Abstract
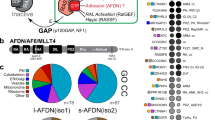
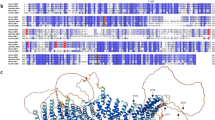
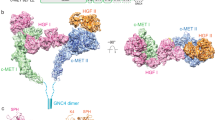
THE proteins Gab1 and the related DOS (for 'daughter of seven-less') each bind to substrates of tyrosine kinases like Grb2 or Corkscrew, and act in signalling pathways downstream of tyrosine kinase receptors1–3. Here we show that Gab1 interacts directly with the c-met-encoded receptor tyrosine kinase but not with a number of other tyrosine kinases from different subfamilies. A newly identified proline-rich domain of Gab1 is responsible for the binding of this protein to the tyrosine-phosphorylated bidentate docking site4,5 in c-Met. Expression of Gab1 in epithelial cells is sufficient to induce the c-Met-specific activities6–9, including branching morphogenesis. Thus we have discovered a new phosphotyrosine interaction domain in Gab1 and shown that Gab1 is the substrate of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase that mediates epithelial morphogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holgado Madruga, M., Emlet, D. R., Moscatello, D. K., Godwin, A. K. & Wong, A. J. Nature 379 560–564 (1996).
Herbst, R. et al. Cell 85, 899–909 (1996).
Raabe, T. et al. Cell 85, 911–920 (1996).
Ponzetto, C. et al. Cell 77, 261–271 (1994).
Weidner, K. M., Sachs, M., Riethmacher, D. & Birchmeier, W. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 2597–2601 (1995).
Stoker, M., Gherardi, E., Perryman, M. & Gray, J. Nature 327, 239–242 (1987).
Weidner, K. M., Sachs, M. & Birchmeier, W. J. Cell Biol. 121, 145–154 (1993).
Nakamura, T. et al. Nature 342, 440–443 (1989).
Montesano, R., Matsumoto, K., Nakamura, T. & Orci, L. Cell 67, 901–908 (1991).
O'Neill, T. J., Craparo, A. & Gustafson, T. A. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 6433–6442 (1994).
Sun, X. J. et al. Nature 377, 173–177 (1995).
van der Geer, P., Hunter, L. & Lindberg, R. A. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 10, 251–337 (1994).
Zhu, H., Naujokas, M. A., Fixman, E. D., Totossian, K. & Park, M. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 29943–29948 (1994).
Gonzatti Haces, M. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 21–25 (1988).
Sonnenberg, E., Meyer, D., Weidner, K. M. & Birchmeier, C. J. Cell Biol. 123, 223–235 (1993).
Schmidt, C. et al. Nature 373, 699–702 (1995).
Uehara, Y. et al. Nature 373, 702–705 (1995).
Brinkmann, V. et al. J. Cell Biol. 131, 215–226 (1995).
Sachs, M. et al. J. Cell Biol. 133, 1095–1107 (1996).
Lemmon, M. A., Ferguson, K. M. & Schlessinger, J. Cell 85, 621–624 (1996).
Waksman, G., Shoelson, S. E., Pant, N., Cowburn, D. & Kuriyan, J. Cell 22, 779–790 (1993).
Eck, M. J., Dhepaganon, S., Trub, T., Nolte, R. T. & Shoelson, S. E. Cell 85, 695–705 (1996).
Zhou, M. M. et al. Nature 378, 584–592 (1995).
Behrens, J. et al. Nature 382, 638–642 (1996).
Miller, J. H. Experiments in Molecular Genetics (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weidner, K., Di Cesare, S., Sachs, M. et al. Interaction between Gab1 and the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase is responsible for epithelial morphogenesis. Nature 384, 173–176 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/384173a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/384173a0
This article is cited by
-
Dysregulated Gab1 signalling in triple negative breast cancer
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
Photodynamic reactions using high-intensity red LED promotes gingival wound healing by ROS induction
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Bacterial inhibition of Fas-mediated killing promotes neuroinvasion and persistence
Nature (2022)
-
Metformin reduces HGF-induced resistance to alectinib via the inhibition of Gab1
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
The AKT-independent MET–V-ATPase–MTOR axis suppresses liver cancer vaccination
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.