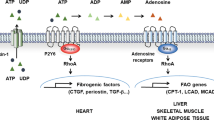
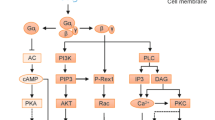
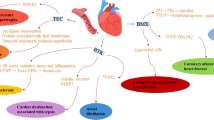
Abstract
G-protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) are serine/threonine protein kinases originally discovered for their role in G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) phosphorylation. Recent studies have demonstrated a much broader function for this kinase family including phosphorylation of cytosolic substrates involved in cell signaling pathways stimulated by GPCRs, as well as by non-GPCRs. In addition, GRKs modulate signaling via phosphorylation-independent functions. Because of these various biochemical functions, GRKs have been shown to affect critical physiological and pathophysiological processes, and thus are considered as drug targets in diseases such as heart failure. Role of GRKs in inflammation and inflammatory diseases is an evolving area of research and several studies including work from our lab in the recent years have demonstrated critical role of GRKs in the immune system. In this review, we discuss the classical and the newly emerging functions of GRKs in the immune system and their role in inflammation and disease processes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takeda S, Kadowaki S, Haga T, Takaesu H, Mitaku S . Identification of G protein-coupled receptor genes from the human genome sequence. FEBS Lett 2002; 520: 97–101.
Howard AD, McAllister G, Feighner SD, Liu Q, Nargund RP, Van der Ploeg LH et al. Orphan G-protein-coupled receptors and natural ligand discovery. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2001; 22: 132–140.
Cabrera-Vera TM, Vanhauwe J, Thomas TO, Medkova M, Preininger A, Mazzoni MR et al. Insights into G protein structure, function, and regulation. Endocr Rev 2003; 24: 765–781.
Downes GB, Gautam N . The G protein subunit gene families. Genomics 1999; 62: 544–552.
Lambert NA . Dissociation of heterotrimeric g proteins in cells. Sci Signal 2008; 1: re5.
Hewavitharana T, Wedegaertner PB . Non-canonical signaling and localizations of heterotrimeric G proteins. Cell Signal 2012; 24: 25–34.
Preininger AM, Hamm HE . G protein signaling: insights from new structures. Sci STKE 2004; 2004: re3.
Oldham WM, Hamm HE . Heterotrimeric G protein activation by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 60–71.
Barker BL, Benovic JL . G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 phosphorylation of hip regulates internalization of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Biochemistry 2011; 50: 6933–6941.
Packiriswamy N, Lee T, Raghavendra PB, Durairaj H, Wang H, Parameswaran N . G-protein-coupled receptor kinase-5 mediates inflammation but does not regulate cellular infiltration or bacterial load in a polymicrobial sepsis model in mice. J Innate Immun 2013; 5: 401–413.
Parameswaran AC, Ott DA, Hadidi F, Cheong BY . Giant left atrial myxoma everything is bigger in Texas. Tex Heart Inst J 2012; 39: 286–287.
Benovic JL, Strasser RH, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ . Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986; 83: 2797–2801.
Frielle T, Collins S, Daniel KW, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Kobilka BK . Cloning of the cDNA for the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987; 84: 7920–7924.
Wacker WB, Donoso LA, Kalsow CM, Yankeelov JA Jr, Organisciak DT . Experimental allergic uveitis. Isolation, characterization, and localization of a soluble uveitopathogenic antigen from bovine retina. J Immunol 1977; 119: 1949–1958.
Wilden U, Hall SW, Kuhn H . Phosphodiesterase activation by photoexcited rhodopsin is quenched when rhodopsin is phosphorylated and binds the intrinsic 48-kDa protein of rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986; 83: 1174–1178.
Zuckerman R, Cheasty JE . A 48 kDa protein arrests cGMP phosphodiesterase activation in retinal rod disk membranes. FEBS Lett 1986; 207: 35–41.
Parameswaran N, Spielman WS . RAMPs: the past, present and future. Trends Biochem Sci 2006; 31: 631–638.
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA, Ward PA . Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture. Nat Protoc 2009; 4: 31–36.
