and direct hyperbilirubinemia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perlman M, Frank JW . Bilirubin beyond the blood – brain barrier. Pediatrics 1988;81:304–315.
Agrawal VK, Shukla R, Misra PK, Kapoor RK, Malik GK . Brainstem auditory evoked response in newborns with hyperbilirubinemia. Indian Pediatr 1998;35:513–518.
Gupta AK, Anand NK, Hans R . Evaluation of risk factors for hearing impairment in at risk neonates by brainstem evoked response auditometry (BERA). Indian J Pediatr 1991;58:849–855.
Kuriyama M, Tomiwa K, Konishi Y, Mikawa H . Improvement of auditory brainstem response of hyperbilirubinemic infants after exchange transfusions. Pediatr Neurol 1986;2:127–132.
Lee CY, Chen SJ, Tang RB . Reevaluation of recent criteria for blood exchange transfusion in term infants with hyperbilirubinemia. Acta Paediatr Tw 2002;43:86–90.
Nakamura H, Takada S, Shimabuku R, Matsuo M, Matsuo T, Negishi H . Auditory nerve and brainstem responses in newborn infants with hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics 1985;75:703–708.
Nwaesei CG, Van Aerde J, Boyden M, Perlman M . Changes in auditory brainstem responses in hyperbilirubinemic infants before and after exchange transfusion. Pediatrics 1984;74:800–803.
Wennberg RP, Ahlfors CE, Bickers R, McMurtry CA, Shetter JL . Abnormal brainstem auditory in newborn infant with hyperbilirubinemia: improvement with exchange transfusion. J Pediatr 1982;100:624.
Chisin R, Perlman M, Sohmer H . Cochlear and brain stem responses in hearing loss following neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1979;88:352–357.
Soares I, Collet L, Delorme C, Salle B, Morgon A . Are click-evoked BAEPs useful in case of neonate hyperbilirubinemia? Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 1989;17:231–237.
Lenhardt ML, McActor R, Bryant B . Effects of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia on the brainstem electric response. J Pediatr 1984;104:281–284.
Vohr BR, Karp D, O’Dea C, et al. Behavioral changes correlated with brain-stem auditory evoked responses in term infants with mderate hyperbilirubinemia. J Pediatr 1990;117:288–291.
DeVries LS, Lary S, Whitelaw AG, Dubowitz LMS . Relationship of serum bilirubin levels and hearing impairment in newborn infants. Early Hum Dev 1987;15:269–277.
Deliac P, Demarquez JL, Barberot JP, Sandler B, Paty J . Brainstem auditory evoked potentials in icteric fullterm newborns: alterations after exchange transfusion. Neuropediatrics 1990;21:115–118.
Bhandari V, Narang A, Mann SBS, Raghunathan M, Bhakoo ON . Brain stem electric response audiometry in neonates with hyperbilirubinemia. Indian J Pediatr 1993;60:409–413.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, C., Barnes, G., Jacobson, C. et al. Auditory Brainstem Response Detects Early Bilirubin Neurotoxicity at Low Indirect Bilirubin Values. J Perinatol 24, 730–732 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211164
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211164
This article is cited by
-
Auditory neuropathy — neural and synaptic mechanisms
Nature Reviews Neurology (2016)
-
Changes in BAER wave amplitudes in relation to total serum bilirubin level in term neonates
European Journal of Pediatrics (2009)