Abstract
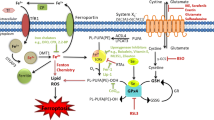
C-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 and 2 (JNK1/2) have been shown to be transiently activated and involved in neurotoxicity. We searched for possible upstream molecules, which are responsible for the regulation of hydrogen peroxide-(H2O2) induced JNK1/2 activation and JNK1/2-mediated apoptotic-like cell death in cultured rat cortical neurons. The results showed that JNK1/2 activation (monitored by anti-diphosphorylated JNK1/2 antibody) was largely prevented by elimination of extracellular Ca2+ or blockage of NMDA-receptors (NMDA-R), and was weakly but significantly decreased by blockage of L-type voltage-gated calcium channel (L-VGCC); furthermore, JNK1/2 activation was largely prevented by inhibition of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-II (CaMKII) and protein-tyrosine kinases (PTK). We also found that H2O2-induced apoptotic-like cell death was partially prevented by elimination of extracellular Ca2+, or by inhibition of NMDA-R, L-VGCC, PTK and CaMKII, respectively. The above results suggest that in H2O2-induced neurotoxicity, JNK1/2 activation is mainly mediated by NMDA-R and L-VGCC. Consequently, PTK and CaMKII are critical intermediaries in JNK1/2 activation and are mainly responsible for JNK1/2-mediated apoptotic-like cell death.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AKIYAMA, T., ISHIDA, J., NAKAGAWA, S., OGAWARA, H., WATANABE, S., ITOH, N., SHIBUYA, M. & FUKAMI, Y. (1987) Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. Journal of Biological Chemistry 262, 5592–5595.
ALMEIDA, A., BOLANOS, J. P. & MEDINA, J. M. (1999) Nitric oxide mediates glutamate-induced mitochondrial depolarization in rat cortical neurons. Brain Research 816, 580–586.
ATZORI, C., GHETTI, B., PIVA, R., SRINIVASAN, A. N., ZOLO, P., DELISLE, M. B., MIRRA, S. S. & MIGHELI, A. (2001) Activation of the JNK/p38 pathway occurs in diseases characterized by tau protein pathology and is related to tau phosphorylation but not to apoptosis. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 60, 1190–1197.
BEHL, C. & MOOSMANN, B. (2002) Oxidative nerve cell death in Alzheimer's disease and stroke: Antioxidants as neuroprotective compounds. Biological Chemistry 383, 521–536.
BENGZON, J., MOHAPEL, P., EKDAHL, C. T. & LINDVALL, O. (2002) Neuronal apoptosis after brief and prolonged seizures. Progress In Brain Research 135, 111–119.
BOST, F., MCKAY, R., DEAN, N. & MERCOLA, D. (1997) The JUN kinase/stress-activated protein kinase pathway is required for epidermal growth factor stimulation of growth of human A549 lung carcinoma cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry 272, 33422–33429.
CARMODY, R. J. & COTTER, T. G. (2001) Signalling apoptosis: A radical approach. Redox Report 6, 77–90.
CHANDRA, J., SAMALI, A. & ORRENIUS, S. (2000) Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free Radical Biology & Medicine 29, 323–333.
CHANG, L. & KARIN, M. (2001) Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410, 37–34
CHETKOVICH, D. M. & SWEATT, J. D. (1993) NMDA receptor activation increases cyclic AMP in area CA1 of the hippocampus via calcium/calmodulin stimulation of adenylyl cyclase. Journal of Neurochemistry 61, 1933–1942.
CHIJIWA, T., MISHIMA, A., HAGIWARA, M., SANO, M., HAYASHI, K., INOUE, T., NAITO, K., TOSHIOKA, T. & HIDAKA, H. (1990) Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry 265, 5267–5272.
CHOI, D. W. (1995) Calcium: Still center-stage in hypoxicischemic neuronal death. Trends In Neuroscience 18, 58–60.
COBB, M. H. (1999) MAP kinase pathways. Progress in Biophysics & Molecular Biology 71, 479–500.
