Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the ability of designer eggs enriched in vitamin E, lutein, selenium (Se) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) to deliver micronutrients to the human in a palatable and visually acceptable form.
Design: Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, two treatment groups balanced for sex and age.
Setting: Department of Biochemistry and Nutrition, SAC, Scotland.
Subjects: Forty healthy adult volunteers completed the study. Volunteers were recruited among staff of the Scottish Agricultural College
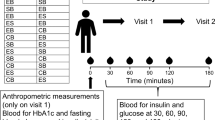
Interventions: Volunteers consumed, for 8 weeks, either a designer egg or a normal table egg per day. Fasting blood samples were taken before and at the end of the study.
Results: Consumption of designer eggs enriched in vitamin E, lutein, Se and DHA significantly increased the levels of α-tocopherol, lutein and DHA in plasma as compared to the changes found after consumption of normal table eggs, with the largest increases found in plasma lutein (1.88-fold increase). The proportion of DHA was increased in all the main lipid classes of the plasma including triacylglycerol (2.3-fold), free fatty acids (1.6-fold), cholesteryl ester (1.4-fold) and phospholipid (1.3-fold). Egg consumption did not change Se concentration in plasma, blood pressure, total plasma lipid concentrations or the concentrations of total cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol in plasma.
Conclusion: Consumption of designer eggs enriched in vitamin E, lutein, DHA and Se as part of normal diet for 8 weeks effectively increased the blood levels of α-tocopherol, lutein and DHA.
Sponsorship: Scottish Office Agriculture, Environment, and Fisheries Department.
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2000) 54, 298–305
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor: PF Surai.
Contributors: PFS was the chief organiser of the study, and vitamins E and A and peroxidation analyses. Main writer of the paper. AMacP was responsible for recruitment of volunteers, ethical approval, organization of blood pressure measurement, blood sampling, cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol analyses and statistical analyses. BKS carried out fatty acid analysis and data analyses and was involved in discussion. NHCS was responsible for chicken diet formulation, egg production and poultry husbandry and was involved in data analyses and discussion.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surai, P., MacPherson, A., Speake, B. et al. Designer egg evaluation in a controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 298–305 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600939
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600939
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Plasma mineral status after a six-month intervention providing one egg per day to young Malawian children: a randomized controlled trial
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Biomarker of food intake for assessing the consumption of dairy and egg products
Genes & Nutrition (2018)
-
Effects of supplementing n-3 fatty acid enriched eggs and walnuts on cardiovascular disease risk markers in healthy free-living lacto-ovo-vegetarians: a randomized, crossover, free-living intervention study
Nutrition Journal (2014)
-
Designer foods and their benefits: A review
Journal of Food Science and Technology (2013)
-
High levels of liver antioxidants are associated with life-history strategies characteristic of slow growth and high survival rates in birds
Journal of Comparative Physiology B (2012)