Abstract
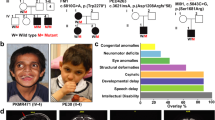
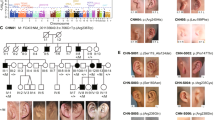
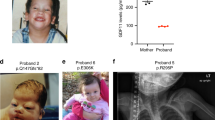
Remodeling of the cytoskeleton is central to the modulation of cell shape and migration. Filamin A, encoded by the gene FLNA, is a widely expressed protein that regulates re-organization of the actin cytoskeleton by interacting with integrins, transmembrane receptor complexes and second messengers1,2. We identified localized mutations in FLNA that conserve the reading frame and lead to a broad range of congenital malformations, affecting craniofacial structures, skeleton, brain, viscera and urogenital tract, in four X-linked human disorders: otopalatodigital syndrome types 1 (OPD1; OMIM 311300) and 2 (OPD2; OMIM 304120), frontometaphyseal dysplasia (FMD; OMIM 305620) and Melnick–Needles syndrome (MNS; OMIM 309350). Several mutations are recurrent, and all are clustered into four regions of the gene: the actin-binding domain and rod domain repeats 3, 10 and 14/15. Our findings contrast with previous observations that loss of function of FLNA is embryonic lethal in males but manifests in females as a localized neuronal migration disorder, called periventricular nodular heterotopia (PVNH; refs. 3–6). The patterns of mutation, X-chromosome inactivation and phenotypic manifestations in the newly described mutations indicate that they have gain-of-function effects, implicating filamin A in signaling pathways that mediate organogenesis in multiple systems during embryonic development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Stossel, T.P. et al. Filamins as integrators of cell mechanics and signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 138–145 (2001).
van der Flier, A. & Sonnenberg, A. Structural and functional aspects of filamins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1538, 99–117 (2001).
Fox, J.W. et al. Mutations in filamin 1 prevent migration of cerebral cortical neurons in human periventricular heterotopia. Neuron 21, 1315–1325 (1998).
Eksioglu, Y.Z. et al. Periventricular heterotopia: an X-linked dominant epilepsy locus causing aberrant cerebral cortical development. Neuron 16, 77–87 (1996).
Sheen, V.L. et al. Mutations in the X-linked filamin 1 gene cause periventricular nodular heterotopia in males as well as in females. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 1775–1783 (2001).
Moro, F. et al. Familial periventricular heterotopia. Missense and distal truncating mutations of the FLN1 gene. Neurology 58, 916–921 (2002).
Robertson, S., Gunn, T., Allen, B., Chapman, C. & Becroft, D. Are Melnick–Needles syndrome and otopalatodigital syndrome type II allelic? Observations in a four generation kindred. Am. J. Med. Genet. 71, 341–347 (1997).
Robertson, S.P. et al. Linkage of otopalatodigital syndrome type 2 (OPD2) to distal Xq28: evidence for allelism with OPD1. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69, 223–227 (2001).
Biancalana, V., Le Marec, B., Odent, S., van den Hurk, J.A. & Hanauer, A. Oto-palato-digital syndrome type1: further evidence for assignment of the locus to Xq28. Hum. Genet. 88, 228–230 (1991).
Kosho, T. et al. Refined mapping of the gene for otopalatodigital syndrome type I. J. Med. Genet. 39, E7 (2002).
Fitch, N., Jequier, S. & Gorlin, R. The otopalatodigital syndrome, proposed type II. Am. J. Med. Genet. 15, 655–664 (1983).
Verloes, A. et al. Fronto-otopalatodigital osteodysplasia: clinical evidence for a single entity encompassing Melnick–Needles syndrome, otopalatodigital syndrome types 1 and 2, and frontometaphyseal dysplasia. Am. J. Med. Genet. 90, 407–422 (2000).
Taybi, H. Generalized skeletal dysplasia with multiple anomalies. Am. J. Roentgen. 88, 450–457 (1962).
Dudding, B.A., Gorlin, R.J. & Langer, L.O. A new symptom complex consisting of deafness, dwarfism, cleft palate, characteristic facies and a generalised bone dysplasia. Am. J. Dis. Child. 113, 214–221 (1967).
