Abstract
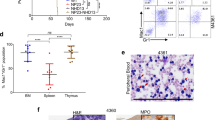
Early T lineage progenitors (ETPs) in the thymus are thought to develop from common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs) in the bone marrow (BM). We compared thymic ETPs to BM CLPs in mice and found that they differed in several respects. Thymic ETPs were not interleukin 7 (IL-7)–responsive and generated B lineage progeny with delayed kinetics, whereas BM CLPs were IL-7–responsive and rapidly generated B cells. ETPs sustained production of T lineage progeny for longer periods of time than BM CLPs. Analysis of Ikaros-deficient mice that exhibit ongoing thymopoiesis without B lymphopoeisis revealed near-normal frequencies of thymic ETPs, yet undetectable numbers of BM CLPs. We conclude that ETPs can develop via a CLP-independent pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
von Boehmer, H. & Fehling, H.J. Structure and function of the pre-T cell receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15, 433–452 (1997).
Foss, D.L., Donskoy, E. & Goldschneider, I. The importation of hematogenous precursors by the thymus is a gated phenomenon in normal adult mice. J. Exp. Med. 193, 365–374 (2001).
Donskoy, E. & Goldschneider, I. Thymocytopoiesis is maintained by blood-borne precursors throughout postnatal life. A study in parabiotic mice. J. Immunol. 148, 1604–1612 (1992).
Wu, L., Antica, M., Johnson, G.R., Scollay, R. & Shortman, K. Developmental potential of the earliest precursor cells from the adult mouse thymus. J. Exp. Med. 174, 1617–1627 (1991).
Matsuzaki, Y. et al. Characterization of c-Kit positive intrathymic stem cells that are restricted to lymphoid differentiation. J. Exp. Med. 178, 1283–1292 (1993).
Kondo, M., Weissman, I.L. & Akashi, K. Identification of clonogenic common lymphoid progenitors in mouse bone marrow. Cell 91, 661–672 (1997).
Izon, D. et al. A common pathway for dendritic cell and early B cell development. J. Immunol. 167, 1387–1392 (2001).
Kondo, M. et al. Cell-fate conversion of lymphoid-committed progenitors by instructive actions of cytokines. Nature 407, 383–386 (2000).
Katsura, Y. Redefinition of lymphoid progenitors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 127–132 (2002).
Shortman, K. & Wu, L. Early T lymphocyte progenitors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 29–47 (1996).
Godfrey, D.I., Zlotnik, A. & Suda, T. Phenotypic and functional characterization of c-Kit expression during intrathymic T cell development. J. Immunol. 149, 2281–2285 (1992).
Laky, K., Lefrancois, L., von Freeden-Jeffry, U., Murray, R. & Puddington, L. The role of IL-7 in thymic and extrathymic development of TCR γδ cells. J. Immunol. 161, 707–713 (1998).
Wu, L. et al. CD4 expressed on earliest T-lineage precursor cells in the adult murine thymus. Nature 349, 71–74 (1991).
Miller, J.P. et al. The earliest step in B lineage differentiation from common lymphoid progenitors is critically dependent upon interleukin 7. J. Exp. Med. 196, 705–711 (2002).
Ikuta, K. & Weissman, I.L. Evidence that hematopoietic stem cells express mouse c-Kit but do not depend on steel factor for their generation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 1502–1506 (1992).
Adolfsson, J. et al. Upregulation of Flt3 expression within the bone marrow Lin− Sca1+ c-kit+ stem cell compartment is accompanied by loss of self-renewal capacity. Immunity 15, 659–669 (2001).
Igarashi, H., Gregory, S., Yokota, T., Sakaguchi, N. & Kincade, P. Transcription from the RAG1 locus marks the earliest lymphocyte progenitors in bone marrow. Immunity 17, 117–130 (2002).
Christensen, J.L. & Weissman, I.L. Flk-2 is a marker in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation: a simple method to isolate long-term stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 14541–14546 (2001).
Rolink, A. et al. A subpopulation of B220+ cells in murine bone marrow does not express CD19 and contains natural killer cell progenitors. J. Exp. Med. 183, 187–194 (1996).
Tudor, K.S., Payne, K.J., Yamashita, Y. & Kincade, P.W. Functional assessment of precursors from murine bone marrow suggests a sequence of early B lineage differentiation events. Immunity 12, 335–345 (2000).
Li, Y.S., Wasserman, R., Hayakawa, K. & Hardy, R.R. Identification of the earliest B lineage stage in mouse bone marrow. Immunity 5, 527–535 (1996).
Foss, D.L., Donskoy, E. & Goldschneider, I. Functional demonstration of intrathymic binding sites and microvascular gates for prothymocytes in irradiated mice. Int. Immunol. 14, 331–338 (2002).
