Abstract
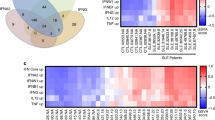
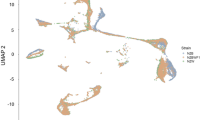
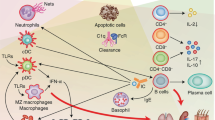
MRLlpr mice develop spontaneous systemic autoimmunity with many hallmarks of the human disease systemic lupus erythematosus. Although a variety of genes have been implicated in this model, disease pathogenesis is still poorly understood. In an effort to identify novel genes and pathways, we performed genome-wide mRNA expression analysis in the spleens and kidneys of MRLlpr mice throughout the disease course. Samples were collected from cohorts of C57BL/6, MRL+/+ and MRLlpr mice, and profiled by flow cytometry and gene expression microarrays. Serum autoantibodies and renal pathology were studied in parallel. We identified 236 genes in MRLlpr spleen that showed significant threefold or greater changes in expression between 6 and 20 weeks. Of interest, a number of interferon-responsive genes were expressed early, and remained dysregulated throughout the disease course. Many chemokines, cell surface proteins, transcription factors and cytokines, including IFN-gamma, also showed altered expression as disease progressed. Analysis of kidneys indicated the presence of severe inflammation that coincided with evidence for changes in kidney function and elevated expression of IFN-inducible genes, complement components and antigen presentation genes. These data provide a unique genomic view of the progression to fatal autoimmunity in MRLlpr mice, and provide new candidate genes and pathways to explore.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leadbetter EA, Rifkin IR, Hohlbaum AM, Beaudette BC, Shlomchik MJ, Marshak-Rothstein A . Chromatin-IgG complexes activate B cells by dual engagement of IgM and Toll-like receptors. Nature 2002; 416: 603–607.
Viglianti GA, Lau CM, Hanley TM, Miko BA, Shlomchik MJ, Marshak-Rothstein A . Activation of autoreactive B cells by CpG dsDNA. Immunity 2003; 19: 837–847.
Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Karypis G, Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ et al. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 2610–2615.
Bennett L, Palucka AK, Arce E, Cantrell V, Borvak J, Banchereau J et al. Interferon and granulopoiesis signatures in systemic lupus erythematosus blood. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 711–723.
Chan RW, Tam LS, Li EK, Lai FM, Chow KM, Lai KB et al. Inflammatory cytokine gene expression in the urinary sediment of patients with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 1326–1331.
Ronnblom L, Eloranta ML, Alm GV . Role of natural interferon-alpha producing cells (plasmacytoid dendritic cells) in autoimmunity. Autoimmunity 2003; 36: 463–472.
Filaci G, Bacilieri S, Fravega M, Monetti M, Contini P, Ghio M et al. Impairment of CD8+ T suppressor cell function in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 2001; 166: 6452–6457.
Sekigawa I, Matsushita M, Lee S, Maeda N, Ogasawara H, Kaneko H et al. A possible pathogenic role of CD8+ T cells and their derived cytokine, IL-16, in SLE. Autoimmunity 2000; 33: 37–44.
Shlomchik MJ, Craft JE, Mamula MJ . From T to B and back again: positive feedback in systemic autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2001; 1: 147–153.
Wakeland EK, Liu K, Graham RR, Behrens TW . Delineating the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 2001; 15: 397–408.
Pollard KM, Hultman P, Kono DH . Using single-gene deletions to identify checkpoints in the progression of systemic autoimmunity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2003; 987: 236–239.
Chu JL, Drappa J, Parnassa A, Elkon KB . The defect in Fas mRNA expression in MRL/lpr mice is associated with insertion of the retrotransposon, ETn. J Exp Med 1993; 178: 723–730.
Reilly CM, Gilkeson GS . Use of genetic knockouts to modulate disease expression in a murine model of lupus, MRL/lpr mice. Immunol Res 2002; 25: 143–153.
Liang B, Gee RJ, Kashgarian MJ, Sharpe AH, Mamula MJ . B7 costimulation in the development of lupus: autoimmunity arises either in the absence of B7.1/B7.2 or in the presence of anti-b7.1/B7.2 blocking antibodies. J Immunol 1999; 163: 2322–2329.
Liang B, Kashgarian MJ, Sharpe AH, Mamula MJ . Autoantibody responses and pathology regulated by B7-1 and B7-2 costimulation in MRL/lpr lupus. J Immunol 2000; 165: 3436–3443.
Takahashi T, Yagi T, Kakinuma S, Kurokawa A, Okada T, Takatsu K et al. Suppression of autoimmune disease and of massive lymphadenopathy in MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice lacking tyrosine kinase Fyn (p59fyn). J Immunol 1997; 159: 2532–2541.
Schwarting A, Tesch G, Kinoshita K, Maron R, Weiner HL, Kelley VR . IL-12 drives IFN-gamma-dependent autoimmune kidney disease in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice. J Immunol 1999; 163: 6884–6891.
