Abstract
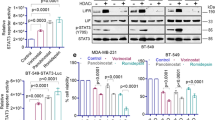
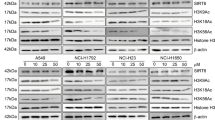
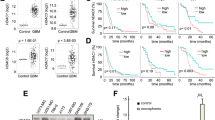
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors (HDIs) are promising anticancer therapies and have been clinically used for the treatment of hematological malignancy. However, their efficacy in solid tumors is marginal and drug resistance hampers their further clinical utility. To develop novel strategies for the HDI-based anticancer therapeutics in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), in the present study, we investigated the mechanisms underlying resistance to HDI treatment in NSCLC cells. We show the STAT3-mediated IGF2/IGF-1R signaling cascade as a key modulator for both acquired and primary HDI resistance. The treatment with HDI upregulated IGF2 transcription in NSCLC cells carrying intrinsic or acquired drug resistance via direct binding of STAT3 in IGF2 P3 and P4 promoters. Acetylated STAT3 emerged upon HDAC inhibition was protected from the proteasome-mediated degradation of STAT3 and functioned as a direct transcription factor for IGF2 expression. Genomic or pharmacological strategies targeting STAT3 diminished the HDI-induced IGF2 mRNA expression and overcame the resistance to HDI treatment in HDI-resistant NSCLC- or patient-derived tumor xenograft models. These findings provide new insights into the role of acetylated STAT3-mediated activation of IGF2 transcription in HDI resistance, suggesting IGF2 or STAT3 as novel targets to overcome HDI resistance in NSCLC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Minucci S, Pelicci PG . Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 38–51.
Duvic M, Talpur R, Ni X, Zhang C, Hazarika P, Kelly C et al. Phase 2 trial of oral vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood 2007; 109: 31–39.
Garcia-Manero G, Yang H, Bueso-Ramos C, Ferrajoli A, Cortes J, Wierda WG et al. Phase 1 study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid [SAHA]) in patients with advanced leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2008; 111: 1060–1066.
O'Connor OA, Heaney ML, Schwartz L, Richardson S, Willim R, MacGregor-Cortelli B et al. Clinical experience with intravenous and oral formulations of the novel histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 166–173.
Olsen EA, Kim YH, Kuzel TM, Pacheco TR, Foss FM, Parker S et al. Phase IIb multicenter trial of vorinostat in patients with persistent, progressive, or treatment refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 3109–3115.
Traynor AM, Dubey S, Eickhoff JC, Kolesar JM, Schell K, Huie MS et al. Vorinostat (NSC# 701852) in patients with relapsed non-small cell lung cancer: a Wisconsin Oncology Network phase II study. J Thorac Oncol 2009; 4: 522–526.
Fantin VR, Richon VM . Mechanisms of resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitors and their therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 7237–7242.
Lee JH, Choy ML, Marks PA . Mechanisms of resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Adv Cancer Res 2012; 116: 39–86.
Kirschbaum M, Gojo I, Goldberg SL, Bredeson C, Kujawski LA, Yang A et al. A phase 1 clinical trial of vorinostat in combination with decitabine in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia or myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol 2014; 167: 185–193.
Dallas NA, Xia L, Fan F, Gray MJ, Gaur P, van Buren G 2nd et al. Chemoresistant colorectal cancer cells, the cancer stem cell phenotype, and increased sensitivity to insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibition. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 1951–1957.
Desbois-Mouthon C, Cacheux W, Blivet-Van Eggelpoel MJ, Barbu V, Fartoux L, Poupon R et al. Impact of IGF-1R/EGFR cross-talks on hepatoma cell sensitivity to gefitinib. Int J Cancer 2006; 119: 2557–2566.
Eckstein N, Servan K, Hildebrandt B, Politz A, von Jonquieres G, Wolf-Kummeth S et al. Hyperactivation of the insulin-like growth factor receptor I signaling pathway is an essential event for cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 2996–3003.
