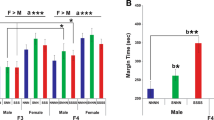
Abstract
Traumatic stress in early-life increases the risk for cognitive and neuropsychiatric disorders later in life. Such early stress can also impact the progeny even if not directly exposed, likely through epigenetic mechanisms. Here, we report in mice that the offspring of males subjected to postnatal traumatic stress have decreased gene expression in molecular pathways necessary for neuronal signaling, and altered synaptic plasticity when adult. Long-term potentiation is abolished and long-term depression is enhanced in the hippocampus, and these defects are associated with impaired long-term memory in both the exposed fathers and their offspring. The brain-specific gamma isoform of protein kinase C (Prkcc) is one of the affected signaling components in the hippocampus. Its expression is reduced in the offspring, and DNA methylation at its promoter is altered both in the hippocampus of the offspring and the sperm of fathers. These results suggest that postnatal traumatic stress in males can affect brain plasticity and cognitive functions in the adult progeny, possibly through epigenetic alterations in the male germline.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Schafer I, Fisher HL Childhood trauma and psychosis—what is the evidence?. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 2011; 13: 360–365.
Norman RE, Byambaa M, De R, Butchart A, Scott J, Vos T The long-term health consequences of child physical abuse, emotional abuse, and neglect: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med 2012; 9: e1001349.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Administration on Children, Youth and Families, Children’s Bureau. (2012). Child Maltreatment 2011.
Gilbert R, Widom CS, Browne K, Fergusson D, Webb E, Janson S Burden and consequences of child maltreatment in high-income countries. Lancet 2009; 373: 68–81.
Lampe A The prevalence of childhood sexual abuse, physical abuse and emotional neglect in Europe. Z Psychosom Med Psychother 2002; 48: 370–380.
Schönbucher V, Maier T, Held L, Mohler-Kuo M, Schnyder U, Landolt MA Prevalence of child sexual abuse in Switzerland: a systematic review. Swiss Med Wkly 2011; 140: w13123.
Weiss IC, Franklin TB, Vizi S, Mansuy IM Inheritable effect of unpredictable maternal separation on behavioral responses in mice. Front Behav Neurosci 2011; 5: 3.
Franklin TB, Russig H, Weiss IC, Gräff J, Linder N, Michalon A et al. Epigenetic transmission of the impact of early stress across generations. Biol Psychiatry 2010; 68: 408–415.
Franklin TB, Linder N, Russig H, Thöny B, Mansuy IM Influence of early stress on social abilities and serotonergic functions across generations in mice. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e21842.
Gapp K, Jawaid A, Sarkies P, Bohacek J, Pelczar P, Prados J et al. Implication of sperm RNAs in transgenerational inheritance of the effects of early trauma in mice. Nat Neurosci 2014;17: 667–669.
Bohacek J, Mansuy IM Epigenetic inheritance of disease and disease risk. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013; 38: 220–236.
Bohacek J, Gapp K, Saab BJ, Mansuy IM Transgenerational epigenetic effects on brain functions. Biol Psychiatry 2012; 73: 313–320.
Pechtel P, Pizzagalli DA Effects of early life stress on cognitive and affective function: an integrated review of human literature. Psychopharmacology 2011; 214: 55–70.
Arts B, Jabben N, Krabbendam L, van Os J Meta-analyses of cognitive functioning in euthymic bipolar patients and their first-degree relatives. Psychol Med 2008; 38: 771–785.
McClintock SM, Husain MM, Greer TL, Cullum CM Association between depression severity and neurocognitive function in major depressive disorder: a review and synthesis. Neuropsychology 2010; 24: 9–34.
Gould F, Clarke J, Heim C, Harvey PD, Majer M, Nemeroff CB The effects of child abuse and neglect on cognitive functioning in adulthood. J Psychiatr Res 2012; 46: 500–506.
McEwen BS, Gianaros PJ Central role of the brain in stress and adaptation: links to socioeconomic status, health, and disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 2010; 1186: 190–222.
Kim JJ, Diamond DM The stressed hippocampus, synaptic plasticity and lost memories. Nat Rev Neurosci 2002; 3: 453–462.