Balomenos D, Rumold R, Theofilopoulos AN . Interferon-gamma is required for lupus-like disease and lymphoaccumulation in MRL-lpr mice. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 364–371.
Sekine H, Reilly CM, Molano ID, Garnier G, Circolo A, Ruiz P et al. Complement component C3 is not required for full expression of immune complex glomerulonephritis in MRL/lpr mice. J Immunol 2001; 166: 6444–6451.
Flier J, Boorsma DM, van Beek PJ, Nieboer C, Stoof TJ, Willemze R et al. Differential expression of CXCR3 targeting chemokines CXCL10, CXCL9, and CXCL11 in different types of skin inflammation. J Pathol 2001; 194: 398–405.
Xanthou G, Duchesnes CE, Williams TJ, Pease JE . CCR3 functional responses are regulated by both CXCR3 and its ligands CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11. Eur J Immunol 2003; 33: 2241–2250.
Rozzo SJ, Allard JD, Choubey D, Vyse TJ, Izui S, Peltz G et al. Evidence for an interferon-inducible gene, Ifi202, in the susceptibility to systemic lupus. Immunity 2001; 15: 435–443.
Sun Y, Chen HM, Subudhi SK, Chen J, Koka R, Chen L et al. Costimulatory molecule-targeted antibody therapy of a spontaneous autoimmune disease. Nat Med 2002; 8: 1405–1413.
Nagafuchi H, Shimoyama Y, Kashiwakura J, Takeno M, Sakane T, Suzuki N . Preferential expression of B7.2 (CD86), but not B7.1 (CD80), on B cells induced by CD40/CD40L interaction is essential for anti-DNA autoantibody production in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2003; 21: 71–77.
Sfikakis PP, Via CS . Expression of CD28, CTLA4, CD80, and CD86 molecules in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases: implications for immunotherapy. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1997; 83: 195–198.
Goodbourn S . The regulation of beta-interferon gene expression. Semin Cancer Biol 1990; 1: 89–95.
Tangye SG, Nichols KE, Hare NJ, van de Weerdt BC . Functional requirements for interactions between CD84 and Src homology 2 domain-containing proteins and their contribution to human T cell activation. J Immunol 2003; 171: 2485–2495.
Wandstrat AE, Nguyen C, Limaye N, Chan AY, Subramanian S, Tian XH et al. Association of extensive polymorphisms in the SLAM/CD2 gene cluster with murine lupus. Immunity 2004; 21: 769–780.
Hosking BM, Wang S-CM, Downes M, Koopman P, Muscat GEO . The VCAM-1 gene that encodes the vascular cell adhesion molecule is a target of the Sry-related high mobility group box gene, Sox18. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 5314–5322.
Pennisi D, Gardner J, Chambers D, Hosking B, Peters J, Muscat G et al. Mutations in Sox18 underlie cardiovascular and hair follicle defects in ragged mice. Nat Genet 2000; 24: 434–437.
Vidal S, Kono DH, Theofilopoulos AN . Loci predisposing to autoimmunity in MRL-Fas lpr and C57BL/6-Faslpr mice. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 696–702.
Kim TG, Kim HY, Lee SH, Cho CS, Park SH, Choi HB et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus with nephritis is strongly associated with the TNFB*2 homozygote in the Korean population. Hum Immunol 1996; 46: 10–17.
Vyse TJ, Morel L, Tanner FJ, Wakeland EK, Kotzin BL . Backcross analysis of genes linked to autoantibody production in New Zealand White mice. J Immunol 1996; 157: 2719–2727.
Tonini T, Bagella L, D'Andrilli G, Claudio PP, Giordano A . Ezh2 reduces the ability of HDAC1-dependent pRb2/p130 transcriptional repression of cyclin A. Oncogene 2004; 23: 4930–4937.
Hron JD, Peng SL . Type I IFN protects against murine lupus. J Immunol 2004; 173: 2134–2142.
Min W, Ghosh S, Lengyel P . The interferon-inducible p202 protein as a modulator of transcription: inhibition of NF-kappa B, c-Fos, and c-Jun activities. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16: 359–368.
Heremans H, Billiau A, Colombatti A, Hilgers J, de Somer P . Interferon treatment of NZB mice: accelerated progression of autoimmune disease. Infect Immun 1978; 21: 925–930.
Adam C, Thoua Y, Ronco P, Verroust P, Tovey M, Morel-Maroger L . The effect of exogenous interferon: acceleration of autoimmune and renal diseases in (NZB/W) F1 mice. Clin Exp Immunol 1980; 40: 373–382.
Santiago-Raber ML, Baccala R, Haraldsson KM, Choubey D, Stewart TA, Kono DH et al. Type-I interferon receptor deficiency reduces lupus-like disease in NZB mice. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 777–788.
Braun D, Geraldes P, Demengeot J . Type I Interferon controls the onset and severity of autoimmune manifestations in lpr mice. J Autoimmun 2003; 20: 15–25.
