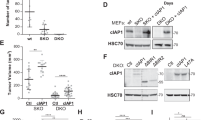
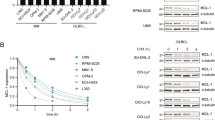
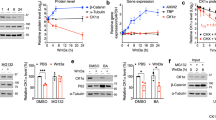
Abstract
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) is the major mediator of interleukin-6 (IL-6) family cytokines. In addition, Stat3 is known to be involved in the pathophysiology of many malignancies. Here, we show that the cis-trans peptidyl-prolyl isomerase cyclophilin (Cyp) B specifically interacts with Stat3, whereas the highly related CypA does not. CypB knockdown inhibited the IL-6-induced transactivation potential but not the tyrosine phosphorylation of Stat3. Binding of CypB to Stat3 target promoters and alteration of the intranuclear localization of Stat3 on CypB depletion suggested a nuclear function of Stat3/CypB interaction. By contrast, CypA knockdown inhibited Stat3 IL-6-induced tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear translocation. The Cyp inhibitor cyclosporine A (CsA) caused similar effects. However, Stat1 activation in response to IL-6 or interferon-γ was not affected by Cyp silencing or CsA treatment. As a result, Cyp knockdown shifted IL-6 signaling to a Stat1-dominated pathway. Furthermore, Cyp depletion or treatment with CsA induced apoptosis in IL-6-dependent multiple myeloma cells, whereas an IL-6-independent line was not affected. Thus, Cyps support the anti-apoptotic action of Stat3. Taken together, CypA and CypB both play pivotal roles, yet at different signaling levels, for Stat3 activation and function. These data also suggest a novel mechanism of CsA action.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allain F, Denys A, Spik G . (1996). Cyclophilin B mediates cyclosporin A incorporation in human blood T-lymphocytes through the specific binding of complexed drug to the cell surface. Biochem J 317 (Pt 2): 565–570.
Arevalo-Rodriguez M, Cardenas ME, Wu X, Hanes SD, Heitman J . (2000). Cyclophilin A and Ess1 interact with and regulate silencing by the Sin3-Rpd3 histone deacetylase. EMBO J 19: 3739–3749.
Bellido T, O’Brien CA, Roberson PK, Manolagas SC . (1998). Transcriptional activation of the p21(WAF1,CIP1,SDI1) gene by interleukin-6 type cytokines. A prerequisite for their pro- differentiating and anti-apoptotic effects on human osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem 273: 21137–21144.
Billich A, Winkler G, Aschauer H, Rot A, Peichl P . (1997). Presence of cyclophilin A in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med 185: 975–980.
Brazin KN, Mallis RJ, Fulton DB, Andreotti AH . (2002). Regulation of the tyrosine kinase Itk by the peptidyl-prolyl isomerase cyclophilin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 1899–1904.
Brocke-Heidrich K, Ge B, Cvijic H, Pfeifer G, Löffler D, Henze C et al. (2006). BCL3 is induced by IL-6 via Stat3 binding to intronic enhancer HS4 and represses its own transcription. Oncogene 25: 7297–7304.
Brocke-Heidrich K, Kretzschmar AK, Pfeifer G, Henze C, Löffler D, Koczan D et al. (2004). Interleukin-6-dependent gene expression profiles in multiple myeloma INA-6 cells reveal a Bcl-2 family-independent survival pathway closely associated with Stat3 activation. Blood 103: 242–251.
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C et al. (1999). Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 98: 295–303.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R . (2002). A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 296: 550–553.
Bukrinsky MI . (2002). Cyclophilins: unexpected messengers in intercellular communications. Trends Immunol 23: 323–325.
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R et al. (1999). Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity 10: 105–115.
Choi KJ, Piao YJ, Lim MJ, Kim JH, Ha J, Choe W et al. (2007). Overexpressed cyclophilin A in cancer cells renders resistance to hypoxia- and cisplatin-induced cell death. Cancer Res 67: 3654–3662.
Cui Y, Mirkia K, Florence Fu YH, Zhu L, Yokoyama KK, Chiu R . (2002). Interaction of the retinoblastoma gene product, RB, with cyclophilin A negatively affects cyclosporin-inhibited NFAT signaling. J Cell Biochem 86: 630–641.
De Ceuninck F, Allain F, Caliez A, Spik G, Vanhoutte PM . (2003). High binding capacity of cyclophilin B to chondrocyte heparan sulfate proteoglycans and its release from the cell surface by matrix metalloproteinases: possible role as a proinflammatory mediator in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48: 2197–2206.
