Abstract
The pentazolate anion, as a polynitrogen species, holds great promise as a high-energy density material for explosive or propulsion applications. Designing pentazole complexes that contain minimal non-energetic components is desirable in order to increase the material’s energy density. Here, we report a solvent-free pentazolate complex, AgN5, and a 3D energetic-framework, [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ, constructed from silver and cyclo-N5ˉ. The complexes are stable up to 90 °C and only Ag and N2 are observed as the final decomposition products. Efforts to isolate pure AgN5 were unsuccessful due to partial photolytical and/or thermal-decomposition to AgN3. Convincing evidence for the formation of AgN5 as the original reaction product is presented. The isolation of a cyclo-N5ˉ complex, devoid of stabilizing molecules and ions, such as H2O, H3O+, and NH4+, constitutes a major advance in pentazole chemistry.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The pentazolate anion, cyclo-N5ˉ, has recently been stabilized as (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl1 and Co(N5)2(H2O)4·4H2O2. This discovery has received much attention due to the potential applications of cyclo-N5ˉ in high-energy density materials (HEDMs) and as a starting material for the syntheses of inorganic ferrocene analogs. However, these cyclo-N5ˉ complexes contained non-energetic counter ions or groups to enhance their stability, thus impacting their energetic properties. The successful synthesis of an essentially naked cyclo-N5ˉ salt still has a huge challenge for the fascinating pentazole chemistry and related materials science.
HEDMs require both low sensitivity and high performance3. Polynitrogen compounds hold great promise due to their fast energy release and eco-friendly decomposition products4,5,6,7. Major advances in this area have been made during the past two decades, the two most remarkable new species discovered in this field are the pentazenium cation, N5+,6,7,8 and the pentazolate anion, cyclo-N5ˉ9,10,11,12. However, the reported N5+ and cyclo-N5ˉ complexes generally contain non-energetic counter ions or groups to enhance their stabilities. For example, SbF6ˉ or SnF62ˉ are non-energetic counter ions in N5+ salts13,14, and H2O, Clˉ, NH4+, and H3O+ are used to stabilize the cyclo-N5ˉ anion1. These non-energetic components impact their energetic properties, such as heat of formation and detonation parameters. Therefore, it is important to reduce or eliminate these non-energetic components.
As part of our long-continued research, here, we report the synthesis of a water-stabilized cyclo-N5ˉ salt, [Mg(H2O)6]2+[(N5)2(H2O)4]2ˉ, in which the non-energetic Clˉ of (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl was removed. For the elimination of the water, a silver cyclo-N5ˉ complex (AgN5) was precipitated by the addition of AgNO3 to the [Mg(H2O)6]2+[(N5)2(H2O)4]2ˉ solution. By treatment with NH3·H2O, this AgN5 complex was converted to a 3D-framework [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ salt, which was characterized by its crystal structure. The AgN5 complex is stable up to 90 °C, is photolytically unstable decomposing to AgN3 and N2, and Ag and N2 are its only final decomposition products. The isolation of a silver cyclo-N5ˉ complex, devoid of stabilizing molecules and ions, such as H2O, H3O+, and NH4+, constitutes a major advance in pentazole chemistry.