Kunapuli P, Benovic JL . Cloning and expression of GRK5: a member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 5588–5592.
Benovic JL, Gomez J . Molecular cloning and expression of GRK6. A new member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase family. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 19521–19527.
Hisatomi O, Matsuda S, Satoh T, Kotaka S, Imanishi Y, Tokunaga F . A novel subtype of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase, GRK7, in teleost cone photoreceptors. FEBS Lett 1998; 424: 159–164.
Weiss ER, Raman D, Shirakawa S, Ducceschi MH, Bertram PT, Wong F et al. The cloning of GRK7, a candidate cone opsin kinase, from cone- and rod-dominant mammalian retinas. Mol Vis 1998; 4: 27.
Premont RT, Macrae AD, Aparicio SA, Kendall HE, Welch JE, Lefkowitz RJ . The GRK4 subfamily of G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Alternative splicing, gene organization, and sequence conservation. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 29381–29389.
Gurevich EV, Tesmer JJ, Mushegian A, Gurevich VV . G protein-coupled receptor kinases: more than just kinases and not only for GPCRs. Pharmacol Ther 2012; 133: 40–69.
Martini JS, Raake P, Vinge LE, DeGeorge BR Jr, Chuprun JK, Harris DM et al. Uncovering G protein-coupled receptor kinase-5 as a histone deacetylase kinase in the nucleus of cardiomyocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 12457–12462.
Jiang X, Benovic JL, Wedegaertner PB . Plasma membrane and nuclear localization of G protein coupled receptor kinase 6A. Mol Biol Cell 2007; 18: 2960–2969.
Li L, Homan KT, Vishnivetskiy SA, Manglik A, Tesmer JJ, Gurevich VV et al. G Protein-coupled receptor kinases of the GRK4 protein subfamily phosphorylate inactive g protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). J Biol Chem 2015; 290: 10775–10790.
DebBurman SK, Ptasienski J, Benovic JL, Hosey MM . G protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK2 is a phospholipid-dependent enzyme that can be conditionally activated by G protein betagamma subunits. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 22552–22562.
Pitcher JA, Fredericks ZL, Stone WC, Premont RT, Stoffel RH, Koch WJ et al. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2)-enhanced G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) activity. Location, structure, and regulation of the PIP2 binding site distinguishes the GRK subfamilies. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 24907–24913.
Chuang TT, Paolucci L, De Blasi A . Inhibition of G protein-coupled receptor kinase subtypes by Ca2+/calmodulin. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 28691–28696.
Carman CV, Lisanti MP, Benovic JL . Regulation of G protein-coupled receptor kinases by caveolin. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 8858–8864.
Horner TJ, Osawa S, Schaller MD, Weiss ER . Phosphorylation of GRK1 and GRK7 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase attenuates their enzymatic activities. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 28241–28250.
Pronin AN, Benovic JL . Regulation of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK5 by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 3806–3812.
Chuang TT, LeVine H III, De Blasi A . Phosphorylation and activation of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 18660–18665.
Whalen EJ, Foster MW, Matsumoto A, Ozawa K, Violin JD, Que LG et al. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptor signaling by S-nitrosylation of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Cell 2007; 129: 511–522.
Boguth CA, Singh P, Huang CC, Tesmer JJ . Molecular basis for activation of G protein-coupled receptor kinases. EMBO J 2010; 29: 3249–3259.
Jaber M, Koch WJ, Rockman H, Smith B, Bond RA, Sulik KK et al. Essential role of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 in cardiac development and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 12974–12979.
Peppel K, Boekhoff I, McDonald P, Breer H, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ . G protein-coupled receptor kinase 3 (GRK3) gene disruption leads to loss of odorant receptor desensitization. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 25425–25428.
Gainetdinov RR, Bohn LM, Sotnikova TD, Cyr M, Laakso A, Macrae AD et al. Dopaminergic supersensitivity in G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6-deficient mice. Neuron 2003; 38: 291–303.
Rockman HA, Choi DJ, Rahman NU, Akhter SA, Lefkowitz RJ, Koch WJ . Receptor-specific in vivo desensitization by the G protein-coupled receptor kinase-5 in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 9954–9959.