Fang F, Flegler AJ, Du P, Lin S, Clevenger CV . (2009). Expression of cyclophilin B is associated with malignant progression and regulation of genes implicated in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. Am J Pathol 174: 297–308.
Gerhartz C, Heesel B, Sasse J, Hemmann U, Landgraf C, Schneider-Mergener J et al. (1996). Differential activation of acute phase response factor/STAT3 and STAT1 via the cytoplasmic domain of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130. I. Definition of a novel phosphotyrosine motif mediating STAT1 activation. J Biol Chem 271: 12991–12998.
Hodge DR, Hurt EM, Farrar WL . (2005). The role of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cancer.
Howard BA, Furumai R, Campa MJ, Rabbani ZN, Vujaskovic Z, Wang XF et al. (2005). Stable RNA interference-mediated suppression of cyclophilin A diminishes non-small-cell lung tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res 65: 8853–8860.
Howard BA, Zheng Z, Campa MJ, Wang MZ, Sharma A, Haura E et al. (2004). Translating biomarkers into clinical practice: prognostic implications of cyclophilin A and macrophage migratory inhibitory factor identified from protein expression profiles in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 46: 313–323.
Ihling C, Berger K, Hofliger MM, Fuhrer D, Beck-Sickinger AG, Sinz A . (2003). Nano-high-performance liquid chromatography in combination with nano-electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion-cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry for proteome analysis. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 17: 1240–1246.
Jensen O, Shevchenko A, Mann M . (1997) In: Creighton TE (ed). Protein Structure, A Practical Approach. Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, pp 48.
Kitahara K, Kawai S . (2007). Cyclosporine and tacrolimus for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 19: 238–245.
Kofron JL, Kuzmic P, Kishore V, Colon-Bonilla E, Rich DH . (1991). Determination of kinetic constants for peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerases by an improved spectrophotometric assay. Biochemistry 30: 6127–6134.
Kretzschmar AK, Dinger MC, Henze C, Brocke-Heidrich K, Horn F . (2004). Analysis of Stat3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) dimerization by fluorescence resonance energy transfer in living cells. Biochem J 377: 289–297.
Leverson JD, Ness SA . (1998). Point mutations in v-Myb disrupt a cyclophilin-catalyzed negative regulatory mechanism. Mol Cell 1: 203–211.
Löffler D, Brocke-Heidrich K, Pfeifer G, Stocsits C, Hackermüller J, Kretzschmar AK et al. (2007). Interleukin-6-dependent survival of multiple myeloma cells involves the Stat3-mediated induction of microRNA-21 through a highly conserved enhancer. Blood.
Lufei C, Koh TH, Uchida T, Cao X . (2007). Pin1 is required for the Ser727 phosphorylation-dependent Stat3 activity. Oncogene 26: 7656–7664.
Lütticken C, Wegenka UM, Yuan J, Buschmann J, Schindler C, Ziemiecki A et al. (1994). Association of transcription factor APRF and protein kinase JAK1 with the IL-6 signal transducer gp130. Science 263: 89–92.
Mamane Y, Sharma S, Petropoulos L, Lin R, Hiscott J . (2000). Posttranslational regulation of IRF-4 activity by the immunophilin FKBP52. Immunity 12: 129–140.
Mariller C, Allain F, Kouach M, Spik G . (1996). Evidence that human milk isolated cyclophilin B corresponds to a truncated form. Biochim Biophys Acta 1293: 31–38.
Obata Y, Yamamoto K, Miyazaki M, Shimotohno K, Kohno S, Matsuyama T . (2005). Role of cyclophilin B in activation of interferon regulatory factor-3. J Biol Chem 280: 18355–18360.
Peters M, Blinn G, Solem F, Fischer M, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Rose-John S . (1998). in vivo and in vitro activities of the gp130-stimulating designer cytokine Hyper-IL-6. J Immunol 161: 3575–3581.
Podar K, Tai YT, Cole CE, Hideshima T, Sattler M, Hamblin A et al. (2003). Essential role of caveolae in interleukin-6- and insulin-like growth factor I-triggered Akt-1-mediated survival of multiple myeloma cells. J Biol Chem 278: 5794–5801.
Puthier D, Thabard W, Rapp M, Etrillard M, Harousseau J, Bataille R et al. (2001). Interferon alpha extends the survival of human myeloma cells through an upregulation of the Mcl-1 anti-apoptotic molecule. Br J Haematol 112: 358–363.
Rawat R, Rainey GJ, Thompson CD, Frazier-Jessen MR, Brown RT, Nordan RP . (2000). Constitutive activation of STAT3 is associated with the acquisition of an interleukin 6-independent phenotype by murine plasmacytomas and hybridomas. Blood 96: 3514–3521.
