Abstract
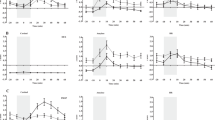
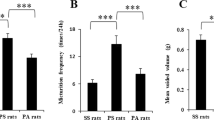
This study was undertaken to investigate whether prolonged stress interferes with sexual behavior and changes biochemical and physiologic mechanisms. Experiments were repeated three times with different rats in each period. In all, 63 female Sprague–Dawley rats were employed, with 21 rats in each period, and the control group was maintained at room temperature with free access to food and water. The stress group was maintained under a scheduled stress condition for 10 days, and seven rats from the group were randomly selected and exposed to the control environment for 10 days as the recovery group. Sexual behavior, hormonal values, and neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (nNOS and eNOS) expressions of vaginal tissue were analyzed and compared. Serum testosterone levels were significantly elevated in the stress and recovery groups (P<0.05). Female rats in the stress group showed reduced receptivity to their male mates (P<0.05). Western blot analysis demonstrated that nNOS and eNOS expressions were significantly lower in the stress group (P<0.05) than in the other groups. We conclude that chronic physical stress modifies the sexual behavior of female rats through a mechanism believed to involve complex changes in sex hormones, endocrine factors, and neurotransmitters.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caggiura AR, Eibergen R . Copulation of virgin male rats evoked by painful peripheral stimulation. J Comp Physiol Psychol 1969; 69: 414–419.
Caggiura AR, Vlahoulis R . Modification in the copulatory performance of male rats produced by repeated peripheral shock. Behav Biol 1974; 11: 269–274.
Menendez-Patterson A, Florez-Lozano JA, Fernandez S, Marin B . Stress and sexual behavior in male rats. Physiol Behav 1978; 24: 403–406.
Ogawa M, Kuwabata H . Psychophysiology of emotion-communication of emotion. Shinshin-Ihaku 1966; 6: 352–357.
Gatenbeck L, Johansson B, Strömberg L, Svensson M . Genital blood flow in male rats subjected to stress stimuli. Urol Res 1987; 15: 297–301.
Graziottin A . Libido: the biologic scenario. Maturitas 2000; 34(Suppl 1): S9–S16.
Munarriz R et al. A review of the physiology and pharmacology of peripheral (vaginal and clitoral) female genital arousal in the animal model. J Urol 2003; 170: S40–S44.
Munarriz R, Kim NN, Goldstein I, Traish AM . Biology of female sexual function. Urol Clin North Am 2002; 29: 685–693.
Burnett AL et al. Immunohistochemical description of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in human clitoris. J Urol 1997; 158: 75–78.
Batra S, Al-Hijji J . Characterization of nitric oxide synthase activity in rabbit uterus and vagina: downregulation by estrogen. Life Sci 1998; 62: 2093–2100.
Traish AM et al. Biochemical and physiological mechanisms of female genital sexual arousal. Arch Sex Behav 2002; 31: 393–400.
Ross GA et al. Plasma and 24-h urinary catecholamine concentrations in normal and patient populations. Ann Clin Biochem 1993; 30: 38–44.
Bradford MM . A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 1976; 72: 248–254.
Retana-Marquez S, Dominguez Salazar E, Velazquez-Moctezuma J . Effect of acute and chronic stress on masculine sexual behavior in the rat. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1996; 21: 39–50.
Sato Y et al. Effects of long-term psychological stress on sexual behavior and brain catecholamine levels. J Androl 1996; 17: 83–90.
Almeida SA, Kempinas WG, Lamano Carvalho TL . Sexual behavior and fertility of male rats submitted to prolonged immobilization-induced stress. Braz J Med Biol Res 2000; 33: 1105–1109.
Biron D, Dauphin C, Di Paolo T . Effects on adrenalectomy and glucocorticoids on rat brain dopamine receptors. Neuroendocrinology 1992; 55: 468–476.
Hull EM et al. Hormone-neurotransmitter interactions in the control of sexual behavior. Behav Brain Res 1999; 105: 105–116.
Miesel ML, Sachs BD . The physiology of male sexual behavior. In: Knobil E, Neill JD (eds) The Physiology of Reproduction. Raven Press: New York, 1994, pp 35–45.
Gonzalez MI, Baker BI, Hole DR, Wilson CA . Behavioral effects of neuropeptide E-I(NEI) in the female rat: interactions with α-MSH, MCH and dopamine. Peptides 1998; 19: 1007–1016.
Setchell B, Waites G, Lindner H . Effect of undernutrition on testicular blood flow and metabolism and the output of testosterone in the rat. J Reprod Fertil 1965; 9: 149–151.
Glover TD . The influence of temperature on flow of blood in the testis and scrotum of rats. Proc R Soc Med 1966; 59: 765–766.
Traish AM et al. Effects of castration and androgen replacement on erectile function in a rabbit model. Endocrinology 1999; 140: 1861–1868.
Zavara P et al. Nitric oxide mediated erectile activity is a testosterone dependent event: a rat erection model. Int J Impot Res 1996; 7: 209–219.
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital Annual Research Grant. We thank Dr Ha Jung Yoon for providing statistical review and Jong Hyun Jeon for his devoted technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, H., Chung, W., Park, Y. et al. Effects of stress on female rat sexual function. Int J Impot Res 17, 33–38 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901223
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901223
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
How mental stress affects endothelial function
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2011)