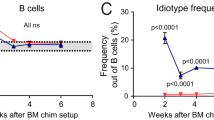
Abstract
THE recessive mouse mutations lpr and gld create deficiencies in an interacting pair of cell surface molecules, CD95 (Fas/APO-1) and Fas-ligand (FasL), respectively1–3, resulting in autoantibody production resembling human systemic lupus erythematosus4. The mechanisms of self-tolerance affected by deficiency in either molecule are not established, but CD95 deficiency both in B cells and in CD4+ T cells recognizing major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules is required for autoimmunity in lpr mice5–8. Here we track the outcome of in vivo interactions between B cells and CD4+T cells that recognize a transgene-encoded autoantigen, hen egg lysozyme (HEL), using cells from mice trans-genic for immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor (TCR) genes. B cells that had not previously encountered HEL autoantigen (naive cells) were triggered into proliferation and antibody production upon interaction with antigen and HEL-specific CD4+T cells. By contrast, B cells that had been chronically exposed to HEL during their development and carried desensitized surface immunoglobulin (slg) antigen receptors9(anergic cells) did not produce antibody but instead were eliminated in the presence of HEL-specific CD4+T cells. CD95-deficient anergic B cells, however, were not eliminated by CD4+T cells and were triggered to proliferate. These findings identify a novel regulatory step for eliminating autoreactive B cells that seems unique in its dependence on CD95.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watanabe-Fukunaga, R., Brannan, C. I., Copeland, N. G., Jenkins, N. A. & Nagata, S. Nature 356, 314–317 (1992).
Takahashi, T. et al. Cell 76, 969–976 (1994).
Lynch, D. H. et al. Immunity 1, 131–136 (1994).
Cohen, P. L. & Eisenberg, R. A. A. Rev. Immun. 9, 243–269 (1991).
Nemazee, D., Guiet, C., Buerki, K. & Marshak-Rothstein, A. J. Immun. 147, 2536–2539 (1991).
Sobel, E. S. et al. J. exp. Med. 173, 1441–1449 (1991).
Sobel, E. S., Cohen, P. L. & Eisenberg, R. A. J. Immun. 150, 4160–4167 (1993).
Jevnikar, A. M., Grusby, M. J. & Glimcher, L. H. J. exp. Med. 179, 1137–1143 (1994).
Cooke, M. P. et al. J. exp. Med. 179, 425–438 (1994).
Goodnow, C. C. et al. Nature 334, 676–682 (1988).
Ho, W. Y., Cooke, M. P., Goodnow, C. C. & Davis, M. M. J. exp. Med. 179, 1539–1549 (1994).
Kanost, D. & McCluskey, J. Eur. J. Immun. 24, 1186–1193 (1994).
Matsuzawa, A. et al. J. exp. Med. 171, 519–531 (1990).
Nemazee, D. A. & Bürki, K. Nature 337, 562–566 (1989).
Hartley, S. B. et al. Nature 353, 765–768 (1991).
Cyster, J. G., Hartley, S. B. & Goodnow, C. C. Nature 371, 389–395 (1994).
Rathmell, J. C. & Goodnow, C. C. J. Immun. 153, 2831–2842 (1994).
Trauth, B. C. et al. Science 245, 301–305 (1989).
Nagata, S. & Golstein, P. Science 267, 1449–1456 (1995).
Rothstein, T. L. et al. Nature 374, 163–165 (1995).
Goodnow, C. C. et al. Adv. Immun. 59, 279–368 (1995).
Weston, K. M., Ju, S., Lu, C. Y. & Sy, M. J. Immun. 141, 1941–1948 (1988).
Zhou, T. et al. J. Immun. 147, 466–474 (1991).
Zhou, T., Bluethmann, H., Zhang, J., Edwards, C. K. & Mountz, J. D. J. exp. Med. 176, 1063–1072 (1992).
Bossu, P. et al. J. Immun. 151, 7233–7239 (1993).
Russell, J. H., Rush, B., Weaver, C. & Wang, R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 4409–4413 (1993).
Gillette-Ferguson, I. & Sidman, C. L. Eur. J. Immun. 4, 1181–1185 (1994).
Singer, G. G. & Abbas, A. K. Immunity 1, 365–371 (1994).
Fulcher, D. A. & Basten, A. J. exp. Med. 179, 125–134 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rathmell, J., Cooke, M., Ho, W. et al. CD95 (Fas)-dependent elimination of self-reactive B cells upon interaction with CD4+T cells. Nature 376, 181–184 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/376181a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/376181a0
This article is cited by
-
De novo identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes
Nature Methods (2024)
-
The endogenous repertoire harbors self-reactive CD4+ T cell clones that adopt a follicular helper T cell-like phenotype at steady state
Nature Immunology (2023)
-
NDRG1 is induced by antigen-receptor signaling but dispensable for B and T cell self-tolerance
Communications Biology (2022)
-
Multiscale engineering of immune cells and lymphoid organs
Nature Reviews Materials (2019)
-
Second signals rescue B cells from activation-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and death
Nature Immunology (2018)