Rycyzyn MA, Clevenger CV . (2002). The intranuclear prolactin/cyclophilin B complex as a transcriptional inducer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 6790–6795.
Rycyzyn MA, Reilly SC, O’Malley K, Clevenger CV . (2000). Role of cyclophilin B in prolactin signal transduction and nuclear retrotranslocation. Mol Endocrinol 14: 1175–1186.
Ryo A, Suizu F, Yoshida Y, Perrem K, Liou YC, Wulf G et al. (2003). Regulation of NF-kappaB signaling by Pin1-dependent prolyl isomerization and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p65/RelA. Mol Cell 12: 1413–1426.
Schwarze MM, Hawley RG . (1995). Prevention of myeloma cell apoptosis by ectopic bcl-2 expression or interleukin 6-mediated up-regulation of bcl-xL. Cancer Res 55: 2262–2265.
Shen J, Person MD, Zhu J, Abbruzzese JL, Li D . (2004). Protein expression profiles in pancreatic adenocarcinoma compared with normal pancreatic tissue and tissue affected by pancreatitis as detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Cancer Res 64: 9018–9026.
Sherry B, Yarlett N, Strupp A, Cerami A . (1992). Identification of cyclophilin as a proinflammatory secretory product of lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 3511–3515.
Song J, Lu YC, Yokoyama K, Rossi J, Chiu R . (2004). Cyclophilin A is required for retinoic acid-induced neuronal differentiation in p19 cells. J Biol Chem 279: 24414–24419.
Syed F, Rycyzyn MA, Westgate L, Clevenger CV . (2003). A novel and functional interaction between cyclophilin A and prolactin receptor. Endocrine 20: 83–90.
Uittenbogaard A, Ying Y, Smart EJ . (1998). Characterization of a cytosolic heat-shock protein-caveolin chaperone complex. Involvement in cholesterol trafficking. J Biol Chem 273: 6525–6532.
Wang P, Heitman J . (2005). The cyclophilins. Genome Biol 6: 226.
Watashi K, Ishii N, Hijikata M, Inoue D, Murata T, Miyanari Y et al. (2005). Cyclophilin B is a functional regulator of hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase. Mol Cell 19: 111–122.
Wegenka UM, Buschmann J, Lütticken C, Heinrich PC, Horn F . (1993). Acute-phase response factor, a nuclear factor binding to acute-phase response elements, is rapidly activated by interleukin-6 at the posttranslational level. Mol Cell Biol 13: 276–288.
Yang Y, Lu N, Zhou J, Chen ZN, Zhu P . (2008). Cyclophilin A up-regulates MMP-9 expression and adhesion of monocytes/macrophages via CD147 signalling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47: 1299–1310.
Yuan J, Wegenka UM, Lütticken C, Buschmann J, Decker T, Schindler C et al. (1994). The signalling pathways of interleukin-6 and gamma interferon converge by the activation of different transcription factors which bind to common responsive DNA elements. Mol Cell Biol 14: 1657–1668.
Zacchi P, Gostissa M, Uchida T, Salvagno C, Avolio F, Volinia S et al. (2002). The prolyl isomerase Pin1 reveals a mechanism to control p53 functions after genotoxic insults. Nature 419: 853–857.
Zheng J, Koblinski JE, Dutson LV, Feeney YB, Clevenger CV . (2008). Prolyl isomerase cyclophilin A regulation of Janus-activated kinase 2 and the progression of human breast cancer. Cancer Res 68: 7769–7778.
Acknowledgements
We thank Hans-Georg Kräusslich, University Heidelberg, Germany, and Stefan Rose-John, University Kiel, Germany, for CypA vector and recombinant IL-6, respectively. INA-6 cells were kindly provided by Renate Burger and Martin Gramatzki, University Kiel, Germany. This work was supported by SFB610 (project C2) from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bauer, K., Kretzschmar, A., Cvijic, H. et al. Cyclophilins contribute to Stat3 signaling and survival of multiple myeloma cells. Oncogene 28, 2784–2795 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.142
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.142
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The effects of CypA on apoptosis: potential target for the treatment of diseases
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2024)
-
High-fat diet induced cyclophilin B enhances STAT3/lncRNA-PVT1 feedforward loop and promotes growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
CypB promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in endometrial carcinoma
BMC Cancer (2021)
-
Cyclophilin A Aggravates Collagen-Induced Arthritis via Promoting Classically Activated Macrophages
Inflammation (2017)
-
Proline isomerisation as a novel regulatory mechanism for p38MAPK activation and functions
Cell Death & Differentiation (2016)