Results
Materials synthesis and structural design
The schematic in Fig. 1 illustrates the procedures for the syntheses of the AgN5 and [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ. In view of previous research, our team have achieved a breakthrough in cyclo-N5ˉ chemistry involving the synthesis and characterization of the stable pentazolate salt, (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl1. We also demonstrated that a cobalt ion can effectively trap cyclo-N5ˉ, forming the stable compound Co(N5)2(H2O)4·4H2O2. As part of our continuing effort to prepare an essentially naked cyclo-N5ˉ salt, we first added magnesium nitrate to an aqueous solution of (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl at room temperature, resulting in the formation of a white crystalline precipitate of [Mg(H2O)6]2+[(N5)2(H2O)4]2ˉ (Fig. 2) in 85% yield based on the cyclo-N5ˉ content of (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl. Subsequently, an aqueous solution of silver nitrate was added dropwise to the stirred [Mg(H2O)6]2+[(N5)2(H2O)4]2ˉ solution in methanol, resulting in the precipitation of the AgN5 complex as a pale white solid. However, the AgN5 complex was light-sensitive and insoluble in all solvents tested. To further characterize this complex, we instantly treated it with 10 equiv. of NH3·H2O (25 wt%) at 0 °C, followed by warming to room temperature to liberate NH3 and to provide colorless crystals of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ (Supplementary Fig. 1). This compound is thermally stable up to about 90 °C, where it starts to decompose with N2 evolution to form AgN3. In contrast to the very sensitive AgN5/AgN3, it is only moderately sensitive to impact and friction, with H50 = 73.8 cm (average) and an explosive probability P (%) = 76 (Supplementary Table 1), respectively.
Crystal structure
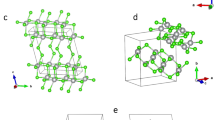
The intermediate synthesis of [Mg(H2O)6]2+[(N5)2(H2O)4]2ˉ is an effective step to get rid of the Clˉ present in the original (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl salt. The crystal structure of the above Mg salt was determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (Fig. 2a, b), which showed that it crystallizes in the triclinic space group P-1. The magnesium center is coordinated to six water molecules in an octahedral fashion with no direct bonding interaction between Mg2+ and cyclo-N5ˉ, in contrast to the structure of Co(N5)2(H2O)4·4H2O, where the cobalt ion acts as a shared center linking two pentagonal N5ˉ rings through two σ-bonds. Interestingly, the cyclo-N5ˉ ring is surrounded by five crystallographically independent H2O molecules, forming the water-stabilized cyclo-N5ˉ salt. Each of these bridging water molecules acts as an H-bond donor for a nitrogen atom of cyclo-N5ˉ. Such a coordination mode for cyclo-N5ˉ is unique and is of vital importance for the further construction of novel pentazolate complexes, because the stability of the water-stabilized cyclo-N5ˉ salt is determined primarily by hydrogen bonding. These hydrogen bonds can be relatively easily broken, if other cations can trap the cyclo-N5ˉ anion by forming strong chemical bonds.
These considerations have sparked our interest in the preparation of other novel cyclo-N5ˉ complexes. As a consequence, we synthesized the AgN5 complex and its 3D-framework complex, [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ. The structure of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ was determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. It crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with a calculated density of 3.2 g/cm3 at 123 K (Supplementary Tables 2–6). The density value is the highest crystal density reported so far for any cyclo-N5ˉ complex15, and is largely due to the presence of four heavy silver atoms. As depicted in the Oak Ridge Thermal Ellipsoid plot (ORTEP) of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ (Fig. 3a), the asymmetrical unit contains half of an [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ molecule, which is composed of two Ag(I) cations (50% occupancy for Ag1 and Ag3, 100% occupancy for Ag2), two cyclo-N5ˉ rings, and one coordinated NH3 molecule. One cyclo-N5ˉ ring is no longer perfectly planar, showing a small degree of distortion, as evident from the torsion angles of N(6)-N(7)-N(8)-N(9) being –0.3° and N(8)-N(9)-N(10)-N(6) being 0.2°. In contrast, the other cyclo-N5ˉ ring resists distortion from planarity, causing a change in the N–N bond lengths (1.323–1.336 Å), which are slightly longer than the N–N bonds (1.318–1.320 Å) in Co(N5)2(H2O)4•4H2O. Figure 3b shows the coordination environment of the Ag cations. There are three crystallographically independent Ag centers in the structure. Ag3 is bridging between two ammonia molecules in a linear configuration with relatively short Ag3–N distances (2.110 Å; N(11)-Ag(3)-N(11), 180°). Ag2 is coordinated by four cyclo-N5ˉ rings, where four N atoms (N1, N4, N6, N9) adopt a distorted tetrahedral configuration around Ag2, with intermediate Ag2–N distances ranging from 2.332 to 2.370 Å, whereas Ag1 is surrounded by three pairs of cyclo-N5ˉ rings (N3, N7, and N10) adopting an octahedral geometry with two cyclo-N5ˉ rings at the apical positions and four cyclo-N5ˉ rings at the equatorial sites. The average Ag1–N distance of 2.519 Å is much longer than the reported values for triazole complexes of Ag(I) (average 2.11 Å)16, and the longest bond in the structure, Ag1-N10 (2.669 Å), indicates that the interaction between Ag and cyclo-N5ˉ is weak.