King, A.G., Kondo, M., Scherer, D.C. & Weissman, I.L. Lineage infidelity in myeloid cells with TCR gene rearrangement: a latent developmental potential of proT cells revealed by ectopic cytokine receptor signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 4508–4513 (2002).
Nichogiannopoulou, A., Trevisan, M., Neben, S., Friedrich, C. & Georgopoulos, K. Defects in hemopoietic stem cell activity in Ikaros mutant mice. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1201–1214 (1999).
Akashi, K., Traver, D., Miyamoto, T. & Weissman, I.L. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature 404, 193–197 (2000).
Schlissel, M.S., Corcoran, L.M. & Baltimore, D. Virus-transformed pre-B cells show ordered activation but not inactivation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and transcription. J. Exp. Med. 173, 711–720 (1991).
Medina, K.L. et al. Identification of very early lymphoid precursors in bone marrow and their regulation by estrogen. Nat. Immunol. 2, 718–724 (2001).
Kronenberg, M., Siu, G., Hood, L.E. & Shastri, N. The molecular genetics of the T-cell antigen receptor and T-cell antigen recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 4, 529–591 (1986).
Godfrey, D.I., Kennedy, J., Suda, T. & Zlotnik, A. A developmental pathway involving four phenotypically and functionally distinct subsets of CD3−CD4−CD8− triple-negative adult mouse thymocytes defined by CD44 and CD25 expression. J. Immunol. 150, 4244–4252 (1993).
Winandy, S., Wu, L., Wang, J.H. & Georgopoulos, K. Pre-T cell receptor (TCR) and TCR-controlled checkpoints in T cell differentiation are set by Ikaros. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1039–1048 (1999).
Kurosawa, Y. et al. Identification of D segments of immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes and their rearrangement in T lymphocytes. Nature 290, 565–570 (1981).
Born, W., White, J., Kappler, J. & Marrack, P. Rearrangement of IgH genes in normal thymocyte development. J. Immunol. 140, 3228–3232 (1988).
Rodewald, H.R., Kretzschmar, K., Takeda, S., Hohl, C. & Dessing, M. Identification of pro-thymocytes in murine fetal blood: T lineage commitment can precede thymus colonization. EMBO J. 13, 4229–4240 (1994).
Soloff, R.S., Wang, T.G., Lybarger, L., Dempsey, D. & Chervenak, R. Transcription of the TCR-β locus initiates in adult murine bone marrow. J. Immunol. 154, 3888–3901 (1995).
Gilbert, S.F. Developmental Biology (Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland, MA, 2000).
Allman, D., Punt, J.A., Izon, D.J., Aster, J.C. & Pear, W.S. An invitation to T and more. Notch signaling in lymphopoiesis. Cell 109 (Suppl.) 1–11 (2002).
Wang, J.H. et al. Selective defects in the development of the fetal and adult lymphoid system in mice with an Ikaros null mutation. Immunity 5, 537–549 (1996).
Sudo, T. et al. Expression and function of the interleukin 7 receptor in murine lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 9125–9129 (1993).
McKearn, J.P., McCubrey, J. & Fagg, B. Enrichment of hematopoietic precursor cells and cloning of multipotential B-lymphocyte precursors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 7414–7418 (1985).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Georgopoulos for Ikaros−/− mice and helpful discussions and W. Pear, M. Cancro and T. Laufer for reviewing this manuscript. We thank D. Fonseca for help with DNA sequencing and W. DeMuth, K. Rudd and R. C. Lindsley for expert technical assistance. We gratefully acknowledge the expert technical support in flow cytometry provided by the Abramson Cancer Center Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting Shared Resource and in particular the efforts of R. Schretzenmair and H. Pletcher. Supported by NIH grants AI52861, AG20818 and AI053284 (to D.A.) and grant number IRG-78-002-25 from the American Cancer Society as well as grants from the Concern Foundation and the McCabe Fund (to A.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allman, D., Sambandam, A., Kim, S. et al. Thymopoiesis independent of common lymphoid progenitors. Nat Immunol 4, 168–174 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni878
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni878
This article is cited by
-
IKAROS: from chromatin organization to transcriptional elongation control
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
TCF-1 promotes chromatin interactions across topologically associating domains in T cell progenitors
Nature Immunology (2022)
-
Leaving no one behind: tracing every human thymocyte by single-cell RNA-sequencing
Seminars in Immunopathology (2021)
-
Global dynamics of stage-specific transcription factor binding during thymocyte development
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Thymus Colonization: Who, How, How Many?
Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis (2018)