Abstract
Objective:
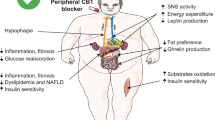
Studies in mice have suggested that endocannabinoid blockade using the cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) blocker rimonabant prevents obesity-induced hepatic steatosis.
Design and subjects:
To determine effects of rimonabant on liver fat in humans, we measured liver fat content by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in 37 subjects who used either a CB1 blocker rimonabant or placebo in a double-blind, randomized manner. This was retrospectively compared with a historical hypocaloric diet weight loss group (n=23).
Results:
Weight loss averaged 8.5±1.4 kg in the rimonabant, 1.7±1.0 kg in the placebo and 7.5±0.2 kg in the hypocaloric diet group (P<0.001, rimonabant vs placebo; NS, rimonabant vs hypocaloric diet). Liver fat decreased more in the rimonabant (5.9% (2.5–14.6%) vs 1.8% (0.9–3.5%), before vs after) than in the placebo group (6.8% (2.2–15.7%) vs 4.9% (1.6–7.8%), before vs after, P<0.05). The percentage change in body weight correlated closely with the percentage loss of liver fat (r=0.70, P>0.0001). The decreases in liver fat were comparable between the rimonabant and the young historical hypocaloric diet groups.
Conclusions:
We conclude that, unlike in mice, in humans rimonabant decreases liver fat in proportion to weight loss.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Younossi ZM, Stepanova M, Afendy M, Fang Y, Younossi Y, Mir H et al. Changes in the prevalence of the most common causes of chronic liver diseases in the United States from 1988 to 2008. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 9: 524–530.
Lewis JR, Mohanty SR . Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review and update. Dig Dis Sci 2010; 55: 560–578.
Yki-Järvinen H . Liver fat in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Dig Dis 2010; 28: 203–209.
Despres JP, Lemieux I . Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2006; 444: 881–887.
Di Marzo V, Bifulco M, De Petrocellis L . The endocannabinoid system and its therapeutic exploitation. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2004; 3: 771–784.
Ravinet TC, Delgorge C, Menet C, Arnone M, Soubrie P . CB1 cannabinoid receptor knockout in mice leads to leanness, resistance to diet-induced obesity and enhanced leptin sensitivity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2004; 28: 640–648.
Osei-Hyiaman D, Liu J, Zhou L, Godlewski G, Harvey-White J, Jeong WI et al. Hepatic CB1 receptor is required for development of diet-induced steatosis, dyslipidemia, and insulin and leptin resistance in mice. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 3160–3169.
Despres JP, Golay A, Sjöström L . Effects of rimonabant on metabolic risk factors in overweight patients with dyslipidemia. NewEngl J Med 2005; 353: 2121–2134.
Van Gaal LF, Rissanen AM, Scheen AJ, Ziegler O, Rossner S . Effects of the cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker rimonabant on weight reduction and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight patients: 1-year experience from the RIO-Europe study. Lancet 2005; 365: 1389–1397.
Pi-Sunyer FX, Aronne LJ, Heshmati HM, Devin J, Rosenstock J . Effect of rimonabant, a cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker, on weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight or obese patients: RIO-North America: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Assoc 2006; 295: 761–775.
Despres JP, Ross R, Boka G, Almeras N, Lemieux I . Effect of rimonabant on the high-triglyceride/low-HDL-cholesterol dyslipidemia, intraabdominal adiposity, and liver fat: the ADAGIO-Lipids trial. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2009; 29: 416–423.
Tiikkainen M, Bergholm R, Vehkavaara S, Rissanen A, Häkkinen AM, Tamminen M et al. Effects of identical weight loss on body composition and features of insulin resistance in obese women with high and low liver fat content. Diabetes 2003; 52: 701–707.
Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J . Metabolic syndrome--a new world-wide definition. A consensus statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med 2006; 23: 469–480.