Iaccarino G, Rockman HA, Shotwell KF, Tomhave ED, Koch WJ . Myocardial overexpression of GRK3 in transgenic mice: evidence for in vivo selectivity of GRKs. Am J Physiol 1998; 275: H1298–H1306.
Parameswaran N, Pao CS, Leonhard KS, Kang DS, Kratz M, Ley SC et al. Arrestin-2 and G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 interact with NFkappaB1 p105 and negatively regulate lipopolysaccharide-stimulated ERK1/2 activation in macrophages. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 34159–34170.
Sorriento D, Ciccarelli M, Santulli G, Campanile A, Altobelli GG, Cimini V et al. The G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 inhibits NFkappaB transcriptional activity by inducing nuclear accumulation of IkappaB alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 17818–17823.
Valanne S, Myllymaki H, Kallio J, Schmid MR, Kleino A, Murumagi A et al. Genome-wide RNA interference in Drosophila cells identifies G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 as a conserved regulator of NF-kappaB signaling. J Immunol 2010; 184: 6188–6198.
Patial S, Luo J, Porter KJ, Benovic JL, Parameswaran N . G-protein-coupled-receptor kinases mediate TNFalpha-induced NFkappaB signalling via direct interaction with and phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha. Biochem J 2009; 425: 169–178.
Patial S, Shahi S, Saini Y, Lee T, Packiriswamy N, Appledorn DM et al. G-protein coupled receptor kinase 5 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced NFkappaB activation in primary macrophages and modulates inflammation in vivo in mice. J Cell Physiol 2011; 226: 1323–1333.
Wu JH, Zhang L, Fanaroff AC, Cai X, Sharma KC, Brian L et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase-5 attenuates atherosclerosis by regulating receptor tyrosine kinases and 7-transmembrane receptors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2012; 32: 308–316.
Sorriento D, Ciccarelli M, Santulli G, Campanile A, Altobelli GG, Cimini V et al. The G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 inhibits NFkappaB transcriptional activity by inducing nuclear accumulation of IkappaB alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 17818–17823.
Islam KN, Bae JW, Gao E, Koch WJ . Regulation of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) in the nucleus of cardiomyocytes by G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5). J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 35683–35689.
Islam KN, Koch WJ . Involvement of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling pathway in regulation of cardiac G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5) expression. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 12771–12778.
Ohba Y, Nakaya M, Watari K, Nagasaka A, Kurose H . GRK6 phosphorylates IkappaBalpha at Ser(32)/Ser(36) and enhances TNF-alpha-induced inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2015; 461: 307–313.
Parameswaran R, Lunning M, Mantha S, Devlin S, Hamilton A, Schwartz G et al. Romiplostim for management of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia. Support Care Cancer 2014; 22: 1217–1222.
Patial S, Saini Y, Parvataneni S, Appledorn DM, Dorn GW II, Lapres JJ et al. Myeloid-specific GPCR kinase-2 negatively regulates NF-kappaB1p105-ERK pathway and limits endotoxemic shock in mice. J Cell Physiol 2011; 226: 627–637.
Loniewski K, Shi Y, Pestka J, Parameswaran N . Toll-like receptors differentially regulate GPCR kinases and arrestins in primary macrophages. Mol Immunol 2008; 45: 2312–2322.
Arraes SM, Freitas MS, da Silva SV, de Paula Neto HA, Alves-Filho JC, Auxiliadora Martins M et al. Impaired neutrophil chemotaxis in sepsis associates with GRK expression and inhibition of actin assembly and tyrosine phosphorylation. Blood 2006; 108: 2906–2913.
Kim J, Ahn S, Ren XR, Whalen EJ, Reiter E, Wei H et al. Functional antagonism of different G protein-coupled receptor kinases for beta-arrestin-mediated angiotensin II receptor signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 1442–1447.
Franklin JM, Carrasco GA . G-protein receptor kinase 5 regulates the cannabinoid receptor 2-induced up-regulation of serotonin 2A receptors. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 15712–15724.
