Abstract
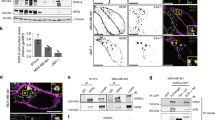
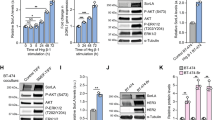
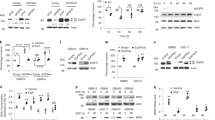
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation is frequently observed in human cancer and contributes to the growth, survival and therapeutic resistance of tumors. EGFRvIII is an oncogenic EGFR mutant resulting from the deletion of exons 2–7 and is the most common EGFR mutant observed in glioblastoma multiforme, an aggressive brain tumor. EGFRvIII is constitutively active but poorly ubiquitinated, leading to inefficient receptor trafficking to lysosomes and unattenuated oncogenic signaling. The mechanism by which EGFRvIII evades downregulation is not fully understood although recent studies suggest that its interaction with the ubiquitin ligase Cbl may be compromised. In this study, we examine the regulation of EGFRvIII by the recently identified negative regulator, LRIG1, which targets EGFR through recognition of its extracellular domain. Here, we determine whether the extracellular domain deletion in EGFRvIII renders it refractory to LRIG1 regulation. We find that EGFRvIII retains interaction with LRIG1 and is in fact more sensitive to LRIG1 action than wild-type receptor. We demonstrate that LRIG1 regulation of EGFRvIII is distinct from the only other known mechanism of EGFR regulation, Cbl-mediated degradation. Ectopic expression of LRIG1 in EGFRvIII(+) glioblastoma cells opposes EGFRvIII-driven tumor cell proliferation, survival, motility and invasion. Finally, RNAi-mediated silencing of LRIG1 alters EGFRvIII intracellular trafficking and leads to enhanced EGFRvIII expression, suggesting that loss of LRIG1 in tumors may contribute to a permissive environment for EGFRvIII overexpression, contributing to EGFRvIII oncogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastasi S, Sala G, Huiping C, Caprini E, Russo G, Iacovelli S et al. (2005). Loss of RALT/MIG-6 expression in ERBB2-amplified breast carcinomas enhances ErbB-2 oncogenic potency and favors resistance to Herceptin. Oncogene 24: 4540–4548.
Aoki T, Hashimoto N, Matsutani M . (2007). Management of glioblastoma. Expert Opin Pharmacother 8: 3133–3146.
Cook PW, Piepkorn M, Clegg CH, Plowman GD, DeMay JM, Brown JR et al. (1997). Transgenic expression of the human amphiregulin gene induces a psoriasis-like phenotype. J Clin Invest 100: 2286–2294.
Davies GC, Ryan PE, Rahman L, Zajac-Kaye M, Lipkowitz S . (2006). EGFRvIII undergoes activation-dependent downregulation mediated by the Cbl proteins. Oncogene 25: 6497–6509.
Ferby I, Reschke M, Kudlacek O, Knyazev P, Pantè G, Amann K et al. (2006). Mig6 is a negative regulator of EGF receptor-mediated skin morphogenesis and tumor formation. Nat Med 12: 568–573.
Goldoni S, Iozzo RA, Kay P, Campbell S, McQuillan A, Agnew C et al. (2007). A soluble ectodomain of LRIG1 inhibits cancer cell growth by attenuating basal and ligand-dependent EGFR activity. Oncogene 26: 368–381.
Grandal MV, Zandi R, Pedersen MW, Willumsen BM, van Deurs B, Poulsen HS . (2007). EGFRvIII escapes down-regulation due to impaired internalization and sorting to lysosomes. Carcinogenesis 7: 1408–1417.
Gur G, Rubin C, Katz M, Amit I, Citri A, Nilsson J et al. (2004). LRIG1 restricts growth factor signaling by enhancing receptor ubiquitylation and degradation. EMBO J 23: 3270–3281.
Han W, Zhang T, Yu H, Foulke JG, Tang CK . (2006). Hypophosphorylation of residue Y1045 leads to defective downregulation of EGFRvIII. Cancer Biol Ther 5: 1361–1368.
Hedman H, Nilsson J, Guo D, Henriksson R . (2002). Is LRIG1 a tumour suppressor gene at chromosome 3p14.3? Acta Oncol 41: 352–354..
Huang HS, Nagane M, Klingbeil CK, Lin H, Nishikawa R, Ji XD et al. (1997). The enhanced tumorigenic activity of a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor common in human cancers is mediated by threshold levels of constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation and unattenuated signaling. J Biol Chem 272: 2927–2935.
Huang PH, Mukasa A, Bonavia R, Flynn RA, Brewer ZE, Cavenee WK et al. (2007). Quantitative analysis of EGFRvIII cellular signaling networks reveals a combinatorial therapeutic strategy for glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 12867–12872.
Kirisits A, Pils D, Krainer M . (2007). Epidermal growth factor receptor degradation: an alternative view of oncogenic pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39: 2173–2182.
Laederich MB, Funes-Duran M, Yen L, Ingalla E, Wu X, Carraway III KL et al. (2004). The leucine-rich repeat protein LRIG1 is a negative regulator of ErbB family receptor tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem 279: 47050–47056.
Learn CA, Hartzell TL, Wikstrand CJ, Archer GE, Rich JN, Friedman AH et al. (2004). Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibition by mutant epidermal growth factor receptor variant III contributes to the neoplastic phenotype of glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Cancer Res 10: 3216–3224.
