Abstract
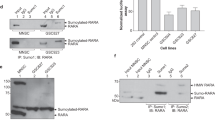
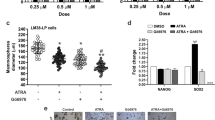
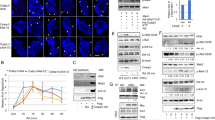
Downregulation of the cellular retinol-binding protein-I (CRBP-I) occurs in breast and other human cancers, but its significance is not well understood. Recently, we showed that restoration of CRBP-I expression in transformed MTSV1-7 breast epithelial cells increased retinoic receptor activity, inhibited anoikis, promoted acinar differentiation and inhibited tumorigenicity, suggesting that CRBP-I suppresses tumor progression. However, the mechanism underlying these effects of CRBP-I was not elucidated. Here we demonstrate, using genetic and pharmacological approaches, that CRBP-I inhibits, in a retinoic acid receptor-dependent manner, the PI3K/Akt survival pathway. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt was necessary and sufficient to explain the antitumor effects of CRBP-I and was mediated by decreased p85 regulatory and p110 catalytic subunit heterodimerization. We present evidence consistent with the idea that this effect is due to CRBP-I inhibition of p85 phosphorylation at Y688. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of PI3K regulation at the level of p85–p110 heterodimerization. These findings lead us to hypothesize that CRBP-I downregulation in cancer promotes tumor progression through inhibition of retinoic acid receptor activity and derepression of PI3K/Akt signaling via a novel mechanism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta JJ, Munoz RM, Gonzalez L, Subtil-Rodriguez A, Dominguez-Caceres MA, Garcia-Martinez JM, Calcabrini A, Lazaro-Trueba I and Martin-Perez J . (2003). Mol. Endocrinol., 17, 2268–2282.
Apfel C, Bauer F, Crettaz M, Forni L, Kamber M, Kaufmann F, LeMotte P, Pirson W and Klaus M . (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 7129–7133.
Bartek J, Bartkova J, Kyprianou N, Lalani EN, Staskova Z, Shearer M, Chang S and Taylor-Papadimitriou J . (1991). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 88, 3520–3524.
Biscardi JS, Ishizawar RC, Silva CM and Parsons SJ . (2000). Breast Cancer Res., 2, 203–210.
Brazil DP, Yang ZZ and Hemmings BA . (2004). Trends Biochem. Sci., 29, 233–242.
Cantley LC . (2002). Science, 296, 1655–1657.
Cantley LC and Neel BG . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 4240–4245.
Chan TO, Rodeck U, Chan AM, Kimmelman AC, Rittenhouse SE, Panayotou G and Tsichlis PN . (2002). Cancer Cell, 1, 181–191.
Cuevas BD, Lu Y, Mao M, Zhang J, LaPushin R, Siminovitch K and Mills GB . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 27455–27461.
Debnath J, Mills KR, Collins NL, Reginato MJ, Muthuswamy SK and Brugge JS . (2002). Cell, 111, 29–40.
Debnath J, Walker SJ and Brugge JS . (2003). J. Cell Biol., 163, 315–326.
del Rincon SV, Rousseau C, Samanta R and Miller Jr WH . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 3353–3360.
Dirami G, Massaro GD, Clerch LB, Ryan US, Reczek PR and Massaro D . (2004). Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol., 286, L249–L256.
Esteller M, Guo M, Moreno V, Peinado MA, Capella G, Galm O, Baylin SB and Herman JG . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 5902–5905.
Farias EF, Ong DE, Ghyselink NB, Nakajo S, Kuppumbatt YS and Mira-y-Lopez R . (2005). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 97, in press.
Frisch SM and Francis H . (1994). J. Cell Biol., 124, 619–626.
Ghyselinck NB, Bavik C, Sapin V, Mark M, Bonnier D, Hindelang C, Dierich A, Nilsson CB, Hakansson H, Sauvant P, Azais-Braesco V, Frasson M, Picaud S and Chambon P . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 4903–4914.
Jimenez C, Hernandez C, Pimentel B and Carrera AC . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 41556–41562.
Kuppumbatti YS, Bleiweiss IJ, Mandeli JP, Waxman S and Mira-y-Lopez R . (2000). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 92, 475–480.
Kuppumbatti YS, Rexer B, Nakajo S, Nakaya K and Mira-y-Lopez R . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 7413–7419.