Guo J, Chen H, Ho J, Mancini J, Sontag T, Laporte SA et al. TGFbeta-induced GRK2 expression attenuates AngII-regulated vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Cell Signal 2009; 21: 899–905.
Zheng H, Worrall C, Shen H, Issad T, Seregard S, Girnita A et al. Selective recruitment of G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) controls signaling of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 7055–7060.
Nick JA, Avdi NJ, Gerwins P, Johnson GL, Worthen GS . Activation of a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in human neutrophils by lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol 1996; 156: 4867–4875.
Dziarski R, Jin YP, Gupta D . Differential activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1, ERK2, p38, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase mitogen-activated protein kinases by bacterial peptidoglycan. J Infect Dis 1996; 174: 777–785.
Zachos G, Clements B, Conner J . Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection stimulates p38/c-Jun N-terminal mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and activates transcription factor AP-1. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 5097–5103.
Lee JC, Laydon JT, McDonnell PC, Gallagher TF, Kumar S, Green D et al. A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature 1994; 372: 739–746.
Marriott JB, Clarke IA, Dalgleish AG . Inhibition of p38 MAP kinase during cellular activation results in IFN-gamma-dependent augmentation of IL-12 production by human monocytes/macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol 2001; 125: 64–70.
Peregrin S, Jurado-Pueyo M, Campos PM, Sanz-Moreno V, Ruiz-Gomez A, Crespo P et al. Phosphorylation of p38 by GRK2 at the docking groove unveils a novel mechanism for inactivating p38MAPK. Curr Biol 2006; 16: 2042–2047.
Liu X, Ma B, Malik AB, Tang H, Yang T, Sun B et al. Bidirectional regulation of neutrophil migration by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Nat Immunol 2012; 13: 457–464.
Nijboer CH, Heijnen CJ, Willemen HL, Groenendaal F, Dorn GW II, van Bel F et al. Cell-specific roles of GRK2 in onset and severity of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal mice. Brain Behav Immun 2010; 24: 420–426.
Subramanian H, Gupta K, Parameswaran N, Ali H . Regulation of FcinRI signaling in mast cells by G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and its RH domain. J Biol Chem 2014; 289: 20917–20927.
Miller WE, Houtz DA, Nelson CD, Kolattukudy PE, Lefkowitz RJ . G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinase phosphorylation and beta-arrestin recruitment regulate the constitutive signaling activity of the human cytomegalovirus US28 GPCR. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 21663–21671.
Willemen HL, Eijkelkamp N, Wang H, Dantzer R, Dorn GW II, Kelley KW et al. Microglial/macrophage GRK2 determines duration of peripheral IL-1beta-induced hyperalgesia: contribution of spinal cord CX3CR1, p38 and IL-1 signaling. Pain 2010; 150: 550–560.
Eijkelkamp N, Heijnen CJ, Carbajal AG, Willemen HL, Wang H, Minett MS et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 acts as a critical regulator of cytokine-induced hyperalgesia by promoting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and inhibiting p38 signaling. Mol Med 2012; 18: 556–564.
Liu Z, Jiang Y, Li Y, Wang J, Fan L, Scott MJ et al. TLR4 signaling augments monocyte chemotaxis by regulating G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 translocation. J Immunol 2013; 191: 857–864.
Knight RJ, Buxton DB . Stimulation of c-Jun kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase by ischemia and reperfusion in the perfused rat heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 218: 83–88.
Komuro I, Kudo S, Yamazaki T, Zou Y, Shiojima I, Yazaki Y . Mechanical stretch activates the stress-activated protein kinases in cardiac myocytes. FASEB J 1996; 10: 631–636.
Liu Y, Gorospe M, Yang C, Holbrook NJ . Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase during the cellular response to genotoxic stress. Inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activity and AP-1-dependent gene activation. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 8377–8380.
Dabrowski A, Grady T, Logsdon CD, Williams JA . Jun kinases are rapidly activated by cholecystokinin in rat pancreas both in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 5686–5690.
Gomez del Arco P, Martinez-Martinez S, Calvo V, Armesilla AL, Redondo JM . JNK (c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase) is a target for antioxidants in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 26335–26340.