Peng SL, Moslehi J, Craft J . Roles of interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 in murine lupus. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 1936–1946.
Hooks JJ, Moutsopoulos HM, Geis SA, Stahl NI, Decker JL, Notkins AL . Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med 1979; 301: 5–8.
Ytterberg SR, Schnitzer TJ . Serum interferon levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1982; 25: 401–406.
Preble OT, Black RJ, Friedman RM, Klippel JH, Vilcek J . Systemic lupus erythematosus: presence in human serum of an unusual acid-labile leukocyte interferon. Science 1982; 216: 429–431.
Blanco P, Palucka AK, Gill M, Pascual V, Banchereau J . Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science 2001; 294: 1540–1543.
Kalkner KM, Ronnblom L, Karlsson Parra AK, Bengtsson M, Olsson Y, Oberg K . Antibodies against double-stranded DNA and development of polymyositis during treatment with interferon. Q J Med 1998; 91: 393–399.
Ronnblom LE, Alm GV, Oberg K . Autoimmune phenomena in patients with malignant carcinoid tumors during interferon-alpha treatment. Acta Oncol 1991; 30: 537–540.
Cederblad B, Blomberg S, Vallin H, Perers A, Alm GV, Ronnblom L . Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus have reduced numbers of circulating natural interferon-alpha- producing cells. J Autoimmun 1998; 11: 465–470.
Vallin H, Blomberg S, Alm GV, Cedarblad B, Ronnblom L . Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have a circulating inducer of interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) production acting on leucocytes resembling immature dendritic cells. Clin Exp Immunol 1999; 115: 196–202.
Manson JJ, Isenberg DA . The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Neth J Med 2003; 61: 343–346.
Crow MK, Wohlgemuth J . Microarray analysis of gene expression in lupus. Arthritis Res Ther 2003; 5: 279–287.
Pascual V, Banchereau J, Palucka AK . The central role of dendritic cells and interferon-alpha in SLE. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003; 15: 548–556.
Cravens PD, Lipsky PE . Dendritic cells, chemokine receptors and autoimmune inflammatory diseases. Immunol Cell Biol 2002; 80: 497–505.
Einav S, Pozdnyakova OO, Ma M, Carroll MC . Complement C4 is protective for lupus disease independent of C3. J Immunol 2002; 168: 1036–1041.
Robson MG, Cook HT, Botto M, Taylor PR, Busso N, Salvi R et al. Accelerated nephrotoxic nephritis is exacerbated in C1q-deficient mice. J Immunol 2001; 166: 6820–6828.
Tze LE, Baness EA, Hippen KL, Behrens TW . Ig light chain receptor editing in anergic B cells. J Immunol 2000; 165: 6796–6802.
Gilkeson GS, Grudier JP, Karounos DG, Pisetsky DS . Induction of anti-double stranded DNA antibodies in normal mice by immunization with bacterial DNA. J Immunol 1989; 142: 1482–1486.
Bernstein KA, Valerio RD, Lefkowith JB . Glomerular binding activity in MRL lpr serum consists of antibodies that bind to a DNA/histone/type IV collagen complex. J Immunol 1995; 154: 2424–2433.
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D . Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 14863–14868.
Li C, Wong WH . Model-based analysis of oligonucleotide arrays: expression index computation and outlier detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 31–36.
Wang Y, Nose M, Kamoto T, Nishimura M, Hiai H . Host modifier genes affect mouse autoimmunity induced by the lpr gene. Am J Pathol 1997; 151: 1791–1798.
Kono DH, Burlingame RW, Owens DG, Kuramochi A, Balderas RS, Balomenos D et al. Lupus susceptibility loci in New Zealand mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 10168–10172.
McBrearty BA, Clark LD, Zhang XM, Blankenhorn EP, Heber-Katz E . Genetic analysis of a mammalian wound-healing trait. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 11792–11797.
Acknowledgements
We thank A Becker, J Plumb-Smith, W Ortmann, and K Espe for assistance with the microarray experiments. We also like to thank Z Tu for technical support in data analysis, and Greg Veltri and J Peller for assistance in cell sorting. This work was carried out in part using resources at the University of Minnesota Supercomputing Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity's website (http://www.nature.com/gene).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Karypis, G., Hippen, K. et al. Genomic view of systemic autoimmunity in MRLlpr mice. Genes Immun 7, 156–168 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364286
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364286
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-targeted therapeutics in rheumatic diseases
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2022)
-
Niclosamide suppresses the expansion of follicular helper T cells and alleviates disease severity in two murine models of lupus via STAT3
Journal of Translational Medicine (2021)
-
Cenerimod, a selective S1P1 receptor modulator, improves organ-specific disease outcomes in animal models of Sjögren’s syndrome
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2021)
-
CKD-506, a novel HDAC6-selective inhibitor, improves renal outcomes and survival in a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
What is damaging the kidney in lupus nephritis?
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2016)