Abstract
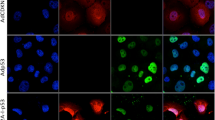
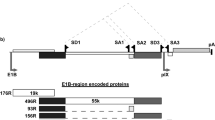
The objective of this study was to develop an adenoviral vector system that would generate a pattern of expression of exogenous therapeutic genes appropriate for the treatment of ovarian cancer. For this purpose, we have generated a replication-deficient recombinant adenoviral vector, AdLPLacZ, which contains the human L-plastin (LP) promoter (LP-P) driving the Escherichia coli LacZ gene. LP is constitutively expressed at high levels in malignant epithelial cells but is not expressed in normal tissues, except at low levels in mature hematopoietic cells. Because adenoviral vectors infect early hematopoietic multilineage precursor cells only poorly or not at all, this vector would be of use in the peritoneal cavity and in vitro for marrow purging. We first analyzed the expression of the LacZ reporter gene in ovarian and breast cancer cell lines, normal fibroblasts, and leukemia cell lines using the adenoviral vector in which the LacZgene is governed by the LP-P promoter (AdLPLacZ) or in which the LacZ gene is governed by the cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter (AdCMVLacZ). We found equivalent and high levels of expression of β-galactosidase (β-gal) by AdLPLacZ and AdCMVLacZ vectors in the breast or ovarian cancer cell lines as well as in a fibrosarcoma cell line, indicating that the adenoviral vectors infected these cells and expressed their transgenes equally with the LP and CMV promoters. Expression of the LacZ gene with the CMV vector but not with the LP-P vector was observed in experiments with normal fibroblasts, indicating that the vectors infected the cells, but that the LP-P was not active within them. In hematopoietic cells such as U937 cells, no measurable β-gal activity was detected in cells infected either by AdLPLacZ or by AdCMVLacZ, indicating that the adenoviral vectors were not infecting the cells. Although β-gal activity was observed in fresh ascitic ovarian cancer cells after infection with adenoviral vectors containing CMV or the LP promoters, β-gal activity was detected in a portion of a biopsy of normal peritoneum when the tissues were exposed to the AdCMVLacZ vector, but not when tissues were exposed to the AdLPLacZ vector. These results suggest that the transcription of therapeutic genes in cells infected by the AdLP vectors would be restricted to LP expression-positive ovarian carcinoma cells but would not be seen in the normal mesothelial cells of the peritoneal cavity. This possibility implies that adenoviral vectors carrying therapeutic genes driven by the LP-P would be of use for the intracavitary treatment ovarian cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, I., Schwartz, P., Crystal, R. et al. Use of L-plastin promoter to develop an adenoviral system that confers transgene expression in ovarian cancer cells but not in normal mesothelial cells. Cancer Gene Ther 6, 99–106 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700017
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700017
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Biology and therapeutic potential of cannabinoid CB2receptor inverse agonists
British Journal of Pharmacology (2008)
-
Cytotoxic effect of a replication-incompetent adenoviral vector with cytosine deaminase gene driven by L-plastin promoter in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2007)
-
Engineering conditionally replication-competent adenoviral vectors carrying the cytosine deaminase gene increases the infectivity and therapeutic effect for breast cancer gene therapy
Cancer Gene Therapy (2006)
-
Delivery of Viral Vectors to Tumor Cells: Extracellular Transport, Systemic Distribution, and Strategies for Improvement
Annals of Biomedical Engineering (2006)
-
Plasmid Engineering for Controlled and Sustained Gene Expression for Nonviral Gene Therapy
Pharmaceutical Research (2006)