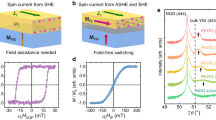
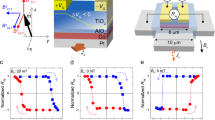
Abstract
The spin Hall effect in heavy metals converts charge current into pure spin current, which can be injected into an adjacent ferromagnet to exert a torque. This spin–orbit torque (SOT) has been widely used to manipulate the magnetization in metallic ferromagnets. In the case of magnetic insulators (MIs), although charge currents cannot flow, spin currents can propagate, but current-induced control of the magnetization in a MI has so far remained elusive. Here we demonstrate spin-current-induced switching of a perpendicularly magnetized thulium iron garnet film driven by charge current in a Pt overlayer. We estimate a relatively large spin-mixing conductance and damping-like SOT through spin Hall magnetoresistance and harmonic Hall measurements, respectively, indicating considerable spin transparency at the Pt/MI interface. We show that spin currents injected across this interface lead to deterministic magnetization reversal at low current densities, paving the road towards ultralow-dissipation spintronic devices based on MIs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garello, K. et al. Symmetry and magnitude of spin–orbit torques in ferromagnetic heterostructures. Nat. Nanotech. 8, 587–593 (2013).
Brataas, A. & Hals, K. M. D. Spin–orbit torques in action. Nat. Nanotech. 9, 86–88 (2014).
Fan, Y. et al. Magnetization switching through giant spin–orbit torque in a magnetically doped topological insulator heterostructure. Nat. Mater. 13, 699–704 (2014).
Fan, Y. et al. Electric-field control of spin–orbit torque in a magnetically doped topological insulator. Nat. Nanotech. 11, 352–360 (2016).
Miron, I. M. et al. Perpendicular switching of a single ferromagnetic layer induced by in-plane current injection. Nature 476, 189–193 (2011).
Liu, L. Q. et al. Spin-torque switching with the giant spin Hall effect of tantalum. Science 336, 555–558 (2012).
Demidov, V. E. et al. Magnetic nano-oscillator driven by pure spin current. Nat. Mater. 11, 1028–1031 (2012).
Liu, L. Q., Pai, C-F., Ralph, D. C. & Buhrman, R. A. Magnetic oscillations driven by the spin Hall effect in 3-terminal magnetic tunnel junction devices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 186602 (2012).
Emori, S., Bauer, U., Ahn, S. M., Martinez, E. & Beach, G. S. D. Current-driven dynamics of chiral ferromagnetic domain walls. Nat. Mater. 12, 611–616 (2013).
Ryu, K. S., Thomas, L., Yang, S. H. & Parkin, S. Chiral spin torque at magnetic domain walls. Nat. Nanotech. 8, 527–533 (2013).
Sinova, J., Valenzuela, S. O., Wunderlich, J., Back, C. H. & Jungwirth, T. Spin Hall effects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 1213–1259 (2015).
Nakayama, H. et al. Spin Hall magnetoresistance induced by a nonequilibrium proximity effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 206601 (2013).
Hahn, C. et al. Comparative measurements of inverse spin Hall effects and magnetoresistance in YIG/Pt and YIG/Ta. Phys. Rev. B 87, 174417 (2013).
Weiler, M. et al. Experimental test of the spin mixing interface conductivity concept. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 176601 (2013).
Vlietstra, N., Shan, J., Castel, V., van Wees, B. J. & Ben Youssef, J. Spin-Hall magnetoresistance in platinum on yttrium iron garnet: dependence on platinum thickness and in-plane/out-of-plane magnetization. Phys. Rev. B 87, 184421 (2013).
Kajiwara, Y. et al. Transmission of electrical signals by spin-wave interconversion in a magnetic insulator. Nature 464, 262–267 (2010).
Hamadeh, A. et al. Full control of the spin-wave damping in a magnetic insulator using spin–orbit torque. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 197203 (2014).
Chumak, A. V., Vasyuchka, V. I. I., Serga, A. A. A. & Hillebrands, B. Magnon spintronics. Nat. Phys. 11, 453–461 (2015).
Kubota, M. et al. Stress-induced perpendicular magnetization in epitaxial iron garnet thin films. Appl. Phys. Exp. 5, 103002 (2012).
Paoletti, A. Physics of Magnetic Garnets (North-Holland Publishing Company, 1978).
Saitoh, E., Ueda, M., Miyajima, H. & Tatara, G. Conversion of spin current into charge current at room temperature: inverse spin-Hall effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 182509 (2006).
Meyer, S. et al. Anomalous Hall effect in YIG vertical bar Pt bilayers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 132402 (2015).
Chen, Y. T. et al. Theory of spin Hall magnetoresistance. Phys. Rev. B 87, 144411 (2013).
Liu, L. Q., Moriyama, T., Ralph, D. C. & Buhrman, R. A. Spin-torque ferromagnetic resonance induced by the spin Hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 36601 (2011).
Kim, J. et al. Layer thickness dependence of the current-induced effective field vector in Ta vertical bar CoFeB vertical bar MgO. Nat. Mater. 12, 240–245 (2013).
Schreier, M. et al. Current heating induced spin Seebeck effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 242404 (2013).
Liu, L. Q., Lee, O. J., Gudmundsen, T. J., Ralph, D. C. & Buhrman, R. A. Current-induced switching of perpendicularly magnetized magnetic layers using spin torque from the spin Hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 96602 (2012).
Ibrahim, I., Schweigert, V. & Peeters, F. Diffusive transport in a Hall junction with a microinhomogeneous magnetic field. Phys. Rev. B 57, 15416–15427 (1998).
Avci, C. O. et al. Fieldlike and antidamping spin-orbit torques in as-grown and annealed Ta/CoFeB/MgO layers. Phys. Rev. B 89, 214419 (2014).
Lee, O. J. et al. Central role of domain wall depinning for perpendicular magnetization switching driven by spin torque from the spin Hall effect. Phys. Rev. B 89, 024418 (2013).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge support from C-SPIN, one of the six SRC STARnet Centers, sponsored by MARCO and DARPA. A.Q. acknowledges funding from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) and from the Max-Planck-Institute of Microstructure Physics. C.O.A. and C.-F.P. thank K. Ueda and A. J. Tan for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.S.D.B. and C.A.R. proposed and supervised the study. C.O.A., M.M., C.-F.P. and G.S.D.B. designed the transport experiments. A.Q., A.S.T. and M.C.O. fabricated the TmIG samples. A.Q. performed structural and magnetic analysis. M.M. carried out photolithography processing. C.O.A., M.M. and A.Q. carried out transport measurements. M.M. and L.C. designed and established the electrical measurement equipment.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 4893 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avci, C., Quindeau, A., Pai, CF. et al. Current-induced switching in a magnetic insulator. Nature Mater 16, 309–314 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4812
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4812
This article is cited by
-
Magnetoresistive detection of perpendicular switching in a magnetic insulator
Communications Physics (2024)
-
Highly efficient field-free switching of perpendicular yttrium iron garnet with collinear spin current
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Ultra-thin lithium aluminate spinel ferrite films with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and low damping
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Large spin–orbit torque in bismuthate-based heterostructures
Nature Electronics (2023)
-
A self-biased non-reciprocal magnetic metasurface for bidirectional phase modulation
Nature Electronics (2023)