Huang GS, Brouwer-Visser J, Ramirez MJ, Kim CH, Hebert TM, Lin J et al. Insulin-like growth factor 2 expression modulates Taxol resistance and is a candidate biomarker for reduced disease-free survival in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 2999–3010.
Shan J, Shen J, Liu L, Xia F, Xu C, Duan G et al. Nanog regulates self-renewal of cancer stem cells through the insulin-like growth factor pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012; 56: 1004–1014.
Villanueva J, Vultur A, Lee JT, Somasundaram R, Fukunaga-Kalabis M, Cipolla AK et al. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and IGF-1R/PI3K. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 683–695.
Kohda M, Hoshiya H, Katoh M, Tanaka I, Masuda R, Takemura T et al. Frequent loss of imprinting of IGF2 and MEST in lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Carcinog 2001; 31: 184–191.
Sakatani T, Kaneda A, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Carter MG, de Boom Witzel S, Okano H et al. Loss of imprinting of Igf2 alters intestinal maturation and tumorigenesis in mice. Science 2005; 307: 1976–1978.
Suzuki H, Ueda R, Takahashi T . Altered imprinting in lung cancer. Nat Genet 1994; 6: 332–333.
Bell AC, Felsenfeld G . Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature 2000; 405: 482–485.
Hark AT, Schoenherr CJ, Katz DJ, Ingram RS, Levorse JM, Tilghman SM . CTCF mediates methylation-sensitive enhancer-blocking activity at the H19/Igf2 locus. Nature 2000; 405: 486–489.
Phillips JE, Corces VG . CTCF: master weaver of the genome. Cell 2009; 137: 1194–1211.
Schoenherr CJ, Levorse JM, Tilghman SM . CTCF maintains differential methylation at the Igf2/H19 locus. Nat Genet 2003; 33: 66–69.
Lui JC, Baron J . Evidence that Igf2 down-regulation in postnatal tissues and up-regulation in malignancies is driven by transcription factor E2f3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 6181–6186.
Tada Y, Yamaguchi Y, Kinjo T, Song X, Akagi T, Takamura H et al. The stem cell transcription factor ZFP57 induces IGF2 expression to promote anchorage-independent growth in cancer cells. Oncogene 2015; 34: 752–760.
Kim JS, Lee SC, Min HY, Park KH, Hyun SY, Kwon SJ et al. Activation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling mediates resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Lett 2015; 361: 197–206.
Nordin M, Bergman D, Halje M, Engstrom W, Ward A . Epigenetic regulation of the Igf2/H19 gene cluster. Cell Prolif 2014; 47: 189–199.
van Dijk MA, van Schaik FM, Bootsma HJ, Holthuizen P, Sussenbach JS . Initial characterization of the four promoters of the human insulin-like growth factor II gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1991; 81: 81–94.
Lee JS, Kang JH, Boo HJ, Hwang SJ, Hong S, Lee SC et al. STAT3-mediated IGF-2 secretion in the tumour microenvironment elicits innate resistance to anti-IGF-1R antibody. Nat Commun 2015; 6: 8499.
Wang K, Wang C, Xiao F, Wang H, Wu Z . JAK2/STAT2/STAT3 are required for myogenic differentiation. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 34029–34036.
Fantin VR, Loboda A, Paweletz CP, Hendrickson RC, Pierce JW, Roth JA et al. Constitutive activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription predicts vorinostat resistance in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 3785–3794.
Schust J, Sperl B, Hollis A, Mayer TU, Berg T . Stattic: a small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem Biol 2006; 13: 1235–1242.
Mayo MW, Denlinger CE, Broad RM, Yeung F, Reilly ET, Shi Y et al. Ineffectiveness of histone deacetylase inhibitors to induce apoptosis involves the transcriptional activation of NF-kappa B through the Akt pathway. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 18980–18989.
