Abstract
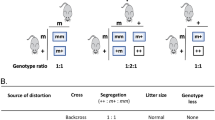
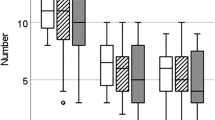
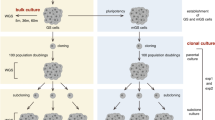
The T region, located on chromosome 17 in the mouse, is a complex genetic locus which includes a series of recessive mutations, tn (refs 1, 2). These mutations include several alleles (also referred to as t-haplotypes2) which are embryonic lethals (tL). An additional phenotypic expression of the recessive lethal mutations is a distorted transmission of the t allele by the heterozygous male parent. Most T/tL and +/tL males transmit the recessive mutation to over 50% of their offspring. Two conditions are known to modify significantly the transmission frequency of some tL alleles: the length of time between insemination and fertilisation3–5 and the genetic background of the female6. The present studies were undertaken to determine if the distorted transmission frequency of one of the lethal alleles, t6, could be reproduced in vitro. The data show that the in vitro transmission frequency of the t6 mutation is non-mendelian and is not significantly different from the frequency of transmission of this mutation following in vivo delayed matings. The in vitro frequency is, however, significantly lower than the normal mating frequency and does not vary as a function of incubation time. These data suggest that the observed delayed and normal mating frequency differences result from time-dependent interactions between the t6-bearing spermatozoon and the female reproductive tract.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, D. Cell 6, 441–454 (1975).
Sherman, M. I. & Wudl, L. R. in Concepts in Mammalian Embryogenesis (ed. Sherman, M. I.) 136–234 (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1977).
Braden, A. W. H. Nature 181, 786–787 (1958).
Yanagisawa, K., Dunn, L. C. & Bennett, D. Genetics 46, 1635–1644 (1961).
Braden, A. W. H. in Proc. Int. Symp. on the Genetics of the Spermatozoon (eds Beatty, R. A. & Gluecksohn-Waelsch, S.) 289–305 (Bogtrykkeriet Forum, Copenhagen, 1972).
Braden, A. W. H. & Weiler, H. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 17, 921–934 (1964).
Hoppe, P. C. & Pitts, S. Biol. Reprod. 8, 420–426 (1973).
Whitten, W. K. Adv. Biosci. 6, 129–139 (1971).
Spindle, A. I. & Pedersen, R. A. J. exp. Zool. 186, 305–318 (1973).
Erickson, R. P. & Pedersen, R. A. J. exp. Zool. 193, 377–384 (1975).
Wudl, L. R., Sherman, M. I. & Hillman, N. Nature 270, 137–140 (1977).
Wudl, L. R. & Sherman, M. I. J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 48, 127–151 (1978).
Whitten, W. K. & Biggers, J. D. J. Reprod. Fert. 17, 399–401 (1968).
Whittingham, D. G. in The Early Development of Mammals (eds Balls, M. & Wild, A. E.) 1–24 (Cambridge University Press, London, 1975).
Braden, A. W. H. & Austin, C. R. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 7, 552–565 (1954).
Erickson, R. P. Nature new Biol. 243, 210–212 (1973).
Nadijcka, M. & Hillman, N. J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 33, 697–713 (1975).
Hoppe, P. C. & Whitten, W. K. J. exp. Zool. 188, 133–136 (1974).
Fraser, L. R. & Drury, L. M. J. exp. Zool. 197, 13–20 (1976).
Olds-Clarke, P. & Carey, J. E. J. exp. Zool. 206, 323–332 (1978).
Yanagisawa, K. Jap. J. Genet. 40, 87–92 (1965).
Yanagisawa, K., Pollard, D. R., Bennett, D., Dunn, L. C. & Boyse, E. A. Immunogenetics 1, 91–96 (1974).
Gluecksohn-Waelsch, S. & Erickson, R. P. Curr. Topics dev. Biol. 5, 281–316 (1970).
Gluecksohn-Waelsch, S. & Erickson, R. P. in Proc. Symp. Immunogenetics of the H-2 System (eds Lengerova, A. & Vojteskova, M.) 120–122 (Karger, Basle, 1971).
Edwards, R. G. & Gates, A. H. J. Endocr. 18, 292–304 (1959).
Abramczuk, J., Solter, D. & Koprowski, H. Devl Biol. 61, 378–383 (1977).
Fraser, L. R. & Drury, L. M. Biol. Reprod. 13, 513–518 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGrath, J., Hillman, N. The in vitro transmission frequency of the t6 allele. Nature 283, 479–481 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/283479a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/283479a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.