Crystal structure of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ. a ORTEP plot of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ at the 50% probability level. b The coordinate diagram of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ. c Unit cell view along the b axis. d Schematic representation of the hydrogen-bonded motifs in the crystal structure: H-bonds are indicated as dotted lines. e π–π stacking interaction in the crystal structure (Cg1 and Cg2 were the centers of cyclo-N5ˉ). f The 3D framework of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ
Energetic metal-organic frameworks (energetic-MOFs) have recently received attention as insensitive HEDMs. The energetic-MOFs are constructed by metal ions and organic ligands, such as azides, furazans, triazoles, and tetrazoles, via coordination bonds, which give one-dimensional (1D), two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) structures17,18,19,20. Especially noteworthy is the fact that 3D frameworks usually possess more complicated connection modes than 1D and 2D frameworks, which could further enhance their structural stability21. As illustrated in Fig. 3c, the silver bridged pentazolate anion in [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ can also be interpreted as a 3D energetic-framework, which is constructed from Ag1, Ag2 and cyclo-N5ˉ. The overall architecture of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ is produced with tandem coordination bonding interactions between Ag+ and cyclo-N5ˉ. Continuous catenation in 3D directions is made possible by independent Ag+ centers as nodes, coordinatively bound to cyclo-N5ˉ linkers. The propagation of both six-coordinated Ag1 and four-coordinated Ag2 to cyclo-N5ˉ generates 3D polycatenated framework (Fig. 3f). Although Ag3 doesnot connect to the 3D framework, the coordinated [Ag(NH3)2]+ is located right in the center of the voids of the crystal structure, and forms hydrogen bonds with the 3D-network (Fig. 3d), (N(11)-H(11 A)···N(2), 2.50 Å; N(11)-H(11 A)···N(8), 2.31 Å; N(11)-H(11B)···N(5), 2.27 Å; N(11)-H(11 C)···N(3), 2.69 Å; N(11)-H(11 C)···N(10), 2.44 Å). To better understand its structure, the 3D framework of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ can be topologically defined as a 3,4,4,6-c net with long Schlfli symbol of (4•62)2(42•63•8)2(43•63)2(44•62•86•103). As shown in Supplementary Fig. 2, topological analysis indicates that the 3D framework of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ can be abstracted as a binodal three- and four-connected net, each silver linker connects three or four cyclo-N5ˉ anions, which corresponds better to the arrangement of atoms in the 3D framework structure. In addition, typical π–π stacking interactions are observed in [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ between the two off-center parallel cyclo-N5ˉ rings (Fig. 3e), with centroid–centroid distances of 3.634(5) Å and 3.838(5) Å, respectively, which are consistent with previously reported π–π stacking distances between aromatic molecules22. The remarkable face-to-face π–π interactions are important contacts, similar to hydrogen bonding, enhancing the stability of the whole [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ structure. Attempts to determine the surface area and porosity of the 3D framework by Brunner−Emmet−Teller (BET) measurements were unsuccessful because of the inability to completely degas the samples due to their limited thermal stability and the small sample sizes used.