Jung S, Yaron A, Alkalay I, Hatzubai A, Avraham A, Ben-Neriah Y . Costimulation requirement for AP-1 and NF-kappa B transcription factor activation in T cells. Ann NY Acad Sci 1995; 766: 245–252.
Eckhart AD, Duncan SJ, Penn RB, Benovic JL, Lefkowitz RJ, Koch WJ . Hybrid transgenic mice reveal in vivo specificity of G protein-coupled receptor kinases in the heart. Circ Res 2000; 86: 43–50.
Cotton M, Claing A . G protein-coupled receptors stimulation and the control of cell migration. Cell Signal 2009; 21: 1045–1053.
Insall R . The interaction between pseudopods and extracellular signalling during chemotaxis and directed migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2013; 25: 526–531.
Penela P, Nogues L, Mayor F Jr . Role of G protein-coupled receptor kinases in cell migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2014; 27: 10–17.
Lafarga V, Mayor F Jr, Penela P . The interplay between G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) and histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) at the crossroads of epithelial cell motility. Cell Adh Migr 2012; 6: 495–501.
Arnon TI, Xu Y, Lo C, Pham T, An J, Coughlin S et al. GRK2-dependent S1PR1 desensitization is required for lymphocytes to overcome their attraction to blood. Science 2011; 333: 1898–1903.
Aragay AM, Mellado M, Frade JM, Martin AM, Jimenez-Sainz MC, Martinez AC et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1-induced CCR2B receptor desensitization mediated by the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 2985–2990.
Olbrich H, Proudfoot AE, Oppermann M . Chemokine-induced phosphorylation of CC chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5). J Leukoc Biol 1999; 65: 281–285.
Raghuwanshi SK, Su Y, Singh V, Haynes K, Richmond A, Richardson RM . The chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2 couple to distinct G protein-coupled receptor kinases to mediate and regulate leukocyte functions. J Immunol 2012; 189: 2824–2832.
Vroon A, Heijnen CJ, Lombardi MS, Cobelens PM, Mayor F Jr, Caron MG et al. Reduced GRK2 level in T cells potentiates chemotaxis and signaling in response to CCL4. J Leukoc Biol 2004; 75: 901–909.
Otten JJ, de Jager SC, Kavelaars A, Seijkens T, Bot I, Wijnands E et al. Hematopoietic G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 deficiency decreases atherosclerotic lesion formation in LDL receptor-knockout mice. FASEB J 2013; 27: 265–276.
Leoratti FM, Trevelin SC, Cunha FQ, Rocha BC, Costa PA, Gravina HD et al. Neutrophil paralysis in Plasmodium vivax malaria. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2012; 6: e1710.
Alves-Filho JC, Sonego F, Souto FO, Freitas A, Verri WA Jr, Auxiliadora-Martins M et al. Interleukin-33 attenuates sepsis by enhancing neutrophil influx to the site of infection. Nat Med 2010; 16: 708–712.
Penela P, Ribas C, Aymerich I, Eijkelkamp N, Barreiro O, Heijnen CJ et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 positively regulates epithelial cell migration. EMBO J 2008; 27: 1206–1218.
Penela P, Ribas C, Aymerich I, Eijkelkamp N, Barreiro O, Heijnen CJ et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 positively regulates epithelial cell migration. EMBO J 2008; 27: 1206–1218.
Cant SH, Pitcher JA . G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of ezrin is required for G protein-coupled receptor-dependent reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. Mol Biol Cell 2005; 16: 3088–3099.
Kahsai AW, Zhu S, Fenteany G . G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 activates radixin, regulating membrane protrusion and motility in epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1803: 300–310.
Tarrant TK, Rampersad RR, Esserman D, Rothlein LR, Liu P, Premont RT et al. Granulocyte chemotaxis and disease expression are differentially regulated by GRK subtype in an acute inflammatory arthritis model (K/BxN). Clin Immunol 2008; 129: 115–122.
Chakraborty PK, Zhang Y, Coomes AS, Kim WJ, Stupay R, Lynch LD et al. G Protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK5 phosphorylates moesin and regulates metastasis in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2014; 74: 3489–3500.
