Abstract
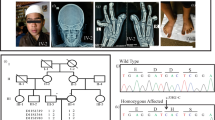
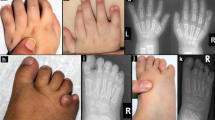
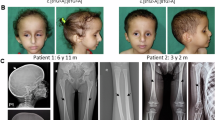
THE Coffin-Lowry syndrome (CLS), an X-linked disorder, is characterized by severe psychomotor retardation, facial and digital dysmorphisms, and progressive skeletal deformations1. Genetic linkage analysis mapped the CLS locus to an interval of 2–3 megabases at Xp22.2. The gene coding for Rsk-2, a member of the growth-factor-regulated protein kinases, maps within the candidate interval, and was tested as a candidate gene for CLS. Initial screening for mutations in the gene for Rsk-2 in 76 unrelated CLS patients revealed one intragenic deletion, a nonsense, two splice site, and two missense mutations. The two missenses affect sites critical for the function of Rsk-2. The mutated Rsk-2 proteins were found to be inactive in a S6 kinase assay. These findings provide direct evidence that abnormalities in the MAPK/RSK signalling pathway cause Coffin-Lowry syndrome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young, I. D. J. Med. Genet 25, 344–348 (1988).
Hanauer, A. et al. Am. J. Med. Genet. 30, 523–530 (1988).
Biancalana, V. et al. Genomics 22, 617–625 (1994).
Bird, H., Collins, A. L., Oley, C. & Lindsay, S. Am. J. Med. Genet. 59, 512–516 (1995).
Bjorbaek, C. et al. Diabetes 44, 90–97 (1995).
Trump, D. et al. Hum. Genet. 97, 60–68 (1996).
Wassarman, D. A., Solomon, N. M. & Rubin, G. M. Gene 144, 309–310 (1994).
Alcorta, D. A. et al. Mol. Cell. Biol. 9, 3850–3859 (1989).
Grove, J. R. et al. Biochemistry 32, 7727–7738 (1993).
Moller, D. E., Xia, C.-H., Tang, T., Zhu, A. & Jakubowsky, M. Am. J. Physiol. 266, C351–C359 (1994).
Zhao, Y. I., Bjorbaek, C., Weremowicz, S., Morton, C. & Moller, D. E. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 4353–4363 (1995).
Jones, S. W., Erikson, E., Blenis, J., Maller, J. & Erikson, R. L. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 3377–3381 (1988).
Blenis, J. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 5889–5892 (1993).
Hanks, S. K. & Hunter, T. FASEB J. 9, 576–596 (1995).
Hanks, S. K., Quinn, A. M. & Hunter, T. Science 241, 42–52 (1988).
Bjorbaek, C., Zhao, Y. & Moller, D. E. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 18848–18852 (1995).
Fisher, T. L. & Blenis, J. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 1212–1219 (1996).
Dent, P. et al. Nature 348, 302–308 (1990).
Xing, J., Ginty, D. D. & Greenberg, M. E. Science 273, 959–963 (1996).
Grigoriadis, A. E. et al. Science 266, 443–448 (1994).
Hu, E. et al. EMBO J. 13, 3094–3103 (1994).
Chonczynski, P. Biotechniques 15, 532 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trivier, E., De Cesare, D., Jacquot, S. et al. Mutations in the kinase Rsk-2 associated with Coffin-Lowry syndrome. Nature 384, 567–570 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/384567a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/384567a0
This article is cited by
-
Deleterious mutations in ALDH1L2 suggest a novel cause for neuro-ichthyotic syndrome
npj Genomic Medicine (2019)
-
Involvement of RSK1 activation in malformin-enhanced cellular fibrinolytic activity
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
RSK2 and its binding partners in cell proliferation, transformation and cancer development
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2017)
-
Feedback activation of neurofibromin terminates growth factor-induced Ras activation
Cell Communication and Signaling (2016)
-
The p90 ribosomal S6 kinase 2 specifically affects mitotic progression by regulating the basal level, distribution and stability of mitotic spindles
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2016)