Physicochemical properties
The [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ 3D framework was further investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Figure 4a shows the XPS wide scan spectrum, which exhibits N1s and Ag3d peaks only. Two peaks at 368.58 and 374.48 eV generated by photoelectrons emitted from the Ag3d core level, can be observed (Fig. 4b), which indicate the presence of only one type of oxidation state for silver that coordinates to the nitrogen atoms in cyclo-N5ˉ and NH3. Figure 4c presents the high-resolution XPS results of N1s. Its binding energy at 401.28 eV is characteristic for the nitrogen atoms that form the cyclo-N5ˉ ring. These XPS spectra also demonstrate the similarity of the AgN5 units in both compounds.
We further analyzed the structure of the AgN5 complex and [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ by Raman and infrared spectroscopy. As can be seen from Fig. 5, the three typical cyclo-N5ˉ RA bands are present at about 1180 cm−1 (A1’), 1120 cm−1 (E2’) and 1020 cm−1 (E2’) in both compounds, in excellent agreement with the frequencies observed for (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl1. For the NH3 coordinated cation in [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ (Fig. 5a), two new characteristic bands are observed at 393 and 3266 cm−1, which are due to the symmetric Ag-N2 stretching mode of [NH3-Ag-NH3]+ and the NH3 stretching modes, respectively23,24. The infrared spectra of the two compounds show the characteristic absorption of the pentazole rings at ca. 1225 ± 10 cm−1 that is generally present in pentazole complexes. The assignments for the NH3 bands in [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ are unequivocal, including the different N-H stretching vibrations in the region of 3000–3400 cm−1, the symmetric deformation around 1601 cm−1, and the rocking mode around 688 cm−1. These absorptions of [Ag(NH3)2]+ in [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ agree with those of other diamine silver complexes, such as [Ag(NH3)2]NO3 and [Ag(NH3)2]2SO425,26. In the infrared spectrum of the AgN5 complex one additional unassigned band is observed at 1704 cm−1. In the vibrational spectra of the AgN5 complex (Fig. 5b), bands due to N3ˉ are observed at 2085, 1335, and 604 cm−1 in the RA spectrum (Supplementary Fig. 3), and at 2016 and 1361 cm−1 in the infrared (IR) spectrum which are due to N3ˉ (ref. 27). The fact that the vibrational spectra of the AgN5 complex essentially show only bands due to N5ˉ and N3ˉ lends further support to our identification of this compound as a mixture of solvent-free AgN5 and AgN3. This conclusion is further supported the crystal structure of [Ag(NH3)2][Ag3(N5)4], in which no evidence for solvate methanol or water molecules was found. Furthermore, the elemental analysis shows the carbon content in the sample of [Ag(NH3)2][Ag3(N5)4] to be lower than 0.5%. If some disordered small molecules, such as methanol, existed, they would result in the carbon content to be higher than 0.5%. In addition, no characteristic absorption bands of H2O or CH3OH were observed in the IR and RA spectra.
The minor slope in the TG curve before 100 °C in the Supplementary Fig. 4 can be attributed to the small sample size and some slight decomposition due to the light-sensitivity of the sample. It is also worth mentioning that there were no endothermic peaks in the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) curve in the 50~90 °C temperature region, as would be expected for the evaporation of H2O or CH3OH. The thermal-decomposition behavior and the stability of Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ were investigated by thermogravimetric differential scanning calorimetry (TG-DSC) under an argon atmosphere. [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ showed a two-step rapid decomposition beginning at 90 °C with a mass loss of about 25% between 90 and 134 °C, followed by the loss of another approximately 25% between 134 and 320 °C (Supplementary Figs. 4 and 5). Using thermogravimetric analysis, coupled with mass spectroscopy (TG-Mass), a change of the MS curve at mass 17 (NH3) was observed along with the release of N2 in the first stage of the decomposition (Supplementary Fig. 6). The second step probably involves the decomposition of AgN3 to give Ag and N228.