Chen Y, Wang F, Long H, Wu Z, Ma L . GRK5 promotes F-actin bundling and targets bundles to membrane structures to control neuronal morphogenesis. J Cell Biol 2011; 194: 905–920.
Vroon A, Heijnen CJ, Raatgever R, Touw IP, Ploemacher RE, Premont RT et al. GRK6 deficiency is associated with enhanced CXCR4-mediated neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro and impaired responsiveness to G-CSF in vivo. J Leukoc Biol 2004; 75: 698–704.
Kavelaars A, Vroon A, Raatgever RP, Fong AM, Premont RT, Patel DD et al. Increased acute inflammation, leukotriene B4-induced chemotaxis, and signaling in mice deficient for G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6. J Immunol 2003; 171: 6128–6134.
Fong AM, Premont RT, Richardson RM, Yu YR, Lefkowitz RJ, Patel DD . Defective lymphocyte chemotaxis in beta-arrestin2- and GRK6-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 7478–7483.
Eijkelkamp N, Heijnen CJ, Lucas A, Premont RT, Elsenbruch S, Schedlowski M et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 controls chronicity and severity of dextran sodium sulphate-induced colitis in mice. Gut 2007; 56: 847–854.
Chen Y, Lu B, Yang Q, Fearns C, Yates JR III, Lee JD . Combined integrin phosphoproteomic analyses and small interfering RNA-based functional screening identify key regulators for cancer cell adhesion and migration. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 3713–3720.
Raghuwanshi SK, Smith N, Rivers EJ, Thomas AJ, Sutton N, Hu Y et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 deficiency promotes angiogenesis, tumor progression, and metastasis. J Immunol 2013; 190: 5329–5336.
Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Konowal A, Freed PW, Westcott JY, Henson PM . Macrophages that have ingested apoptotic cells in vitro inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production through autocrine/paracrine mechanisms involving TGF-beta, PGE2, and PAF. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 890–898.
Peng Y, Martin DA, Kenkel J, Zhang K, Ogden CA, Elkon KB . Innate and adaptive immune response to apoptotic cells. J Autoimmun 2007; 29: 303–309.
Stuart LM, Lucas M, Simpson C, Lamb J, Savill J, Lacy-Hulbert A . Inhibitory effects of apoptotic cell ingestion upon endotoxin-driven myeloid dendritic cell maturation. J Immunol 2002; 168: 1627–1635.
Brinks H, Boucher M, Gao E, Chuprun JK, Pesant S, Raake PW et al. Level of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 determines myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via pro- and anti-apoptotic mechanisms. Circ Res 2010; 107: 1140–1149.
Weng TP, Fu TC, Wang CH, Hsu CC, Wang JS . Activation of lymphocyte autophagy/apoptosis reflects haemodynamic inefficiency and functional aerobic impairment in patients with heart failure. Clin Sci 2014; 127: 589–602.
Chen X, Zhu H, Yuan M, Fu J, Zhou Y, Ma L . G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 phosphorylates p53 and inhibits DNA damage-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 12823–12830.
Liu P, Wang X, Gao N, Zhu H, Dai X, Xu Y et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5, overexpressed in the alpha-synuclein up-regulation model of Parkinson's disease, regulates bcl-2 expression. Brain Res 2010; 1307: 134–141.
Nakaya M, Tajima M, Kosako H, Nakaya T, Hashimoto A, Watari K et al. GRK6 deficiency in mice causes autoimmune disease due to impaired apoptotic cell clearance. Nat Commun 2013; 4: 1532.
Suo WZ, Li L . Dysfunction of G protein-coupled receptor kinases in Alzheimer's disease. ScientificWorldJournal 2010; 10: 1667–1678.
Vroon A, Kavelaars A, Limmroth V, Lombardi MS, Goebel MU, Van Dam AM et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 2005; 174: 4400–4406.
Bychkov ER, Gurevich VV, Joyce JN, Benovic JL, Gurevich EV . Arrestins and two receptor kinases are upregulated in Parkinson's disease with dementia. Neurobiol Aging 2008; 29: 379–396.