COFFEY, E. T., HONGISTO, V., DICKENS, M., DAVIS, R. J. & COURTNEY, M. J. (2000) Dual roles for C-Jun N-terminal kinase in developmental and stress responses in cerebellar granule neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 20, 7602–7613.
CROSSTHWAITE, A. J., HASAN, S. & WILLIAMS, R. J. (2002) Hydrogen peroxide-mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2, Akt/PKB and JNK in cortical neurones: Dependence on Ca(2+) and PI3-kinase. Journal of Neurochemistry 80, 24–35.
DAJAS-BAILADOR, F. A., MOGG, A. J. & WONNACOTT, S. (2002) Intracellular Ca2+ signals evoked by stimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in SH-SY5Y cells: Contribution of voltageoperated Ca2+ channels and Ca2+ stores. Journal of Neurochemistry 81, 606–614.
DAVIES, K. J. (2000)Anoverview of oxidative stress.IUBMB Life Journal 50, 241–244.
DENU, J. M. & TANNER, K. G. (1998) Specific and reversible inactivation of protein tyrosine phosphatases by hydrogen peroxide: Evidence for a sulfenic acid intermediate and implications for redox regulation. Biochemistry 37, 5633–5642.
DWYER, M. A., BREDT, D. S. & SNYDER, S. H. (1991) Nitric oxide synthase: Irreversible inhibition by L-NGnitroarginine in brain in vitro and in vivo. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications 176, 1136–1141.
FLEMING, Y., ARMSTRONG, C. G., MORRICE, N., PATERSON, A., GOEDERT, M. & COHEN, P. (2000) Synergistic activation of stress-activated protein kinase 1/C-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAPK1/JNK) isoforms by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MKK4) and MKK7. Biochemical Journal 352 Pt 1, 145–154.
FREEMAN, B. A. & CRAPO, J. D. (1982) Biology of disease: Free radicals and tissue injury. Laboratory Investigation 47, 412–426.
GO, Y. M., LEVONEN, A. L., MOELLERING, D., RAMACHANDRAN, A., PATEL, R. P., JO, H. & DARLEY-USMAR, V. M. (2001) Endothelial NOSdependent activation of c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase by oxidized low-density lipoprotein. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology 281, H2705–H2713.
HONORE, T., DAVIES, S. N., DREJER, J., FLETCHER, E. J., JACOBSEN, P., LODGE, D. & NIELSEN, F. E. (1988) Quinoxalinediones: Potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science 241, 701–703.
HOU, X. Y., ZHANG, G. Y., YAN, J. Z., CHEN, M. & LIU, Y. (2002) Activation of NMDA receptors and Ltype voltage-gated calcium channels mediates enhanced formation of Fyn-PSD95-NR2A complex after transient brain ischemia. Brain Research 955, 123–132.
HOWE, C. J., LAHAIR, M. M., MAXWELL, J. A., LEE, J. T., ROBINSON, P. J., RODRIGUEZ-MORA, O., MCCUBREY, J. A. & FRANKLIN, R. A. (2002) Participation of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinases in hydrogen peroxide-induced Ikappa B phosphorylation in human T lymphocytes. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277, 30469–30476.
ISHIKAWA, Y., SATOH, T., ENOKIDO, Y., NISHIO, C., IKEUCHI, T. & HATANAKA, H. (1999) Generation of reactive oxygen species, release of L-glutamate and activation of caspases are required for oxygen-induced apoptosis of embryonic hippocampal neurons in culture. Brain Research 824, 71–80.
JIANG, Q., GU, Z., ZHANG, G. & JING, G. (2000) Nmethyl-D-aspartate receptor activation results in regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by protein kinases and phosphatases in glutamate-induced neuronal apototic-like death. Brain Research 887, 285–292.
JUNG, C., RONG, Y., DOCTROW, S., BAUDRY, M., MALFROY, B. & XU, Z. (2001) Synthetic superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics reduce oxidative stress and prolong survival in a mouse amyotrophic lateral sclerosis model. Neuroscience Letters 304, 157–160.