To confirm the overall decomposition process, the decomposition residue from the first weight loss was investigated by slowly heating the complexes under argon to 100 °C and then cooling them back to room temperature, followed by IR and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses. The IR spectrum of the [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ residue exhibited the characteristic N3ˉ peaks. An additional peak at 3320 cm−1 was assigned to HN329, suggesting the generation of HN3 during the first stage of the decomposition, followed by its absorption on the surface of AgN3. In the XRD analysis (Fig. 6h), the position and relative intensity of all diffraction peaks match well with those from a standard AgN3 sample, further confirming the composition of the first-step residue as AgN3. The XRD powder pattern of the decomposition residue (Fig. 6h) is distinct from that of the original pattern of the starting material before decomposition (Supplementary Fig. 7). One major difference between these complexes and the previously reported (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl or Co(N5)2(H2O)4·4H2O is that during the decomposition silver particles are produced along with complete release of N2. The final thermal-decomposition residue from [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ was verified by optical microscopy as pure Ag, which has brilliant metallic luster and an irregular, faceted structure (Supplementary Fig. 8). We have further confirmed this result by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX) to characterize the morphology and determine the chemical phases. Figure 6a indicates that the Ag formed from the thermal-decomposition process consists of multiple nano-layers. Each nano-layer is formed by silver nanoparticles (Fig. 6b), which have small crystallites as evidenced by the XRD analysis. The corresponding intensities of all diffraction peaks are weak due to the relatively low degree of crystallinity (Fig. 6d). The EDX spectrum shows that Ag is the only element detected in the selected region (Fig. 6c), The EDX mappings (Figs. 6e–g) recorded in the whole SEM image indicate that the element on the surface is Ag. By contrast, nitrogen is not observed in the sample region, suggesting the absence of nitrides on the Ag surface. The structure of the AgN5 complex was also studied in more detail. The XPS wide scan spectrum of the AgN5 complex showed no significant changes compared to that of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ, indicating a similar chemical composition (except for hydrogen). The core-level spectra of N1s, and Ag3d are presented in the Fig. 4a. The only difference between the AgN5 complex and [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ is that the N1s core levels are centered at 401.08 and 401.28 eV, respectively, which illustrates that the presence of different types of nitrogen groups in the AgN5 complex has resulted in a slight shift. The IR and RA spectra (Fig. 5b) show only the characteristic peaks of cyclo-N5ˉ and AgN3. To explain the formation of AgN3, a sample of the AgN5 complex was exposed to light for 24 h, and then the IR spectrum was re-recorded. It was found that the AgN5 complex is extremely sensitive to light and completely decomposes to AgN3, while the [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ salt is photolytically less sensitive due to the stabilization effect by the 3D framework. In combination with the structure of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ and the aforementioned data, it, therefore, can be concluded that the AgN5 complex is composed of AgN5 and AgN3. This conclusion was further supported by elemental analysis. The total silver content was determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). The found silver content in the AgN5 complex was 62.3 wt%, intermediate between 60.7% (theoretical silver content in AgN5) and 72% (theoretical silver content in AgN3). The nitrogen content of another sample was also found to be intermediate between the theoretical values for AgN5 and AgN3. Furthermore, the thermal stability and decomposition behavior of the AgN5 complex were also compared to those of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ. As shown in Supplementary Fig. 9, the TG curve also shows two decomposition stages. The first stage involves loss of N2 from AgN5 at 120 °C to give AgN3, and the second stage comprises the complete decomposition of AgN3 at 337 °C to metallic Ag and N2.