Obrenovich ME, Palacios HH, Gasimov E, Leszek J, Aliev G . The GRK2 overexpression is a primary hallmark of mitochondrial lesions during early Alzheimer disease. Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol 2009; 2009: 327360.
Sorensen SD, Conn PJ . G protein-coupled receptor kinases regulate metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 function and expression. Neuropharmacology 2003; 44: 699–706.
Degos V, Peineau S, Nijboer C, Kaindl AM, Sigaut S, Favrais G et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and group I metabotropic glutamate receptors mediate inflammation-induced sensitization to excitotoxic neurodegeneration. Ann Neurol 2013; 73: 667–678.
Eijkelkamp N, Heijnen CJ, Willemen HL, Deumens R, Joosten EA, Kleibeuker W et al. GRK2: a novel cell-specific regulator of severity and duration of inflammatory pain. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 2138–2149.
Eijkelkamp N, Wang H, Garza-Carbajal A, Willemen HL, Zwartkruis FJ, Wood JN et al. Low nociceptor GRK2 prolongs prostaglandin E2 hyperalgesia via biased cAMP signaling to Epac/Rap1, protein kinase Cepsilon, and MEK/ERK. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 12806–12815.
Wang H, Heijnen CJ, Eijkelkamp N, Garza Carbajal A, Schedlowski M, Kelley KW et al. GRK2 in sensory neurons regulates epinephrine-induced signalling and duration of mechanical hyperalgesia. Pain 2011; 152: 1649–1658.
Wang H, Heijnen CJ, van Velthoven CT, Willemen HL, Ishikawa Y, Zhang X et al. Balancing GRK2 and EPAC1 levels prevents and relieves chronic pain. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 5023–5034.
Ferrari LF, Bogen O, Alessandri-Haber N, Levine E, Gear RW, Levine JD . Transient decrease in nociceptor GRK2 expression produces long-term enhancement in inflammatory pain. Neuroscience 2012; 222: 392–403.
Liu J, Rasul I, Sun Y, Wu G, Li L, Premont RT et al. GRK5 deficiency leads to reduced hippocampal acetylcholine level via impaired presynaptic M2/M4 autoreceptor desensitization. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 19564–19571.
Sadot E, Gurwitz D, Barg J, Behar L, Ginzburg I, Fisher A . Activation of m1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor regulates tau phosphorylation in transfected PC12 cells. J Neurochem 1996; 66: 877–880.
Vinge LE, von Lueder TG, Aasum E, Qvigstad E, Gravning JA, How OJ et al. Cardiac-restricted expression of the carboxyl-terminal fragment of GRK3 Uncovers Distinct Functions of GRK3 in regulation of cardiac contractility and growth: GRK3 controls cardiac alpha1-adrenergic receptor responsiveness. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 10601–10610.
Zhang Y, Matkovich SJ, Duan X, Gold JI, Koch WJ, Dorn GW II . Nuclear effects of G-protein receptor kinase 5 on histone deacetylase 5-regulated gene transcription in heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 2011; 4: 659–668.
Chen EP, Bittner HB, Akhter SA, Koch WJ, Davis RD . Myocardial function in hearts with transgenic overexpression of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5. Ann Thorac Surg 2001; 71: 1320–1324.
Brinks H, Boucher M, Gao E, Chuprun JK, Pesant S, Raake PW et al. Level of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 determines myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via pro- and anti-apoptotic mechanisms. Circ Res 2010; 107: 1140–1149.
Raake PW, Vinge LE, Gao E, Boucher M, Rengo G, Chen X et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 ablation in cardiac myocytes before or after myocardial infarction prevents heart failure. Circ Res 2008; 103: 413–422.
Shah AS, White DC, Emani S, Kypson AP, Lilly RE, Wilson K et al. In vivo ventricular gene delivery of a beta-adrenergic receptor kinase inhibitor to the failing heart reverses cardiac dysfunction. Circulation 2001; 103: 1311–1316.
