Abstract
Objective:
Adipogenesis can be spatially and temporally regulated by extracellular matrix (ECM). We hypothesized that the regulation of hyaluronic acid (HA), a component of the ECM, can affect adipogenesis in fat cells. The effects of HA on adipogenesis were investigated in vitro in 3T3-L1 cells and in vivo in high-fat diet-feeding C57BL/6J mice.
Methods:
We investigated the effects of HA by degradation of pre-existing or synthesized HA and artificial inhibition of HA synthesis in adipogenesis.
Results:
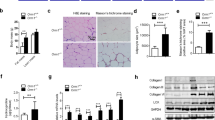
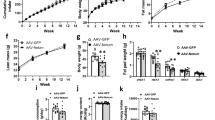
In vitro adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells was inhibited by treating them with exogenous hyaluronidase (HYAL) and with 4-methylumbelliferone, which inhibited the synthesis of HA in a concentration-dependent manner. In vivo, abdominal fat accumulation in high-fat diet-feeding C57BL/6J mice was suppressed by exogenous HYAL 104 IU injections, which was associated with reduction of lipid accumulation in liver and increase of insulin sensitivity.
Conclusion:
Changes in the ECM such as accumulation of high molecular weight of HA by HAS and degradation of HA by endogenous HYAL were essential for adipogenesis both in vitro and in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haslam DW, James WP . Obesity. Lancet 2005; 366: 1197–1209.
Green H, Kehinde O . Spontaneous heritable changes leading to increased adipose conversion in 3T3 cells. Cell 1976; 7: 105–113.
Green H, Meuth M . An established pre-adipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. Cell 1974; 3: 127–133.
Chapman AB, Knight DM, Dieckmann BS, Ringold GM . Analysis of gene expression during differentiation of adipogenic cells in culture and hormonal control of the developmental program. J Biol Chem 1984; 259: 15548–15555.
Negrel R, Grimaldi P, Ailhaud G . Establishment of pre-adipocyte clonal line from epididymal fat pad of ob/ob mouse that responds to insulin and to lipolytic hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1978; 75: 6054–6058.
Green H, Kehinde O . Formation of normally differentiated subcutaneous fat pads by an established preadipose cell line. J CellPhysiol 1979; 101: 169–171.
Vannier C, Gaillard D, Grimaldi P, Amri EZ, Djian P, Cermolacce C et al. Adipose conversion of ob17 cells and hormone-related events. Int J Obes 1985; 9 (Suppl 1): 41–53.
Rosen ED, Sarraf P, Troy AE, Bradwin G, Moore K, Milstone DS et al. PPAR gamma is required for the differentiation of adipose tissue in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell 1999; 4: 611–617.
Cao Z, Umek RM, McKnight SL . Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev 1991; 5: 1538–1552.
Mariman EC, Wang P . Adipocyte extracellular matrix composition, dynamics and role in obesity. Cell Mol Life Sci 2010; 67: 1277–1292.
Soukas A, Socci ND, Saatkamp BD, Novelli S, Friedman JM . Distinct transcriptional profiles of adipogenesis in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 34167–34174.
Gregoire FM, Smas CM, Sul HS . Understanding adipocyte differentiation. Physiol Rev 1998; 78: 783–809.
McBeath R, Pirone DM, Nelson CM, Bhadriraju K, Chen CS . Cell shape, cytoskeletal tension, and RhoA regulate stem cell lineage commitment. Dev Cell 2004; 6: 483–495.
Aratani Y, Kitagawa Y . Enhanced synthesis and secretion of type IV collagen and entactin during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells and production of unorthodox laminin complex. J Biol Chem 1988; 263: 16163–16169.
Kawaguchi N, Sundberg C, Kveiborg M, Moghadaszadeh B, Asmar M, Dietrich N et al. ADAM12 induces actin cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix reorganization during early adipocyte differentiation by regulating beta1 integrin function. J Cell Sci 2003; 116 (Pt 19): 3893–3904.
Demeulemeester D, Collen D, Lijnen HR . Effect of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition on adipose tissue development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 329: 105–110.
Coutinho PM, Deleury E, Davies GJ, Henrissat B . An evolving hierarchical family classification for glycosyltransferases. J Mol Biol 2003; 328: 307–317.
Prehm P . Hyaluronate is synthesized at plasma membranes. Biochem J 1984; 220: 597–600.
Stern R, Asari AA, Sugahara KN . Hyaluronan fragments: an information-rich system. Eur J Cell Biol 2006; 85: 699–715.
Day AJ, Prestwich GD . Hyaluronan-binding proteins: tying up the giant. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 4585–4588.
Laurent TC, Fraser JR . Hyaluronan. FASEB J 1992; 6: 2397–2404.
Calvo JC, Gandjbakhche AH, Nossal R, Hascall VC, Yanagishita M . Rheological effects of the presence of hyaluronic acid in the extracellular media of differentiated 3T3-L1 pre-adipocyte cultures. Arch Biochem Biophys 1993; 302: 468–475.
Allingham PG, Brownlee GR, Harper GS, Pho M, Nilsson SK, Brown TJ . Gene expression, synthesis and degradation of hyaluronan during differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 2006; 452: 83–91.
Zizola CF, Julianelli V, Bertolesi G, Yanagishita M, Calvo JC . Role of versican and hyaluronan in the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells into pre-adipocytes and mature adipocytes. Matrix Biol 2007; 26: 419–430.
Halbleib M, Skurk T, de Luca C, von Heimburg D, Hauner H . Tissue engineering of white adipose tissue using hyaluronic acid-based scaffolds. I: in vitro differentiation of human adipocyte precursor cells on scaffolds. Biomaterials 2003; 24: 3125–3132.