Wang X-D, Rammes G, Kraev I, Wolf M, Liebl C, Scharf SH et al. Forebrain CRF1 modulates early-life stress-programmed cognitive deficits. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 13625–13634.
Ivy AS, Rex CS, Chen Y, Dubé C, Maras PM, Grigoriadis DE et al. Hippocampal dysfunction and cognitive impairments provoked by chronic early-life stress involve excessive activation of CRH receptors. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 13005–13015.
Murgatroyd C, Patchev AV, Wu Y, Micale V, Bockmühl Y, Fischer D et al. Dynamic DNA methylation programs persistent adverse effects of early-life stress. Nat Neurosci 2009; 12: 1559–1566.
Abeliovich A, Paylor R, Chen C, Kim JJ, Wehner JM, Tonegawa S .PKC gamma mutant mice exhibit mild deficits in spatial and contextual learning. Cell 1993; 75: 1263–1271.
Abeliovich A, Chen C, Goda Y, Silva AJ, Stevens CF, Tonegawa S Modified hippocampal long-term potentiation in PKC gamma-mutant mice. Cell 1993; 75: 1253–1262.
Hickman DL, Swan MP Effects of age of pups and removal of existing litter on pup survival during cross-fostering between multiparous outbred mice. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 2011; 50: 641–646.
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 2003; 19: 185–193.
Smyth GK Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions using R and Bioconductor (Gentleman R, Carey V, Dudoit S, Irizarry RA, Huber W). Springer, 2005, pp 397–420.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 15545–15550.
Nam D, Kim SY Gene-set approach for expression pattern analysis. Brief Bioinform 2008; 9: 189–197.
Cerami EG, Gross BE, Demir E, Rodchenkov I, Babur O, Anwar N et al. Pathway Commons, a web resource for biological pathway data. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39: D685–D690.
Untergasser A, Nijveen H, Rao X, Bisseling T, Geurts R, Leunissen JA Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: W71–W74.
Arvidsson S, Kwasniewski M, Riaño-Pachón DM, Mueller-Roeber B QuantPrime—a flexible tool for reliable high-throughput primer design for quantitative PCR. BMC Bioinformatics 2008; 9: 465.
Knobloch M, Farinelli M, Konietzko U, Nitsch RM, Mansuy IM Abeta oligomer-mediated long-term potentiation impairment involves protein phosphatase 1-dependent mechanisms. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 7648–7653.
Humeau Y, Shaban H, Bissiere S, Luthi A Presynaptic induction of heterosynaptic associative plasticity in the mammalian brain. Nature 2003; 426: 841–845.
Daniel JM, Bohacek J The critical period hypothesis of estrogen effects on cognition: insights from basic research. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1800: 1068–1076.
Genoux D, Haditsch U, Knobloch M, Michalon A, Storm D, Mansuy IM Protein phosphatase 1 is a molecular constraint on learning and memory. Nature 2002; 418: 970–975.
Small SA, Schobel SA, Buxton RB, Witter MP, Barnes CA A pathophysiological framework of hippocampal dysfunction in ageing and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011; 12: 585–601.
Gray JD, Rubin TG, Hunter RG, McEwen BS . Hippocampal gene expression changes underlying stress sensitization and recovery. Mol Psychiatry advance online publication, 17 December 2013; doi:10.1038/mp.2013.175.
Huang YY, Kandel ER Recruitment of long-lasting and protein kinase A-dependent long-term potentiation in the CA1 region of hippocampus requires repeated tetanization. Learn Mem 1994; 1: 74–82.
Schulz PE, Cook EP, Johnston D Changes in paired-pulse facilitation suggest presynaptic involvement in long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 1994; 14: 5325–5337.
Takanaga H, Mukai H, Shimakawa M, Konishi H, Kikkawa U, Koizumi T et al. Functional characterization of the promoter region of the mouse protein kinase C gamma gene. FEBS Lett 1995; 368: 276–278.
Chen KH, Widen SG, Wilson SH, Huang KP Characterization of the 5′-flanking region of the rat protein kinase C gamma gene. J Biol Chem 1990; 265: 19961–19965.