Characterization of the thermal-decomposition residues of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ. a SEM image at low magnification. b SEM image at high magnification. c EDS spectrum. d XRD pattern (JCPDS: 65-2871). e SEM image for mapping. f EDX mapping distribution of Ag. g EDX mapping distribution of N. h XRD analysis of the residue from the decomposition process of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ in the first weight loss step
Discussion
Our results demonstrate the successful syntheses of a solvent-free silver cyclo-pentazolate complex and [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ. The complexes are stable up to 90 °C and only Ag and N2 are observed as the final decomposition products. The original product from the [Mg(H2O)6]2+[(N5)2(H2O)4]2ˉ/AgNO3 reaction is AgN5, which subsequently undergoes partial photolytical and/or thermal-decomposition to AgN3. Although we could not obtain a crystal structure for AgN5, the indirect evidence for its formation is convincing. The isolation of a cyclo-N5ˉ metal complex, devoid of stabilizing molecules and ions, such as H2O, H3O+, and NH4+, constitutes a major advance in cyclo-pentazolate chemistry.
Methods
General information
Caution! Solid silver azide and pentazolate are highly energetic and shock and friction sensitive. They should be handled only on a small scale with appropriate safety precautions, i.e., safety glasses, face shields, heavy leather gloves and jackets, and ear plugs.
Materials characterization
All reagents and solvents used were of analytical grade. (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl was produced according to the methods described in the literature1. Fourier-transforminfrared spectra were recorded on a Thermo Nicolet IS10 instrument. Raman spectra were measured with a Renishaw (inVia) Raman spectrometer (785 nm excitation). TG-DSC-mass spectrometry (MS) measurements were performed on a Netzsch STA 409 PC/PG thermal analyzer at a heating rate of 5 K/min under argon atmosphere. X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) were carried out on a RBD upgraded PHI-5000C electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA) system (Perkin Elmer) with Mg Kα radiation (hν = 1486.6 eV). The crystalline structure was characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) with a X-ray diffractometer (D8 advance), using a monochromatized Cu target radiation source. The SEM mapping was observed under SEM (FEI verios 460).
Synthesis of [Mg(H2O)6]2+[(N5)2(H2O)4]2ˉ
A solution of Mg(NO3)2•6H2O (0.79 g, 3.08 mmol) in a mixture of solvents (20 mL) of methanol and water (v/v, 1/1) was added to a methanol solution of (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl (0.2 g, 0.34 mmol) and stirred at 20 °C for 8 h. The collected filtrate was evaporated under vacuum to furnish a residue. The targeted compound could be recrystallized from the mixture of acetone and methanol and dried in vacuum at room temperature for 4 h to afford the product with an 85% yield of [Mg(H2O)6]2+[(N5)2(H2O)4]2ˉ as an air-stable white solid.
Synthesis of [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ
An aqueous solution of silver nitrate (0.34 g, 1.91 mmol) was added dropwise to a solution of [Mg(H2O)6]2+[(N5)2(H2O)4]2ˉ (0.3 g, 0.87 mmol) in methanol while stirring at 20 °C for 30 min, producing the silver pentazolate complex as a pale solid. It was quickly dissolved in 10 equiv. of NH4OH and stirred at 0 °C for 20 min, followed by warming to room temperature to liberate NH3, providing the target product, [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ, in 80% yield as an air-stable white solid.
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Information files. All other relevant data supporting the findings of this study are available on request. Structural data for [Ag(NH3)2]+[Ag3(N5)4]ˉ and [Mg(H2O)6]2+[(N5)2(H2O)4]2ˉ were deposited with the Inorganic Crystal Structure Database (ICSD) under deposition numbers CSD: 433114 and 433851, respectively.
References
Zhang, C., Sun, C. G., Hu, B. C., Yu, C. M. & Lu, M. Synthesis and characterization of the pentazolate anion cyclo-N5ˉ in (N5)6(H3O)3(NH4)4Cl. Science 355, 374–376 (2017).
Zhang, C. et al. A symmetric Co(N5)2(H2O)4 4H2O high-nitrogen compound formed by cobalt (II) cation trapping of a cyclo-N5ˉ anion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 4512–4514 (2017).
