Abstract
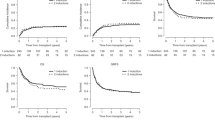
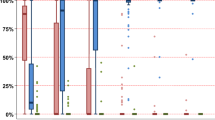
Delayed or failed engraftment remains a concern after cord blood transplantation (CBT) even when using double-unit grafts. Therefore, we analyzed the association between BM assessment performed approximately 21 days after transplantation, and the speed and success of sustained donor-derived neutrophil engraftment in 56 myeloablative double-unit CBT (DCBT) recipients. Overall, the cumulative incidence of sustained neutrophil engraftment was 95% (95% confidence intervals (CI): 89–100). Of the percentage of myeloid precursors, the BM cellularity and the total donor chimerism the total donor chimerism percentage had the most critical association with the speed and success of engraftment. DCBT recipients who were 100% donor achieved a 98% engraftment rate at a median of 22 days. This compared with 100% engraftment in patients who were 90–99% donor, but at a delayed median of 29 days and only 68% engraftment in patients <90% donor at a median of 37 days (P=0.001). Multivariate analysis was performed in the subgroup of patients who had not engrafted at the time the BM analysis was performed, the subgroup of most clinical concern. This confirmed donor chimerism was predictive of subsequent neutrophil recovery (P=0.004). These findings demonstrate the importance of the day 21 BM chimerism determinations after DCBT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rubinstein P, Carrier C, Scaradavou A, Kurtzberg J, Adamson J, Migliaccio AR et al. Outcomes among 562 recipients of placental-blood transplants from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: 1565–1577.
Wagner JE, Barker JN, DeFor TE, Baker KS, Blazar BR, Eide C et al. Transplantation of unrelated donor umbilical cord blood in 102 patients with malignant and nonmalignant diseases: influence of CD34 cell dose and HLA disparity on treatment-related mortality and survival. Blood 2002; 100: 1611–1618.
Rocha V, Gluckman E . Improving outcomes of cord blood transplantation: HLA matching, cell dose and other graft- and transplantation-related factors. Br J Haematol 2009; 147: 262–274.
Barker JN, Scaradavou A, Stevens CE . Combined effect of total nucleated cell dose and HLA match on transplantation outcome in 1061 cord blood recipients with hematologic malignancies. Blood 2010; 115: 1843–1849.
Page KM, Zhang L, Mendizabal A, Wease S, Carter S, Gentry T et al. Total colony-forming units are a strong, independent predictor of neutrophil and platelet engraftment after unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation: a single-center analysis of 435 cord blood transplants. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 1362–1374.
Avery S, Shi W, Lubin M, Gonzales AM, Heller G, Castro-Malaspina H et al. Influence of infused cell dose and HLA match on engraftment after double-unit cord blood allografts. Blood 2011; 117: 3277–3285.
Barker JN, Weisdorf DJ, DeFor TE, Blazar BR, McGlave PB, Miller JS et al. Transplantation of 2 partially HLA-matched umbilical cord blood units to enhance engraftment in adults with hematologic malignancy. Blood 2005; 105: 1343–1347.
Brunstein CG, Barker JN, Weisdorf DJ, DeFor TE, Miller JS, Blazar BR et al. Umbilical cord blood transplantation after nonmyeloablative conditioning: impact on transplantation outcomes in 110 adults with hematologic disease. Blood 2007; 110: 3064–3070.
Barker JN, Abboud M, Rice RD, Hawke R, Schaible A, Heller G et al. A ‘no-wash’ albumin-dextran dilution strategy for cord blood unit thaw: high rate of engraftment and a low incidence of serious infusion reactions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1596–1602.
Scharf SJ, Smith AG, Hansen JA, McFarland C, Erlich HA . Quantitative determination of bone marrow transplant engraftment using fluorescent polymerase chain reaction primers for human identity markers. Blood 1995; 85: 1954–1963.
Schichman SA, Suess P, Vertino AM, Gray PS . Comparison of short tandem repeat and variable number tandem repeat genetic markers for quantitative determination of allogeneic bone marrow transplant engraftment. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 29: 243–248.
Scaradavou A, Smith KM, Hawke R, Schaible A, Abboud M, Kernan NA et al. Cord blood units with low CD34+ cell viability have a low probability of engraftment after double unit transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 500–508.
Maeda T, Shiozawa E, Mayumi H, Usui T, Nakashima H, Hattori N et al. Histopathology of bone marrow reconstitution after umbilical cord blood transplantation for hematological diseases. Pathol Int 2008; 58: 126–132.
Moscardo F, Sanz J, Senent L, Cantero S, de la Rubia J, Montesinos P et al. Impact of hematopoietic chimerism at day +14 on engraftment after unrelated donor umbilical cord blood transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Haematologica 2009; 94: 827–832.
McKenna DH, Rupp C, Wagner J, McGlennen R, Hirsch B, Dolan M et al. Increased lymphoblast-like cells following umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation do not predict recurrent acute leukemia. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2171–2172.
Antin JH, Childs R, Filipovich AH, Giralt S, Mackinnon S, Spitzer T et al. Establishment of complete and mixed donor chimerism after allogeneic lymphohematopoietic transplantation: recommendations from a workshop at the 2001 Tandem Meetings of the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry and the American Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2001; 7: 473–485.
Baron F, Sandmaier BM . Chimerism and outcomes after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation following nonmyeloablative conditioning. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1690–1700.
Mossallam GI, Kamel AM, Storer B, Martin PJ . Prognostic utility of routine chimerism testing at 2 to 6 months after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 352–359.
Mickelson DM, Sproat L, Dean R, Sobecks R, Rybicki L, Kalaycio M et al. Comparison of donor chimerism following myeloablative and nonmyeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 84–89.
Sideri A, Neokleous N, De La Grange PB, Guerton B, Le Bousse Kerdilles MC, Uzan G et al. An overview of the progress on double umbilical cord blood transplantation. Haematologica 2011; 96: 1213–1220.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Gabrielle's Angel Foundation for Cancer Research, the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Society, the Translational and Integrative Medicine Research Grant and P01 CA23766 from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health.
Author contributions: SA and CES analyzed and interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. MV, AG and ML analyzed the data. NK and AS wrote the manuscript. HCM and CH analyzed the BM specimens and wrote the manuscript. JNB directed the research, interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avery, S., Voss, M., Gonzales, A. et al. Importance of day 21 BM chimerism in sustained neutrophil engraftment following double-unit cord blood transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 47, 1056–1060 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2011.236
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2011.236
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Chimerism analysis for clinicians: a review of the literature and worldwide practices
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for myelofibrosis using fludarabine-, intravenous busulfan- and low-dose TBI-based conditioning
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
The impact of CD34+ cell dose on engraftment after SCTs: personalized estimates based on mathematical modeling
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)