Rengo G, Lymperopoulos A, Zincarelli C, Donniacuo M, Soltys S, Rabinowitz JE et al. Myocardial adeno-associated virus serotype 6-betaARKct gene therapy improves cardiac function and normalizes the neurohormonal axis in chronic heart failure. Circulation 2009; 119: 89–98.
Harding VB, Jones LR, Lefkowitz RJ, Koch WJ, Rockman HA . Cardiac beta ARK1 inhibition prolongs survival and augments beta blocker therapy in a mouse model of severe heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 5809–5814.
Sorriento D, Santulli G, Fusco A, Anastasio A, Trimarco B, Iaccarino G . Intracardiac injection of AdGRK5-NT reduces left ventricular hypertrophy by inhibiting NF-kappaB-dependent hypertrophic gene expression. Hypertension 2010; 56: 696–704.
Eckhart AD, Ozaki T, Tevaearai H, Rockman HA, Koch WJ . Vascular-targeted overexpression of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 in transgenic mice attenuates beta-adrenergic receptor signaling and increases resting blood pressure. Mol Pharmacol 2002; 61: 749–758.
Keys JR, Zhou RH, Harris DM, Druckman CA, Eckhart AD . Vascular smooth muscle overexpression of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 elevates blood pressure, which segregates with sex and is dependent on Gi-mediated signaling. Circulation 2005; 112: 1145–1153.
Melamed A, Sorvillo FJ . The burden of sepsis-associated mortality in the United States from 1999 to 2005: an analysis of multiple-cause-of-death data. Crit Care 2009; 13: R28.
Packiriswamy N, Lee T, Raghavendra PB, Durairaj H, Wang H, Parameswaran N . G-protein-coupled receptor kinase-5 mediates inflammation but does not regulate cellular infiltration or bacterial load in a polymicrobial sepsis model in mice. J Innate Immun 2013; 5: 401–413.
Packiriswamy N, Parvataneni S, Parameswaran N . Overlapping and distinct roles of GRK5 in TLR2-, and TLR3-induced inflammatory response in vivo. Cell Immunol 2012; 272: 107–111.
Parvataneni S, Gonipeta B, Packiriswamy N, Lee T, Durairaj H, Parameswaran N . Role of myeloid-specific G-protein coupled receptor kinase-2 in sepsis. Int J Clin Exp Med 2011; 4: 320–330.
Matkovich SJ, Diwan A, Klanke JL, Hammer DJ, Marreez Y, Odley AM, Brunskill EW, Koch WJ, Schwartz RJ, Dorn GW 2nd . Cardiac-specific ablation of G-protein receptor kinase 2 redefines its roles in heart development and beta-adrenergic signaling. Circ Res 2006; 99: 996–1003.
Lymperopoulos A, Rengo G, Gao E, Ebert SN, Dorn GW 2nd, Koch WJ . Reduction of sympathetic activity via adrenal-targeted GRK2 gene deletion attenuates heart failure progression and improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 16378–16386.
Terman GW, Jin W, Cheong YP, Lowe J, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Chavkin C . G-protein receptor kinase 3 (GRK3) influences opioid analgesic tolerance but not opioid withdrawal. Br J Pharmacol 2004; 141: 55–64.
Virlon B, Firsov D, Cheval L, Reiter E, Troispoux C, Guillou F, Elalouf JM . Rat G protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK4: identification, functional expression, and differential tissue distribution of two splice variants. Endocrinology 1998; 139: 2784–2795.
Gainetdinov RR, Bohn LM, Walker JK, Laporte SA, Macrae AD, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Premont RT . Muscarinic supersensitivity and impaired receptor desensitization in G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5-deficient mice. Neuron 1999; 24: 1029–1036.
Lodowski DT, Tesmer VM, Benovic JL, Tesmer JJ . The structure of G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK)-6 defines a second lineage of GRKs. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 16785–16793.
Acknowledgements
Research in Dr Parameswaran’s lab is supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health (Grant Nos. HL095637, AR055726 and AI099404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Packiriswamy, N., Parameswaran, N. G-protein-coupled receptor kinases in inflammation and disease. Genes Immun 16, 367–377 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2015.26
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2015.26
This article is cited by
-
Mechanistic diversity involved in the desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2021)