Klapötke, T. M. & Sabaté, C. M. Bistetrazoles: Nitrogen-rich, high-performing, insensitive energetic compounds. Chem. Mater. 20, 3629–3637 (2008).
Nguyen, M. T. Polynitrogen compounds: 1. Structure and stability of N4 and N5 systems. Coord. Chem. Rev. 244, 93–113 (2003).
Eremets, M. I., Gavriliuk, A. G., Trojan, I. A., Dzivenko, D. A. & Boehler, R. Single-bonded cubic form of nitrogen. Nat. Mater. 3, 558–563 (2004).
Perera, S. A. & Bartlett, R. J. Coupled-cluster calculations of Raman intensities and their application to N4 and N5ˉ. Chem. Phys. Lett. 314, 381–387 (1999).
Haiges, R. et al. Polyazide chemistry: The first binary group 6 azides, Mo(N3)6, W(N3)6, [Mo(N3)7]ˉ, and [W(N3)7]ˉ, and the [NW(N3)4]ˉ and [NMo(N3)4]ˉ ions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44, 1860–1865 (2005).
Vij, A. et al. Polynitrogen chemistry. Synthesis, characterization, and crystal structure of surprisingly stable fluoroantimonate salts of N5 +. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 6308–6313 (2001).
Vij, A., Pavlovich, J. G., Wilson, W. W., Vij, V. & Christe, K. O. Experimental Detection of the pentaazacyclopentadienide (pentazolate) anion, cyclo-N5ˉ. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41, 3051–3054 (2002).
Steele, B. A. & Oleynik, I. I. Pentazole and ammonium pentazolate: Crystalline hydro-nitrogens at high pressure. J. Phys. Chem. A. 121, 1808–1813 (2017).
Bazanov, B. et al. Detection of cyclo-N5ˉ in THF solution. Ang. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 13233–13235 (2016).
Christe, K. O. Recent advances in the chemistry of N5 +, N5ˉ and high-oxygen compounds. Prop. Explos. Pyrotech. 32, 194–204 (2007).
Christe, K. O., Wilson, W. W., Sheehy, J. A. & Boatz, J. A. N5 +: A novel homoleptic polynitrogen ion as a high energy density material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 38, 2004–2009 (1999).
Haiges, R., Schneider, S., Schroer, T. & Christe, K. O. High-energy-density materials: Synthesis and characterization of N5 +[P(N3)6]ˉ, N5 +[B(N3)4]ˉ, N5 +[HF2]ˉ⋅nHF, N5 +[BF4]ˉ, N5 + [PF6]ˉ, and N5 +[SO3F]ˉ. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 4919–4924 (2004).
Qu, X. N. et al. An Ag(I) energetic metal–organic framework assembled with the energetic combination of furazan and tetrazole: Synthesis, structure and energetic performance. Dalton. Trans. 45, 6968–6973 (2016).
Borrajo-Calleja, G. M. et al. Synthesis of silver(I) and gold(I) complexes containing enantiopure pybox ligands. First assays on the silver(I)-catalyzed asymmetric addition of alkynes to imines. Inorg. Chem. 55, 8794–8807 (2016).
Krawiec, M. et al. Hydronium copper(II)-tris(5-nitrotetrazolate) trihydrate-a primary explosive. Prop. Explos. Pyrotech. 40, 457–459 (2015).
Zhang, J. H., Dharavath, S., Mitchell, L. A., Parrish, D. A. & Shreeve, J. M. Energetic salts based on 3, 5-bis (dinitromethyl)-1, 2, 4-triazole monoanion and dianion: controllable preparation, characterization, and high performance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 7500–7503 (2016).
McDonald, K. A., Seth, S. & Matzger, A. J. Coordination polymers with high energy density: An emerging class of explosives. Cryst. Growth Des. 15, 5963–5972 (2015).
