Abstract
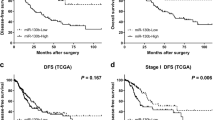
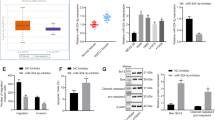
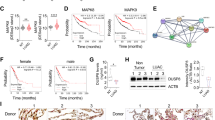
The disabled homolog 2 (DAB2) gene was recently identified as a tumor suppressor gene with its expression downregulated in multiple cancer types. The role of DAB2 in lung tumorigenesis, however, is not fully characterized, and the mechanisms of DAB2 dysregulation in lung cancer are not defined. Here we show that low DAB2 levels in lung tumor specimens are significantly correlated with poor patient survival, and that DAB2 overexpression significantly inhibits cell growth in cultured lung cancer cells, indicating its potent tumor suppressor function. We next identify that microRNA miR-93 functions as a potent repressor of DAB2 expression by directly targeting the 3′UTR of the DAB2 mRNA. Using in vitro and in vivo approaches, we demonstrate that miR-93 overexpression has an important role in promoting lung cancer cell growth, and that its oncogenic function is primarily mediated by downregulating DAB2 expression. Our clinical investigations further indicate that high tumor levels of miR-93 are correlated with poor survival of lung cancer patients. The correlations of both low DAB2 and high miR-93 expression levels with poor patient survival strongly support the critical role of the miR-93/DAB2 pathway in determining lung cancer progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karam JA, Shariat SF, Huang HY, Pong RC, Ashfaq R, Shapiro E et al. Decreased DOC-2/DAB2 expression in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13 (15 Pt 1): 4400–4406.
Mok SC, Chan WY, Wong KK, Cheung KK, Lau CC, Ng SW et al. DOC-2, a candidate tumor suppressor gene in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncogene 1998; 16: 2381–2387.
Fazili Z, Sun W, Mittelstaedt S, Cohen C, Xu XX . Disabled-2 inactivation is an early step in ovarian tumorigenicity. Oncogene 1999; 18: 3104–3113.
Tseng CP, Ely BD, Li Y, Pong RC, Hsieh JT . Regulation of rat DOC-2 gene during castration-induced rat ventral prostate degeneration and its growth inhibitory function in human prostatic carcinoma cells. Endocrinology 1998; 139: 3542–3553.
Bagadi SA, Prasad CP, Srivastava A, Prashad R, Gupta SD, Ralhan R . Frequent loss of Dab2 protein and infrequent promoter hypermethylation in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2007; 104: 277–286.
Anupam K, Tusharkant C, Gupta SD, Ranju R . Loss of disabled-2 expression is an early event in esophageal squamous tumorigenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12: 6041–6045.
Yang DH, Fazili Z, Smith ER, Cai KQ, Klein-Szanto A, Cohen C et al. Disabled-2 heterozygous mice are predisposed to endometrial and ovarian tumorigenesis and exhibit sex-biased embryonic lethality in a p53-null background. Am J Pathol 2006; 169: 258–267.
Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Gorden A, Farina M, Lee JS, Conner EA et al. Mechanistic and prognostic significance of aberrant methylation in the molecular pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 2713–2722.
Hannigan A, Smith P, Kalna G, Lo Nigro C, Orange C, O'Brien DI et al. Epigenetic downregulation of human disabled homolog 2 switches TGF-beta from a tumor suppressor to a tumor promoter. J Clin Invest 2010; 120: 2842–2857.
Wikman H, Kettunen E, Seppanen JK, Karjalainen A, Hollmen J, Anttila S et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes in pulmonary adenocarcinoma by using cDNA array. Oncogene 2002; 21: 5804–5813.
Xu HT, Yang LH, Li QC, Liu SL, Liu D, Xie XM et al. Disabled-2 and Axin are concurrently colocalized and underexpressed in lung cancers. Hum Pathol 2011; 42: 1491–1498.
Xu HT, Xie XM, Li QC, Liu SL, Dai SD, Liu Y et al. Atonal homolog 1 expression in lung cancer correlates with inhibitors of the Wnt pathway as well as the differentiation and primary tumor stage. APMIS 2013; 121: 111–119.
Chao A, Lin CY, Lee YS, Tsai CL, Wei PC, Hsueh S et al. Regulation of ovarian cancer progression by microRNA-187 through targeting Disabled homolog-2. Oncogene 2012; 31: 764–775.
Mayorga ME, Penn MS . miR-145 is differentially regulated by TGF-beta1 and ischaemia and targets Disabled-2 expression and wnt/beta-catenin activity. J Cell Mol Med 2012; 16: 1106–1113.
Fang L, Du WW, Yang W, Rutnam ZJ, Peng C, Li H et al. MiR-93 enhances angiogenesis and metastasis by targeting LATS2. Cell Cycle 2012; 11: 4352–4365.
Borchert GM, Holton NW, Larson ED . Repression of human activation induced cytidine deaminase by miR-93 and miR-155. BMC Cancer 2011; 11: 347.
Fang L, Deng Z, Shatseva T, Yang J, Peng C, Du WW et al. MicroRNA miR-93 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting integrin-beta8. Oncogene 2011; 30: 806–821.
Kim K, Chadalapaka G, Lee SO, Yamada D, Sastre-Garau X, Defossez PA et al. Identification of oncogenic microRNA-17-92/ZBTB4/specificity protein axis in breast cancer. Oncogene 2012; 31: 1034–1044.
Du L, Schageman JJ, Subauste MC, Saber B, Hammond SM, Prudkin L et al. miR-93, miR-98, and miR-197 regulate expression of tumor suppressor gene FUS1. Mol Cancer Res 2009; 7: 1234–1243.
