Abstract
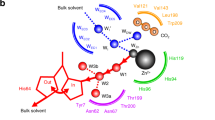
The X-ray crystal structure of the subtilisin-type enzyme proteinase K at 1.5 Å resolution1 shows that is has two binding sites for Ca2+. Scatchard analysis2 indicates that one Ca2+ binds tightly, with pK 7.6 × 10−8 M−1, and the other only weakly. Although Ca2+ is not directly involved in the catalytic mechanism and is 16.6 Å away from the α-carbon atoms of the catalytic triad Asp 39-His 69-Ser 224, the activity of proteinase K towards the synthetic substrate succinyl-Ala-Ala-Ala-p-nitroanilide drops slowly to ∼20% of its original value when it is depleted of Ca2+. This is not due to autolysis of the enzyme2. The X-ray crystal structure of Ca2+-free proteinase K shows that removal of Ca2+ from the tight binding site triggers a concerted domino-like movement of five peripheral loops and of two α-helices. At a distance of 25 Å from this calcium-binding site, the geometry of both the secondary substrate binding site and of the catalytic triad is affected by this movement thereby reducing the activity of the enzyme.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Betzel, C., Pal, G. P. & Saenger, W. Eur. J. Biochem. 178, 155–171 (1988).
Bajorath, J., Hinrichs, W. & Saenger, W. Eur. J. Biochem. 176, 441–447 (1988).
Ebeling, W. et al. Eur. J. Biochem. 47, 91–97 (1974).
Kraus, E., Kiltz, H. H. & Femfert, U. E. Hoppe-Seyler's Z. physiol. Chem. 357, 233–237 (1976).
Betzel, C., Pal, G. P., Struck, M., Jany, K. D. & Saenger, W. FEBS Lett. 197, 105–110 (1986).
Pal, G. P., Saenger, W., Bellemann, M., Wilson, K. S. & Betzel, C. Proteins 4, 157–164 (1988).
Voordouw, G., Mils, C. & Roche, R. S. Biochemistry 15, 3716–3723 (1977).
Birnbaum, E. R., Abbott, F., Gomez, J. E. & Darnoll, P. W. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 179, 469–476 (1977).
Frömmel, C. & Höhne, W. Biochim. biophys. Acta 670, 25–31 (1981).
Wells, J. A. & Estell, D. A. Trends biochem. Sci. 13, 291–295 (1988).
Bott, R. et al. J. biol. Chem. 263, 7895–7906 (1988).
Jones, T. A. J. appl. Crystallogr. 11, 268–272 (1978).
Hendrickson, W. A. & Konnert, J. H. in Biomolecular Structure, Function, Conformation and Evolution Vol. 1 (ed. Srinivasan, R.) 43–57 (Pergamon, Oxford, 1981).
Lesk, A. M. & Hardmann, K. D. Science 216, 539–540 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bajorath, J., Raghunathan, S., Hinrichs, W. et al. Long-range structural changes in proteinase K triggered by calcium ion removal. Nature 337, 481–484 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/337481a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/337481a0
This article is cited by
-
High-resolution crystal structures of a “half sandwich”-type Ru(II) coordination compound bound to hen egg-white lysozyme and proteinase K
JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry (2020)
-
A Simple and Affordable Method of DNA Extraction from Fish Scales for Polymerase Chain Reaction
Biochemical Genetics (2013)
-
The effect of calciums on molecular motions of proteinase K
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2011)
-
Unusual clustering of carboxyl side chains in the core of iron-free ribonucleotide reductase
Nature (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.