Kurlandsky SB, Gamble MV, Ramakrishnan R and Blaner WS . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 17850–17857.
Lango M, Wentzel AL, Song JI, Xi S, Johnson DE, Lamph WW, Miller L and Grandis JR . (2003). Clin. Cancer Res., 9, 4205–4213.
Liu H, Radisky DC, Wang F and Bissell MJ . (2004). J. Cell Biol., 164, 603–612.
Mangelsdorf DJ . (1994). Nutr. Rev., 52, S32–S44.
Mira-y-Lopez R, Zheng WL, Kuppumbatti YS, Rexer B, Jing Y and Ong DE . (2000). J. Cell Physiol., 185, 302–309.
Muthuswamy SK, Li D, Lelievre S, Bissell MJ and Brugge JS . (2001). Nat. Cell Biol., 3, 785–792.
Napoli JL . (1999). Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1440, 139–162.
Neve RM, Holbro T and Hynes NE . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 4567–4576.
Nguyen KT, Wang WJ, Chan JL and Wang LH . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 5385–5397.
Nilsson A, Troen G, Petersen LB, Reppe S, Norum KR and Blomhoff R . (1997). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 29, 381–389.
Seewaldt VL, Johnson BS, Parker MB, Collins SJ and Swisshelm K . (1995). Cell Growth Differ., 6, 1077–1088.
Singh B, Reddy PG, Goberdhan A, Walsh C, Dao S, Ngai I, Chou TC, P OC, Levine AJ, Rao PH and Stoffel A . (2002). Genes Dev., 16, 984–993.
Torchia J, Glass C and Rosenfeld MG . (1998). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 10, 373–383.
Wang F, Hansen RK, Radisky D, Yoneda T, Barcellos-Hoff MH, Petersen OW, Turley EA and Bissell MJ . (2002). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 94, 1494–1503.
Wang F, Weaver VM, Petersen OW, Larabell CA, Dedhar S, Briand P, Lupu R and Bissell MJ . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 14821–14826.
Weaver VM, Petersen OW, Wang F, Larabell CA, Briand P, Damsky C and Bissell MJ . (1997). J. Cell Biol., 137, 231–245.
Woods Ignatoski KM, Livant DL, Markwart S, Grewal NK and Ethier SP . (2003). Mol. Cancer Res., 1, 551–560.
Yu Y and Alwine JC . (2002). J. Virol., 76, 3731–3738.
Zhao JJ, Gjoerup OV, Subramanian RR, Cheng Y, Chen W, Roberts TM and Hahn WC . (2003). Cancer Cell, 3, 483–495.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs P Chambon (CRBP-I null mice and pSG5.CRBP-I), J Taylor-Papadimitriou (MTSV1-7 cells), S Nakajo (CRBP-I peptide antibody), M Klaus (Ro 41-5253), Y Jing (T47D clone stably expressing TetR), R Krauss (pBabePuro-SV40 LT), L-H Wang (constitutively active p110), Gordon Mills (p85Y688D), Jim Manfredi (CD20) for reagent gifts, S Bertran for skillful technical assistance, and Drs L Ossowski and J Aguirre-Ghiso for helpful discussions. This work was supported by NCI Grant R01 CA54273 to RML, the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation, The Norman and Rosita Winston Foundation, The Chemotherapy Foundation, and the NCI shared resources Grant R24 CA88302 to MSSM's Mouse Genetics Shared Research Facility. RML is an SWCRF investigator.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farias, E., Marzan, C. & Mira-y-Lopez, R. Cellular retinol-binding protein-I inhibits PI3K/Akt signaling through a retinoic acid receptor-dependent mechanism that regulates p85–p110 heterodimerization. Oncogene 24, 1598–1606 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208347
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208347
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cellular retinol-binding protein 1: a therapeutic and diagnostic tumor marker
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
Cellular retinol binding protein 1 transfection reduces proliferation and AKT-related gene expression in H460 non-small lung cancer cells
Molecular Biology Reports (2020)
-
C-SH2 point mutation converts p85β regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase to an anti-aging gene
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Activation of Akt pathway by transcription-independent mechanisms of retinoic acid promotes survival and invasion in lung cancer cells
Molecular Cancer (2013)
-
Reversal by RARα agonist Am580 of c-Myc-induced imbalance in RARα/RARγ expression during MMTV-Myc tumorigenesis
Breast Cancer Research (2012)