Li L, Davie JR The role of Sp1 and Sp3 in normal and cancer cell biology. Ann Anat 2010; 192: 275–283.
Lupien SJ, McEwen BS, Gunnar MR, Heim C Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009; 10: 434–445.
Hedges DW, Woon FL . Early-life stress and cognitive outcome. Psychopharmacology 2011; 214: 121–130.
Roceri M, Hendriks W, Racagni G, Ellenbroek BA, Riva MA . Early maternal deprivation reduces the expression of BDNF and NMDA receptor subunits in rat hippocampus. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 609–616.
Pickering C, Gustafsson L, Cebere A, Nylander I, Liljequist S . Repeated maternal separation of male Wistar rats alters glutamate receptor expression in the hippocampus but not the prefrontal cortex. Brain Res 2006; 1099: 101–108.
Ryan B, Musazzi L, Mallei A, Tardito D, Gruber SH, El Khoury A et al. Remodelling by early-life stress of NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity in a gene-environment rat model of depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2009; 12: 553–559.
Kandel ER . The molecular biology of memory storage: a dialogue between genes and synapses. Science 2001; 294: 1030–1038.
Lisman J, Yasuda R, Raghavachari S . Mechanisms of CaMKII action in long-term potentiation. Nat Rev Neurosci 2012; 13: 169–182.
Li S, Tian X, Hartley DM, Feig LA . Distinct roles for Ras-guanine nucleotide-releasing factor 1 (Ras-GRF1) and Ras-GRF2 in the induction of long-term potentiation and long-term depression. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 1721–1729.
Xu L, Anwyl R, Rowan MJ . Behavioural stress facilitates the induction of long-term depression in the hippocampus. Nature 1997; 387: 497–500.
Yang C-H, Huang C-C, Hsu K-S . Behavioral stress enhances hippocampal CA1 long-term depression through the blockade of the glutamate uptake. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 4288–4293.
Kim JJ, Foy MR, Thompson RF . Behavioral stress modifies hippocampal plasticity through N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 4750–4753.
Artola A, von Frijtag JC, Fermont PC, Gispen WH, Schrama LH, Kamal A et al. Long-lasting modulation of the induction of LTD and LTP in rat hippocampal CA1 by behavioural stress and environmental enrichment. Eur J Neurosci 2006; 23: 261–272.
Rioult-Pedotti MS, Donoghue JP, Dunaevsky A . Plasticity of the synaptic modification range. J Neurophysiol 2007; 98: 3688–3695.
Dudek SM, Bear MF . Homosynaptic long-term depression in area CA1 of hippocampus and effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992; 89: 4363–4367.
Bienenstock EL, Cooper LN, Munro PW . Theory for the development of neuron selectivity: orientation specificity and binocular interaction in visual cortex. J Neurosci 1982; 2: 32–48.
Danielewicz J, Hess G . Early life stress alters synaptic modification range in the rat lateral amygdala. Behav Brain Res 2014; 265C: 32–37.
Rodgers AB, Morgan CP, Bronson SL, Revello S, Bale TL . Paternal stress exposure alters sperm microRNA content and reprograms offspring HPA stress axis regulation. J Neurosci 2013; 33: 9003–9012.
Aisa B, Tordera R, Lasheras B, Del Río J, Ramírez MJ . Cognitive impairment associated to HPA axis hyperactivity after maternal separation in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007; 32: 256–266.
Batalha VL, Pego JM, Fontinha BM, Costenla AR, Valadas JS, Baqi Y et al. Adenosine A2A receptor blockade reverts hippocampal stress-induced deficits and restores corticosterone circadian oscillation. Mol Psychiatry 2012; 18: 320–331.
Saavedra-Rodríguez L, Feig LA . Chronic social instability induces anxiety and defective social interactions across generations. Biol Psychiatry 2013; 73: 44–53.
Arai JA, Li S, Hartley DM, Feig LA . Transgenerational rescue of a genetic defect in long-term potentiation and memory formation by juvenile enrichment. J Neurosci 2009; 29: 1496–1502.
Dunn GA, Morgan CP, Bale TL . Sex-specificity in transgenerational epigenetic programming. Horm Behav 2011; 59: 290–295.