Lindström AK, Ekman K, Stendahl U, Tot T, Henriksson R, Hedman H et al. (2008). LRIG1 and squamous epithelial uterine cervical cancer: correlation to prognosis, other tumor markers, sex steroid hormones, and smoking. Int J Gynecol Cancer 18: 312–317.
Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I, Haas-Kogan DA, Zhu S, Dia EQ et al. (2005). Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med 353: 2012–2024.
Moscatello DK, Holgado-Madruga M, Emlet DR, Montgomery RB, Wong AJ . (1998). Constitutive activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by a naturally occurring mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 273: 200–206.
Nagane M, Levitzki A, Gazit A, Cavenee WK, Huang HJ . (1998). Drug resistance of human glioblastoma cells conferred by a tumor-specific mutant epidermal growth factor receptor through modulation of Bcl-XL and caspase-3-like proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 5724–5729.
Nagane M, Narita Y, Mishima K, Levitzki A, Burgess AW, Cavenee WK et al. (2001). Human glioblastoma xenografts overexpressing a tumor-specific mutant epidermal growth factor receptor sensitized to cisplatin by the AG1478 tyrosine kinase inhibitor. J Neurosurg 95: 472–479.
Nicholas MK, Lukas RV, Jafri NF, Faoro L, Salgia R . (2006). Epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated signal transduction in the development and therapy of gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 12: 7261–7270.
Peschard P, Kozlov G, Lin T, Mirza IA, Berghuis AM, Lipkowitz S et al. (2007). Structural basis for ubiquitin-mediated dimerization and activation of the ubiquitin protein ligase Cbl-b. Mol Cell 27: 474–485.
Raizer JJ . (2005). HER1/EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 74: 77–86.
Rosell R, Taron M, Reguart N, Isla D, Moran T . (2006). Epidermal growth factor receptor activation: how exon 19 and 21 mutations changed our understanding of the pathway. Clin Cancer Res 12: 7222–7231.
Shattuck DL, Miller JK, Laederich M, Funes M, Petersen H, Carraway III KL et al. (2007). LRIG1 is a novel negative regulator of the Met receptor and opposes Met and Her2 synergy. Mol Cell Biol 27: 1934–1946.
Sibilia M, Kroismayr R, Lichtenberger BM, Natarajan A, Hecking M, Holcmann M . (2007). The epidermal growth factor receptor: from development to tumorigenesis. Differentiation 75: 770–787.
Sweeney C, Miller JK, Shattuck D, Carraway III KL . (2006). ErbB receptor negative regulatory mechanisms: implications in cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 11: 89–99.
Suzuki Y, Miura H, Tanemura A, Kobayashi K, Kondoh G, Sano S et al. (2002). Targeted disruption of LIG-1 gene results in psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia. FEBS Lett 521: 67–71.
Tanemura A, Nagasawa T, Inui S, Itami S . (2005). LRIG-1 provides a novel prognostic predictor in squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: immunohistochemical analysis for 38 cases. Dermatol Surg 31: 423–430.
Thomasson M, Hedman H, Guo D, Ljungberg B, Henriksson R . (2003). LRIG1 and epidermal growth factor receptor in renal cell carcinoma: a quantitative RT–PCR and immunohistochemical analysis. Br J Cancer 89: 1285–1289.
Vassar R, Fuchs E . (1991). Transgenic mice provide new insights into the role of TGF-alpha during epidermal development and differentiation. Genes Dev 5: 714–727.
Wang MY, Lu KV, Zhu S, Dia EQ, Vivanco I, Shackleford GM et al. (2006). Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition promotes responses to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors in PTEN-deficient and PTEN-intact glioblasma cells. Cancer Research 66: 7864–7869.
Waterman H, Katz M, Rubin C, Shtiegman K, Lavi S, Elson A et al. (2002). A mutant EGF-receptor defective in ubiquitylation and endocytosis unveils a role for Grb2 in negative signaling. EMBO J 21: 303–313.
Wells A, Welsh JB, Lazar CS, Wiley HS, Gill GN, Rosenfeld MG . (1990). Ligand-induced transformation by a noninternalizing epidermal growth factor receptor. Science 247: 962–964.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Webster Cavenee from the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, University of California at San Diego, La Jolla, California for the U87MG parental and EGFRvIII expressing glioblastoma cells. We thank Dr Laurel Beckett, Chief of the Division of Biostatistics at UC Davis School of Medicine, for statistical consultation. We thank Carol Oxford, Manager of the UC Davis Optical Biology Core, for her assistance in the flow cytometry experiments. This work was supported by NIH grants CA118384 (CS) and GM068994 (KLC). DLS is a recipient of a DOD BCRP predoctoral fellowship Award no. W81XWH-06-1-0772.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stutz, M., Shattuck, D., Laederich, M. et al. LRIG1 negatively regulates the oncogenic EGF receptor mutant EGFRvIII. Oncogene 27, 5741–5752 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.185
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.185
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
LRIG proteins regulate lipid metabolism via BMP signaling and affect the risk of type 2 diabetes
Communications Biology (2021)
-
LRIG1 is a pleiotropic androgen receptor-regulated feedback tumor suppressor in prostate cancer
Nature Communications (2019)
-
FHL2 interacts with EGFR to promote glioblastoma growth
Oncogene (2018)
-
Essential Role of Linx/Islr2 in the Development of the Forebrain Anterior Commissure
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Decreased LRIG1 in fulvestrant-treated luminal breast cancer cells permits ErbB3 upregulation and increased growth
Oncogene (2016)