Seth, S. & Matzger, A. J. Coordination polymerization of 5, 5′-dinitro-2H, 2H′-3, 3′-bi-1, 2, 4-triazole leads to a dense explosive with high thermal stability. Inorg. Chem. 56, 561–565 (2017).
Li, S. H. et al. 3D energetic metal-organic frameworks: Synthesis and properties of high energy materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 14031–14035 (2013).
Janiak, C. A critical account on π–π stacking in metal complexes with aromatic nitrogen-containing ligands. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton. Trans. 21, 3885–3896 (2000).
Nilsson, K. B., Persson, I. & Kessler, V. G. Coordination chemistry of the solvated AgI and AuI ions in liquid and aqueous ammonia, trialkyl and triphenyl phosphite, and tri-n-butylphosphine solutions. Inorg. Chem. 45, 6912–6921 (2006).
Ujike, T. & Tominaga, Y. Raman spectral analysis of liquid ammonia and aqueous solution of ammonia. J. Raman Spectrosc. 33, 485–493 (2002).
Woidy, P. & Kraus, F. The diammine silver(I) acetate [Ag(NH3)2]OAc. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 639, 2643–2647 (2013).
Geddes, A. L. & Bottger, G. L. Infrared spectra of silver-ammine complexes. Inorg. Chem. 8, 802–807 (1969).
Grocholl, L., Wang, J. J. & Gillan, E. G. Synthesis of sub-micron silver and silver sulfide particles via solvothermal silver azide decomposition. Mater. Res. Bull. 38, 213–220 (2003).
Iqbal, Z., Prask, H. J. & Trevino, S. F. in Energetic Materials (eds Fair, H. D. & Walker, R. F.) 131–191 (Plenum Press, New York, 1977).
Dows, D. A. & Pimentel, G. C. Infrared spectra of gaseous and solid hydrazoic acid and deutero-hydrazoic acid: The thermodynamic properties of HN3. J. Chem. Phys. 23, 1258–1263 (1955).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for financial support provided by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 30917011101), University of Science and Technology Liaoning Fund for Young Talent (No. 601011506-8), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions. We also thank Huaping Bai (Analysis and Testing Center of Nanjing University of Science and Technology) for testing of the XRD spectra, Wanying Tang (Analysis and Testing Center of Nanjing University of Science and Technology) for testing of the IR spectra, Wenxian Wei (Yangzhou University) for testing of the Raman spectra, Chuanqiang Zhou (Yangzhou University) for testing of the XPS spectra and Fengfeng Wang (Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Science & Peking Union Medical College) for his expert crystallographic analysis. Karl Christe gratefully acknowledges financial support from the Office of Naval Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.H. designed the scheme and conducted experiments. C.S., C.Z., C.J., C.Y., Y.D., Z.Z., and Y.Z. conducted the experiments. All the authors contributed to discussions of the results for the manuscript. C.S. and C.Z. wrote the manuscript. B.H., C.J., and Y.D. reviewed this manuscript. K.C. gave important suggestions on the paper and discussed the characterization of the silver pentazolate complex, he also revised this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Zhang, C., Jiang, C. et al. Synthesis of AgN5 and its extended 3D energetic framework. Nat Commun 9, 1269 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03678-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03678-y
This article is cited by
-
Taming cyclo-pentazolate anions with a hydrogen-bonded organic framework
Communications Materials (2024)
-
Aromatic hexazine [N6]4− anion featured in the complex structure of the high-pressure potassium nitrogen compound K9N56
Nature Chemistry (2023)
-
Theoretical design of new insensitive high energy metal complexes based on the double fused-ring insensitive ligands strategy
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2023)
-
Stabilization of hexazine rings in potassium polynitride at high pressure
Nature Chemistry (2022)
-
Molding preparation and research on performance of low-electrostatic-sensitivity, high-output carbon-based copper azide based on metal–organic framework/graphene oxide
Journal of Materials Science (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.