Pineau P, Volinia S, McJunkin K, Marchio A, Battiston C, Terris B et al. miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 264–269.
Kim YK, Yu J, Han TS, Park SY, Namkoong B, Kim DH et al. Functional links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37: 1672–1681.
He J, Smith ER, Xu XX . Disabled-2 exerts its tumor suppressor activity by uncoupling c-Fos expression and MAP kinase activation. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 26814–26818.
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP . Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 2009; 19: 92–105.
Garcia DM, Baek D, Shin C, Bell GW, Grimson A, Bartel DP . Weak seed-pairing stability and high target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2011; 18: 1139–1146.
Du L, Subauste MC, DeSevo C, Zhao Z, Baker M, Borkowski R et al. miR-337-3p and its targets STAT3 and RAP1A modulate taxane sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancers. PLoS One 2012; 7: e39167.
Wang T, Lv M, Shen S, Zhou S, Wang P, Chen Y et al. Cell-free microRNA expression profiles in malignant effusion associated with patient survival in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One 2012; 7: e43268.
Zhoul J, Hernandez G, Tu SW, Huang CL, Tseng CP, Hsieh JT . The role of DOC-2/DAB2 in modulating androgen receptor-mediated cell growth via the nongenomic c-Src-mediated pathway in normal prostatic epithelium and cancer. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 9906–9913.
Long J, Wang Y, Wang W, Chang BH, Danesh FR . Identification of microRNA-93 as a novel regulator of vascular endothelial growth factor in hyperglycemic conditions. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 23457–23465.
Yeung ML, Yasunaga J, Bennasser Y, Dusetti N, Harris D, Ahmad N et al. Roles for microRNAs, miR-93 and miR-130b, and tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 tumor suppressor in cell growth dysregulation by human T-cell lymphotrophic virus 1. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 8976–8985.
Chuang TD, Luo X, Panda H, Chegini N . miR-93/106b and their host gene, MCM7, are differentially expressed in leiomyomas and functionally target F3 and IL-8. Mol Endocrinol 2012; 26: 1028–1042.
Smith AL, Iwanaga R, Drasin DJ, Micalizzi DS, Vartuli RL, Tan AC et al. The miR-106b-25 cluster targets Smad7, activates TGF-beta signaling, and induces EMT and tumor initiating cell characteristics downstream of Six1 in human breast cancer. Oncogene 2012; 31: 5162–5171.
Yang L, Cheng P, Chen C, He HB, Xie GQ, Zhou HD et al. miR-93/Sp7 function loop mediates osteoblast mineralization. J Bone Miner Res 2012; 27: 1598–1606.
Fu X, Tian J, Zhang L, Chen Y, Hao Q . Involvement of microRNA-93, a new regulator of PTEN/Akt signaling pathway, in regulation of chemotherapeutic drug cisplatin chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer cells. FEBS Lett 2012; 586: 1279–1286.
Wang Z, Liu M, Zhu H, Zhang W, He S, Hu C et al. Suppression of p21 by c-Myc through members of miR-17 family at the post-transcriptional level. Int J Oncol 2010; 37: 1315–1321.
Li Y, Tan W, Neo TW, Aung MO, Wasser S, Lim SG et al. Role of the miR-106b-25 microRNA cluster in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci 2009; 100: 1234–1242.
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, Shah MH, Nicoloso MS, de Martino I et al. E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 272–286.
Carney DN, Minna JD . Small cell cancer of the lung. Clin Chest Med 1982; 3: 389–398.
Carney DN, Gazdar AF, Nau M, Minna JD . Biological heterogeneity of small cell lung cancer. Semin Oncol 1985; 12: 289–303.
Prudkin L, Behrens C, Liu DD, Zhou X, Ozburn NC, Bekele BN et al. Loss and reduction of FUS1 protein expression is a frequent phenomenon in the pathogenesis of lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 41–47.
Naldini L, Blomer U, Gallay P, Ory D, Mulligan R, Gage FH et al. In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a lentiviral vector. Science 1996; 272: 263–267.
Kluiver J, Gibcus JH, Hettinga C, Adema A, Richter MK, Halsema N et al. Rapid generation of microRNA sponges for microRNA inhibition. PLoS One 2012; 7: e29275.
Grimson A, Farh KK, Johnston WK, Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP, Bartel DP . MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell 2007; 27: 91–105.
Acknowledgements
We thank Vivienne Rebel and Nicholas Dybdal-Hargreaves for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported in part by R01 CA129632 (A Pertsemlidis) and Lung Cancer SPORE P50 CA70907 (JD Minna and II Wistuba) from the NCI, W81XWH-07-1-0306 from the Department of Defense (II Wistuba), Academic Excellence grant EDUD-7824-021007-US (A Pertsemlidis) from Sun Microsystems and Cancer Center Support grants P30 CA054174, P30 CA142543 and P30 CA016672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, L., Zhao, Z., Ma, X. et al. miR-93-directed downregulation of DAB2 defines a novel oncogenic pathway in lung cancer. Oncogene 33, 4307–4315 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.381
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.381
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
microRNA-93-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via a microRNA-93-5p/MAP3K2/c-Jun positive feedback circuit
Oncogene (2020)
-
High-throughput RNA sequencing from paired lesional- and non-lesional skin reveals major alterations in the psoriasis circRNAome
BMC Medical Genomics (2019)
-
Differential expression analysis at the individual level reveals a lncRNA prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma
Molecular Cancer (2017)
-
17β-Estradiol sensitizes ovarian surface epithelium to transformation by suppressing Disabled-2 expression
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
MiR-106b and miR-93 regulate cell progression by suppression of PTEN via PI3K/Akt pathway in breast cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2017)