Abstract
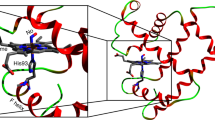
Myoglobin, a small globular haem protein that binds gaseous ligands such as O2, CO and NO reversibly at the haem iron, serves as a model for studying structural and dynamic aspects of protein reactions. Time-resolved spectroscopic measurements after photodissociation of the ligand revealed a complex ligand-binding reaction with multiple kinetic intermediates, resulting from protein relaxation and movements of the ligand within the protein1,2,3. To observe the structural changes induced by ligand dissociation, we have carried out X-ray crystallographic investigations of carbon monoxy-myoglobin (MbCO mutant L29W) crystals illuminated below and above 180 K, complemented by time-resolved infrared spectroscopy of CO rebinding. Here we show that below 180 K photodissociated ligands migrate to specific sites within an internal cavity—the distal haem pocket—of an essentially immobilized, frozen protein, from where they subsequently rebind by thermally activated barrier crossing. Upon photodissociation above 180 K, ligands escape from the distal pocket, aided by protein fluctuations that transiently open exit channels. We recover most of the ligands in a cavity on the opposite side of the haem group.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin, R. H., Beeson, K. W., Eisenstein, L., Frauenfelder, H. & Gunsalus, I. C. Dynamics of ligand binding to myoglobin. Biochemistry 14, 5355– 5373 (1975).
Steinbach, P. J. et al. Ligand binding to heme proteins: connection between dynamics and function. Biochemistry 30, 3988– 4001 (1991).
Olson, J. S. & Phillips, G. N. Jr. Kinetic pathways and barriers for ligand binding to myoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 17593–17596 (1996).
Henry, E. R., Sommer, J. H., Hofrichter, J. & Eaton, W. A. Geminate recombination of carbon-monoxide to myoglobin. J. Mol. Biol. 166, 443–451 ( 1983).
Huang, X. & Boxer, S. G. Discovery of new ligand binding pathways in myoglobin by random mutagenesis. Nature Struct. Biol. 1, 226–229 ( 1994).
Quillin, M. L. et al. Structural and functional effects of apolar mutations of the distal valine in myoglobin. J. Mol. Biol. 245, 416–436 (1995).
Scott, E. E. & Gibson, Q. H. Ligand migration in sperm whale myoglobin. Biochemistry 36, 11909– 11917 (1997).
Parak, F., Knapp, E. W. & Kucheida, D. Protein dynamics: Mössbauer-spectroscopy on deoxymyoglobin crystals. J. Mol. Biol. 161, 177– 194 (1982).
Doster, W., Cusack, S. & Petry, W. Dynamical transition of myoglobin revealed by inelastic neutron-scattering. Nature 337, 754– 756 (1989).
Nienhaus, G. U., Heinzl, J., Huenges, E. & Parak, F. Protein crystal dynamics studied by time-resolved analysis of X-ray diffuse scattering. Nature 338, 665–666 ( 1989).
Rasmussen, B. F., Stock, A. M., Ringe, D. & Petsko, G. A. Crystalline ribonuclease A loses function below the dynamical transition at 220 K. Nature 357, 423–424 ( 1992).
Schlichting, I., Berendzen, J., Phillips, G. N. Jr & Sweet, R. M. Crystal structure of photolysed carbonmonoxy-myoglobin. Nature 371, 808–812 ( 1994).
Teng, T. Y., Srajer, V. & Moffat, K. Photolysis-induced structural changes in single crystals of carbonmonoxy myoglobin at 40 K. Nature Struct. Biol. 1, 701–705 (1994).
Hartmann, H. et al. X-ray structure determination of a metastable state of carbonmonoxy myoglobin after photodissociation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 7013–7016 (1996).
Lim, M., Jackson, T. A. & Anfinrud, P. A. Ultrafast rotation and trapping of carbon monoxide dissociated from myoglobin. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 209–214 (1997).
Srajer, V. et al. Photolysis of the carbon-monoxide complex of myoglobin: nanosecond time-resolved crystallography. Science 274, 1726–1729 (1996).
Vitkup, D., Petsko, G. A. & Karplus, M. A comparison between molecular dynamics and X-ray results for dissociated CO in myoglobin. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 202–208 (1997).
Nienhaus, G. U., Mourant, J. R. & Frauenfelder, H. Spectroscopic evidence for conformational relaxation in myoglobin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 2902–2906 (1992).
Springer, B. A., Sligar S. G., Olson J. S. & Phillips, G. N. Jr. Mechanisms of ligand recognition in myoglobin. Chem. Rev. 94, 699–714 (1994).
Tilton, R. F., Kuntz, I. D. & Petsko, G. A. Cavities in proteins: structure of a metmyoglobin-xenon complex solved to 1.9-Å. Biochemistry 23, 2849–2857 (1984).
Hirota, S. et al. Perturbation of the Fe-O2 bond by nearby residues in heme pocket: Observation of vFe-O2 Raman bands for oxymyoglobin mutants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 7845– 7846 (1996).
Schoenborn, B. P., Watson, H. C. & Kendrew, J. C. Binding of xenon to sperm whale myoglobin. Nature 207, 28–30 ( 1965).
Elber, R. & Karplus, M. Enhanced sampling in molecular-dynamics: use of the time-dependent Hartree approximation for a simulation of carbon-monoxide diffusion through myoglobin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 9161–9175 (1990).
Frauenfelder, H., Parak, F. & Young, R. D. Conformational substates in proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 17, 451– 479 (1988).
Nienhaus, G. U. & Young, R. D. Protein dynamics. Encyclopedia Appl. Phys. 15, 163– 184 (1996).
Alben, J. O. et al. Infrared spectroscopy of photodissociated carboxymyoglobin at low temperatures. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 79, 3744–3748 (1982).
Nienhaus, G. U., Mourant, J. R., Chu, K. & Frauenfelder, H. Ligand binding to heme proteins: the effect of light on ligand binding in myoglobin. Biochemistry 33, 13413–13430 (1994).
Springer, B. A. & Sligar, S. G. High-level expression of sperm whale myoglobin in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 84, 8961–8965 (1987).
Bailey, S. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 ( 1994).
Brünger, A. T. X-PLOR Version 3.1. (Yale Univ. Press, New Haven, CT, 1992 ).
Read, R. J. Improved Fourier coefficients for maps using phases from partial structures with errors. Acta Crystallogr. A 42, 140 –149 (1986).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. S. Olson for providing the L29W plasmid, K. Nienhaus for the sample preparation, and E. Haustein for expert assistance with the kinetic experiments. This work was supported by DFG Sonderforschungsbereich 533 and Graduiertenkolleg 328, Stiftung Volkswagenwerk and the University of Ulm.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ostermann, A., Waschipky, R., Parak, F. et al. Ligand binding and conformational motions in myoglobin. Nature 404, 205–208 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35004622
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35004622
This article is cited by
-
Experimental demonstration of the novel “van-Hove integral method (vHI)” for measuring diffusive dynamics by elastic neutron scattering
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
A Minireview on Temperature Dependent Protein Conformational Sampling
The Protein Journal (2021)
-
The Impact of Electron Correlation on Describing QM/MM Interactions in the Attendant Molecular Dynamics Simulations of CO in Myoglobin
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
A Quantitative Comparison of the Counting Significance of van Hove Integral Spectroscopy and Quasielastic Neutron Scattering
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Structure and energy based quantitative missense variant effect analysis provides insights into drug resistance mechanisms of anaplastic lymphoma kinase mutations
Scientific Reports (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.