Abstract
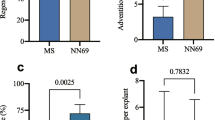
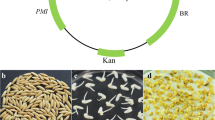
We developed an efficient method for in vitro selection of Medicago truncatula cv. Jemalong lines transformed with the nptII gene and subsequent confirmation of phenotype inheritance in these lines. For in vitro selection, the concentration of kanamycin inhibitory to embryogenic callus development and somatic embryo differentiation was identified by placing wounded leaves of non-transformed M. truncatula cv. Jemalong on Embryo Inducing Medium supplemented with 0, 85.8, 128.7, 171.6, 214.6, 257.5 and 343.3 µM of kanamycin. Differentiation of somatic embryos was inhibited with 171.6 µM of kanamycin but callus development was not altered. To confirm transgene inheritance, the kanamycin concentration to distinguish between resistant and non-resistant seedlings was identified by germinating non-transformed seeds of M. truncatula cv. Jemalong on 0.8% (w/v) water-agar plates containing 0, 171.6, 343.3, 514.9 and 686.6 µM of kanamycin. These concentrations did not impair seed germination since all the seedlings exhibited green cotyledons. The effect of kanamycin was only observed at 514.9 and 686.6 µM and on the first pair of leaves, which became white. Due to the high level of resistance to kanamycin of the seedlings the highest concentration is thought to be use to assure the selection efficiency. This optimised antibiotic selection scheme eliminates the regeneration of non-transformed escapes and discriminates between resistant and non-resistant seedlings, confirming the inheritance of the phenotype in transformed M. truncatula cv. Jemalong lines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AraÚjo SS, Duque ASLRA, Santos DMMF & Fevereiro MPS (2004) An efficient transformation method to regenerate a high number of transgenic plants using a new embryogenic line of Medicago truncatula cv. Jemalong. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 78: 123–131
Barker DG, Bianchi S, Blondon F, Datté Y, Duc G, Essad S, Flament P, Gallusci P, Génier G, Guy P, Muel X, Tourneur J, Dénarié J & Huguet T (1990) Medicago truncatula, a model plant for studying the molecular genetics of the Rhizobium-Legume symbiosis. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 8: 40–49
Chabaud M, Larsonneau C, Marmouget C & Huguet T (1996) Transformation of the barrel medic (Medicago truncatula Gaertn.) by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and regeneration via somatic embryogenesis of transgenics plants with the MtENOD12 nodulin promoter fused to the gus reporter gene. Plant Cell Rep. 15: 305–310
Christou P (1994) The biotechnology of crop legumes. Euphytica 74: 165–185
Cook DR (1999) Medicago truncatula - a model in the making! Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2: 301–304
d'Erfurth I, Cosson V, Eschstruch A, Lucas H, Kondorosi A & Ratet P (2003) Efficient transposition of the Tnt1 tobacco retrotransposon in the model legume Medicago truncatula. Plant J. 34: 95–106
Neves LO (2000) Regeneration and transformation of barrel medic (Medicago truncatula Gaertner. cv. Jemalong). PhD Dissertation, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal
Neves LO, Duque SRL, Almeida JS & Fevereiro PS (1999) Repetitive somatic embryogenesis in Medicago truncatula ssp. Narbonensis and M. truncatula Gaertn cv. Jemalong. Plant Cell Rep. 18: 398–405
Neves LO, Tomaz L & Fevereiro MPS (2001) Micropropagation of Medicago truncatula Gaertn. cv. Jemalong and Medicago truncatula ssp. Narbonensis. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 67: 81–84
Trinh TH, Ratet P, Kondorosi E, Durand P, Kamaté K, Bauer P & Kondorosi A (1998) Rapid and efficient transformation of diploid Medicago truncatula and Medicago sativa ssp. falcate lines improved in somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Rep. 17: 345–355
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duque, A.S.R.L.A., Sousa de Araújo, S., Santos, D.M.M.F.d. et al. Optimisation of a Selection Scheme using Kanamycin to Improve Transformation of Medicago truncatula cv. Jemalong. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 78, 277–280 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TICU.0000025646.98932.dc
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TICU.0000025646.98932.dc