Min HY, Yun HJ, Lee JS, Lee HJ, Cho J, Jang HJ et al. Targeting the insulin-like growth factor receptor and Src signaling network for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer 2015; 14: 113.
Shin DH, Min HY, El-Naggar AK, Lippman SM, Glisson B, Lee HY . Akt/mTOR counteract the antitumor activities of cixutumumab, an anti-insulin-like growth factor I receptor monoclonal antibody. Mol Cancer Ther 2011; 10: 2437–2448.
Shin DH, Lee HJ, Min HY, Choi SP, Lee MS, Lee JW et al. Combating resistance to anti-IGFR antibody by targeting the integrin beta3-Src pathway. J Natl Cancer Inst 2013; 105: 1558–1570.
Lee H, Zhang P, Herrmann A, Yang C, Xin H, Wang Z et al. Acetylated STAT3 is crucial for methylation of tumor-suppressor gene promoters and inhibition by resveratrol results in demethylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 7765–7769.
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R, Jove R . Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: new and unexpected biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer 2014; 14: 736–746.
Yuan ZL, Guan YJ, Chatterjee D, Chin YE . Stat3 dimerization regulated by reversible acetylation of a single lysine residue. Science 2005; 307: 269–273.
Dhe-Paganon S, Syeda F, Park L . DNA methyl transferase 1: regulatory mechanisms and implications in health and disease. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 2011; 2: 58–66.
Wang X, Crowe PJ, Goldstein D, Yang JL . STAT3 inhibition, a novel approach to enhancing targeted therapy in human cancers (review). Int J Oncol 2012; 41: 1181–1191.
Yee D . Insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibitors: baby or the bathwater? J Natl Cancer Inst 2012; 104: 975–981.
Licciardi PV, Ververis K, Tang ML, El-Osta A, Karagiannis TC . Immunomodulatory effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Curr Mol Med 2013; 13: 640–647.
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW . NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 2012; 9: 671–675.
Singh P, Dai B, Given RL, Lu X, Holthuizen PE . Differential activation of IGF-II promoters P3 and P4 in Caco-2 cells during growth and differentiation. Gastroenterology 1998; 114: 1221–1229.
Zhang X, Guo C, Chen Y, Shulha HP, Schnetz MP, LaFramboise T et al. Epitope tagging of endogenous proteins for genome-wide ChIP-chip studies. Nat Methods 2008; 5: 163–165.
Lawson EA, Zhang X, Crocker JT, Wang WL, Klibanski A . Hypoglycemia from IGF2 overexpression associated with activation of fetal promoters and loss of imprinting in a metastatic hemangiopericytoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94: 2226–2231.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD . Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 2001; 25: 402–408.
Jin Q, Lee HJ, Min HY, Smith JK, Hwang SJ, Whang YM et al. Transcriptional and posttranslational regulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 by Akt3. Carcinogenesis 2014; 35: 2232–2243.
McCue J, Freed B . Measuring lymphocyte transcription factor activity by ELISA. Curr Protoc Toxicol 2005; Chapter 18: Unit 18.5.
Mathelier A, Zhao X, Zhang AW, Parcy F, Worsley-Hunt R, Arenillas DJ et al. JASPAR 2014: an extensively expanded and updated open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42: D142–D147.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Tomas Ekström (Karolinska Hospital, Sweden) to kindly provide the information on the structure and sequence of IGF2 promoters. This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP), Republic of Korea ((Nos. NRF-2011-0017639 and NRF-2011-0030001), the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (1520250)) and the National Institutes of Health (R01 CA100816).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SC., Min, HY., Jung, H. et al. Essential role of insulin-like growth factor 2 in resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Oncogene 35, 5515–5526 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.92
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.92
This article is cited by
-
FOXA1 prevents nutrients deprivation induced autophagic cell death through inducing loss of imprinting of IGF2 in lung adenocarcinoma
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
The contributing factors of resistance or sensitivity to epigenetic drugs in the treatment of AML
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2022)