Morgan CP, Bale TL . Early prenatal stress epigenetically programs dysmasculinization in second-generation offspring via the paternal lineage. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 11748–11755.
Dietz DM, Laplant Q, Watts EL, Hodes GE, Russo SJ, Feng J et al. Paternal transmission of stress-induced pathologies. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 70: 408–414.
Guerrero-Bosagna C, Settles M, Lucker B, Skinner MK . Epigenetic transgenerational actions of vinclozolin on promoter regions of the sperm epigenome. PLoS ONE 2010; 5: e13100.
Wolstenholme JT, Edwards M, Shetty SR, Gatewood JD, Taylor JA, Rissman EF et al. Gestational exposure to bisphenol a produces transgenerational changes in behaviors and gene expression. Endocrinology 2012; 153: 3828–3838.
Dunn GA, Bale TL . Maternal high-fat diet effects on third-generation female body size via the paternal lineage. Endocrinology 2011; 152: 2228–2236.
Carone BR, Fauquier L, Habib N, Shea JM, Hart CE, Li R et al. Paternally induced transgenerational environmental reprogramming of metabolic gene expression in mammals. Cell 2010; 143: 1084–1096.
Vassoler FM, White SL, Schmidt HD, Sadri-Vakili G, Pierce RC . Epigenetic inheritance of a cocaine-resistance phenotype. Nat Neurosci 2013; 16: 42–47.
Gapp K, von Ziegler L, Tweedie-Cullen RY, Mansuy IM . Early life epigenetic programming and transmission of stress-induced traits in mammals: how and when can environmental factors influence traits and their transgenerational inheritance? Bioessays 2014; 36: 491–502.
Curley JP, Mashoodh R . Parent-of-origin and trans-generational germline influences on behavioral development: the interacting roles of mothers, fathers, and grandparents. Dev Psychobiol 2010; 52: 312–330.
Gowaty PA, Anderson WW, Bluhm CK, Drickamer LC, Kim YK, Moore AJ et al. The hypothesis of reproductive compensation and its assumptions about mate preferences and offspring viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 15023–15027.
Jirtle RL, Skinner MK . Environmental epigenomics and disease susceptibility. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8: 253–262.
Davies G, Tenesa A, Payton A, Yang J, Harris SE, Liewald D et al. Genome-wide association studies establish that human intelligence is highly heritable and polygenic. Mol Psychiatry 2011; 16: 996–1005.
Nisbett RE, Aronson J, Blair C, Dickens W, Flynn J, Halpern DF et al. Intelligence: new findings and theoretical developments. Am Psychol 2012; 67: 130–159.
Deary I, Johnson W, Houlihan LM . Genetic foundations of human intelligence. Hum Genet 2009; 126: 215–232.
Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ, Goldstein DB, Hindorff LA, Hunter DJ et al. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 2009; 461: 747–753.
Acknowledgements
We thank Carl Kashuk for help with microarray data processing, Heidi Rosenbaum for help in microarray data acquisition, Bechara Saab for technical help, and Heiko Hörster, Gisep Bazzell and Yvonne Zipfel for animal care. The lab of IMM is supported by the University Zürich, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zürich, the Swiss National Science Foundation, Roche, the National Center of Competence in Research Neural Plasticity and Repair. JB is supported by a postdoc ETHZ fellowship and a Roche fellowship. MF is supported by a Roche postdoc fellowship. KG is supported by a DOC-fFORTE Fellowship from the Austrian Academy of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bohacek, J., Farinelli, M., Mirante, O. et al. Pathological brain plasticity and cognition in the offspring of males subjected to postnatal traumatic stress. Mol Psychiatry 20, 621–631 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.80
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.80
This article is cited by
-
Psychosis spectrum illnesses as disorders of prefrontal critical period plasticity
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Effects of paternal high-fat diet and maternal rearing environment on the gut microbiota and behavior
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Paternal environmental exposure-induced spermatozoal small noncoding RNA alteration meditates the intergenerational epigenetic inheritance of multiple diseases
Frontiers of Medicine (2022)
-
Exploring the evidence for epigenetic regulation of environmental influences on child health across generations
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Mapping the past, present and future research landscape of paternal effects
BMC Biology (2020)