Ryysy L, Häkkinen AM, Goto T, Vehkavaara S, Westerbacka J, Halavaara J et al. Hepatic fat content and insulin action on free fatty acids and glucose metabolism rather than insulin absorption are associated with insulin requirements during insulin therapy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 2000; 49: 749–758.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Larson-Meyer DE, Heilbronn LK, Redman LM, Newcomer BR, Frisard MI, Anton S et al. Effect of calorie restriction with or without exercise on insulin sensitivity, beta-cell function, fat cell size, and ectopic lipid in overweight subjects. Diabetes Care 2006; 29: 1337–1344.
Shah K, Stufflebam A, Hilton TN, Sinacore DR, Klein S, Villareal DT . Diet and exercise interventions reduce intrahepatic fat content and improve insulin sensitivity in obese older adults. Obesity 2009; 17: 2162–2168.
Szczepaniak LS, Babcock EE, Schick F, Dobbins RL, Garg A, Burns DK et al. Measurement of intracellular triglyceride stores by H spectroscopy: validation in vivo. Am J Physiol 1999; 276: E977–E989.
Gary-Bobo M, Elachouri G, Gallas JF, Janiak P, Marini P, Ravinet-Trillou C et al. Rimonabant reduces obesity-associated hepatic steatosis and features of metabolic syndrome in obese Zucker fa/fa rats. Hepatology 2007; 46: 122–129.
Hezode C, Zafrani ES, Roudot-Thoraval F, Costentin C, Hessami A, Bouvier-Alias M et al. Daily cannabis use: a novel risk factor of steatosis severity in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2008; 134: 432–439.
Engeli S, Bohnke J, Feldpausch M, Gorzelniak K, Janke J, Batkai S et al. Activation of the peripheral endocannabinoid system in human obesity. Diabetes 2005; 54: 2838–2843.
Bluher M, Engeli S, Kloting N, Berndt J, Fasshauer M, Batkai S et al. Dysregulation of the peripheral and adipose tissue endocannabinoid system in human abdominal obesity. Diabetes 2006; 55: 3053–3060.
Westerbacka J, Kotronen A, Fielding BA, Wahren J, Hodson L, Perttilä J et al. Splanchnic balance of free fatty acids, endocannabinoids, and lipids in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2010; 139: 1961–1971.
Kantartzis K, Thamer C, Peter A, Machann J, Schick F, Schraml C et al. High cardiorespiratory fitness is an independent predictor of the reduction in liver fat during a lifestyle intervention in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2009; 58: 1281–1288.
Kirk E, Reeds DN, Finck BN, Mayurranjan SM, Patterson BW, Klein S . Dietary fat and carbohydrates differentially alter insulin sensitivity during caloric restriction. Gastroenterology 2009; 136: 1552–1560.
Topol EJ, Bousser MG, Fox KA, Creager MA, Despres JP, Easton JD et al. Rimonabant for prevention of cardiovascular events (CRESCENDO): a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2010; 376: 517–523.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by research grants from the Academy of Finland, the Sigrid Juselius Foundation and the Novo Nordisk Foundation. This work is part of the project ‘Hepatic and adipose tissue functions in the metabolic syndrome’ (www.hepadip.org), which is supported by the European Commission as an Integrated Project under the 6th Framework Program (Contract LSHM-CT-2005–018734). We gratefully acknowledge Katja Sohlo and Pentti Pölönen for excellent technical assistance, and the volunteers for their help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergholm, R., Sevastianova, K., Santos, A. et al. CB1 blockade-induced weight loss over 48 weeks decreases liver fat in proportion to weight loss in humans. Int J Obes 37, 699–703 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.116
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.116
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effect of cannabis and subproducts on anthropometric measures: a systematic review and meta-analysis
International Journal of Obesity (2024)
-
Alpha-linolenic acid modulates systemic and adipose tissue-specific insulin sensitivity, inflammation, and the endocannabinoid system in dairy cows
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Circulating endocannabinoid levels in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus: a case–control study
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2022)
-
Endocannabinoid receptor blockade reduces alanine aminotransferase in polycystic ovary syndrome independent of weight loss
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2017)
-
Blockade of CB1 cannabinoid receptor alters gut microbiota and attenuates inflammation and diet-induced obesity
Scientific Reports (2017)