Gorlin, R.J. & Cohen, M.M. Frontometaphyseal dysplasia. A new syndrome. Am. J. Dis. Child. 118, 487–494 (1969).
Melnick, J.C. & Needles, C.F. An undiagnosed bone dysplasia. A 2 family study of 4 generations and 3 generations. Am. J. Roentgen. 97, 39–48 (1966).
Donnenfeld, A.E., Conard, K.A., Roberts, N.S., Borns, P.F. & Zackai, E.H. Melnick–Needles syndrome in males: a lethal multiple congenital anomalies syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 27, 159–173 (1987).
Sheen, V.L. et al. Filamin A and filamin B are co-expressed within neurons during periods of neuronal migration and can physically interact. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 2845–2854 (2002).
Le Marec, B. et al. Syndrome oto-palato-digital de type I atteignant cinq générations relations avec la forme de type II. Ann. Génét. 31, 155–161 (1988).
Hassoun, H. et al. Characterization of the underlying molecular defect in hereditary spherocytosis associated with spectrin deficiency. Blood 90, 398–406 (1997).
Kaplan, J.M. et al. Mutations in ACTN4, encoding α-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat. Genet. 24, 251–256 (2000).
Norwood, F.L., Sutherland-Smith, A.J., Keep, N.H. & Kendrick-Jones, J. The structure of the N-terminal actin-binding domain of human dystrophin and how mutations in this domain may cause Duchenne or Becker muscular dystrophy. Structure 8, 481–491 (2000).
Carugo, K.D., Bañuelos, S. & Saraste, M. Crystal structure of a calponin homology domain. Nat. Struct. Biol. 4, 175–179 (1997).
McCoy, A.J., Fucini, P., Noegel, A.A. & Stewart, M. Structural basis for dimerization of the Dictyostelium gelation factor (ABP120) rod. Nat. Struct. Biol. 6, 836–841 (1999).
Allen, R.C., Zoghbi, H.Y., Moseley, A.B., Rosenblatt, H.M. & Belmont, J.W. Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X-chromosome inactivation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 51, 1229–1239 (1992).
André, M., Vigneron, J. & Didier, F. Abnormal facies, cleft palate and generalised dysostosis: a lethal X-linked syndrome. J. Pediatr. 98, 747–752 (1981).
Stratton, R.F. & Bluestone, D.F. Oto-palatal-digital syndrome type II with X-linked cerebellar hypoplasia/hydrocephalus. Am. J. Med. Genet. 41, 169–172 (1991).
Kristiansen, M., Knudsen, G.P., Søyland, A., Westvik, J. & Ørstavik, K.H. Phenotypic variation in Melnick–Needles syndrome is not reflected in X inactivation patterns from blood or buccal smear. Am. J. Med. Genet. 108, 120–127 (2002).
Esnouf, R.M. An extensively modified version of MolScript that includes greatly enhanced coloring capabilities. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 15, 132–134 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the individuals, families and members of the MNS Support Group who participated in this research, A. McCoy for discussions on filamin A structure, M. Cossee and B. Hane for sharing unpublished results and N. Elanko, I. Taylor, S. Butler and K. Clark for technical assistance. This work was supported by a Nuffield Medical Fellowship (S.P.R.) and a Wellcome Trust Senior Research Fellowship in Clinical Science (A.O.M.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robertson, S., Twigg, S., Sutherland-Smith, A. et al. Localized mutations in the gene encoding the cytoskeletal protein filamin A cause diverse malformations in humans. Nat Genet 33, 487–491 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1119
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1119
This article is cited by
-
Prenatal detection and molecular cytogenetic characterization of Xp deletion and Xq duplication: a case report and literature review
BMC Medical Genomics (2024)
-
Clinical genetics evaluation and testing of connective tissue disorders: a cross-sectional study
BMC Medical Genomics (2022)
-
A novel FLNA variant in a fetus with skeletal dysplasia
Human Genome Variation (2022)
-
Bipolar disorder with Melnick–Needles syndrome and periventricular nodular heterotopia: two case reports and a review of the literature
Journal of Medical Case Reports (2021)
-
The variants at FLNA and FLNB contribute to the susceptibility of hypertension and stroke with differentially expressed mRNA
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2021)