Hemmrich K, von Heimburg D, Rendchen R, Di Bartolo C, Milella E, Pallua N . Implantation of pre-adipocyte-loaded hyaluronic acid-based scaffolds into nude mice to evaluate potential for soft tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005; 26: 7025–7037.
Flynn L, Prestwich GD, Semple JL, Woodhouse KA . Adipose tissue engineering in vivo with adipose-derived stem cells on naturally derived scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A 2009; 89: 929–941.
Kultti A, Pasonen-Seppanen S, Jauhiainen M, Rilla KJ, Karna R, Pyoria E et al. 4-Methylumbelliferone inhibits hyaluronan synthesis by depletion of cellular UDP-glucuronic acid and downregulation of hyaluronan synthase 2 and 3. Exp Cell Res 2009; 315: 1914–1923.
Song NJ, Yoon HJ, Kim KH, Jung SR, Jang WS, Seo CR et al. Butein is a novel anti-adipogenic compound. J Lipid Res 2013; 54: 1385–1396.
Soria B, Roche E, Berna G, Leon-Quinto T, Reig JA, Martin F . Insulin-secreting cells derived from embryonic stem cells normalize glycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Diabetes 2000; 49: 157–162.
Yeom CH, Lee G, Park JH, Yu J, Park S, Yi SY et al. High dose concentration administration of ascorbic acid inhibits tumor growth in BALB/C mice implanted with sarcoma 180 cancer cells via the restriction of angiogenesis. Journa Transl Med 2009; 7: 70.
Waki H, Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, Uchida S, Kita S et al. Impaired multimerization of human adiponectin mutants associated with diabetes. Molecular structure and multimer formation of adiponectin. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 40352–40363.
Lynch MJ . Medical Laboratory Technology and Clinical Pathology 2nd edn, W. B. Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1969.
Farmer SR . Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab 2006; 4: 263–273.
Rosen ED, Hsu CH, Wang X, Sakai S, Freeman MW, Gonzalez FJ et al. C/EBPalpha induces adipogenesis through PPARgamma: a unified pathway. Genes Dev 2002; 16: 22–26.
Lowe CE, O'Rahilly S, Rochford JJ . Adipogenesis at a glance. J Cell Sci 2011; 124: 2681–2686.
Rector RS, Thyfault JP, Wei Y, Ibdah JA . Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the metabolic syndrome: an update. World JGastroenterol 2008; 14: 185–192.
Ibrahimi A, Bonino F, Bardon S, Ailhaud G, Dani C . Essential role of collagens for terminal differentiation of pre-adipocytes. Biochem Biophys ResCommun 1992; 187: 1314–1322.
Lijnen HR, Maquoi E, Hansen LB, Van Hoef B, Frederix L, Collen D . Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition impairs adipose tissue development in mice. Arterioscler ThrombVasc Biol 2002; 22: 374–379.
Stern R . Hyaluronan catabolism: a new metabolic pathway. Eur J Cell Biol 2004; 83: 317–325.
Menzel EJ, Farr C . Hyaluronidase and its substrate hyaluronan: biochemistry, biological activities and therapeutic uses. Cancer Lett 1998; 131: 3–11.
Hay ED . Development of the vertebrate cornea. Int Rev Cytol 1980; 63: 263–322.
Toole BP . Hyaluronan in morphogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2001; 12: 79–87.
Bourguignon LY, Singleton PA, Diedrich F, Stern R, Gilad E . CD44 interaction with Na+-H+ exchanger (NHE1) creates acidic microenvironments leading to hyaluronidase-2 and cathepsin B activation and breast tumor cell invasion. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 26991–27007.
Culty M, Nguyen HA, Underhill CB . The hyaluronan receptor (CD44) participates in the uptake and degradation of hyaluronan. J Cell Biol 1992; 116: 1055–1062.
West DC, Hampson IN, Arnold F, Kumar S . Angiogenesis induced by degradation products of hyaluronic acid. Science 1985; 228: 1324–1326.
Fieber C, Baumann P, Vallon R, Termeer C, Simon JC, Hofmann M et al. Hyaluronan-oligosaccharide-induced transcription of metalloproteases. J Cell Sci 2004; 117: 359–367.
Lesley J, Hascall VC, Tammi M, Hyman R . Hyaluronan binding by cell surface CD44. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 26967–26975.
Toole BP . Hyaluronan: from extracellular glue to pericellular cue. Nat Rev 2004; 4: 528–539.
Jensen MD . Role of body fat distribution and the metabolic complications of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93: S57–S63.
Mirza MS . Obesity, visceral fat, and nafld: querying the role of adipokines in the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. ISRNGastroenterol 2011; 2011: 592404.
Wang QA, Tao C, Gupta RK, Scherer PE . Tracking adipogenesis during white adipose tissue development, expansion and regeneration. Nat Med 2013; 19: 1338–1344.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from KAVITA Co. Mr. Hyenho Myeong from Korea BMI supplied the HYAL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, E., Jung, M., Park, J. et al. Inhibition of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and suppression of abdominal fat accumulation in high-fat diet-feeding C57BL/6J mice after downregulation of hyaluronic acid. Int J Obes 38, 1035–1043 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.202
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.202
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
4-Methylumbelliferone suppresses hyaluronan and adipogenesis in primary cultured orbital fibroblasts from Graves’ orbitopathy
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2020)
-
Differential effects of a combination of Hibiscus sabdariffa and Lippia citriodora polyphenols in overweight/obese subjects: A randomized controlled trial
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
4-Methylumbelliferone improves the thermogenic capacity of brown adipose tissue
Nature Metabolism (2019)