KNEBEL, A., RAHMSDORF, H. J., ULLRICH, A. & HERRLICH, P. (1996) Dephosphorylation of receptor c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation in oxidative neurotoxicity 151 tyrosine kinases as target of regulation by radiation, oxidants or alkylating agents. EMBO Journal 15, 5314–5325.
KOLES, L., WIRKNER, K. & ILLES, P. (2001) Modulation of ionotropic glutamate receptor channels. Neurochemical Research 26, 925–932.
LEIST, M. & NICOTERA, P. (1998) Calcium and neuronal death. Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology 132, 79–125.
LEV, S., MORENO, H., MARTINEZ, R., CANOLL, P., PELES, E., MUSACCHIO, J. M., PLOWMAN, G. D., RUDY, B. & SCHLESSINGER, J. (1995) Protein tyrosine kinase PYK2 involved in Ca(2+)-induced regulation of ion channel and MAP kinase functions. Nature 376, 737–745.
LIN, M. Q. & CHANG, Z. L. (1999) Immunomodulated signaling in macrophages: Regulation of the MAPK signaling pathways by PKA and PKC. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao. (Shanghai) 31, 701–706.
MAHER, P. & SCHUBERT, D. (2000) Signaling by reactive oxygen species in the nervous system. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 57, 1287–1305.
MAILLY, F., MARIN, P., ISRAEL, M., GLOWINSKI, J. & PREMONT, J. (1999) Increase in external glutamate and NMDA receptor activation contribute to H2O2-induced neuronal apoptosis. Journal of Neurochemistry 73, 1181–1188.
MARONEY, A. C., FINN, J. P., BOZYCZKO-COYNE, D., O'KANE, T. M., NEFF, N. T., TOLKOVSKY, A. M., PARK, D. S., YAN, C. Y., TROY, C. M. & GREENE, L. A. (1999)cep-1347 (kt7515), an inhibitor of jnk activation, rescues sympathetic neurons and neuronally differentiated pc12 cells from death evoked by three distinct insults. Journal of Neurochemistry 73, 1901–1912.
PAHLAVANI, M. A. (1998) T cell signaling: Effect of age. Frontiers in Bioscience 3, D1120–D1133.
POLLACK, M. & LEEUWENBURGH, C. (2001) Apoptosis and aging: Role of the mitochondria. Journal of Gerontology: Biological Sciences 56, B475–B482.
SCHULZE-OSTHOFF, K., FERRARI, D., LOS, M., WESSELBORG, S. & PETER, M. E. (1998) Apoptosis signaling by death receptors. European Journal of Biochemistry 254, 439–459.
SHAULIAN, E., SCHREIBER, M., PIU, F., BEECHE, M., WAGNER, E. F. & KARIN, M. (2000) The mammalian UV response: C-Jun induction is required for exit from p53-imposed growth arrest. Cell 103, 897–907.
SHUAI, J. W. & JUNG, P. (2002) Optimal intracellular calcium signaling. Physical Review Letters 88, 068102.
SULLIVAN, S. G., CHIU, D. T., ERRASFA, M., WANG, J. M., QI, J. S. & STERN, A. (1994) Effects of H2O2 on protein tyrosine phosphatase activity in HER14 cells. Free Radical Biology & Medicine 16, 399–403.
SUZUKI, Y. J., FORMAN, H. J. & SEVANIAN, A. (1997) Oxidants as stimulators of signal transduction. Free Radical Biology & Medicine 22, 269–285.
TABNER, B. J., TURNBULL, S., EL AGNAF, O. & ALLSOP, D. (2001) Production of reactive oxygen species from aggregating proteins implicated in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 1, 507–517.
TAKAHASHI, H., HONMA, M., ISHIDA-YAMAMOTO, A., NAMIKAWA, K., KIYAMA, H. & IIZUKA, H. (2001) Expression of human cystatin A by keratinocytes is positively regulated via the Ras/MEKK1/MKK7/JNK signal transduction pathway but negatively regulated via the Ras/Raf-1/MEK1/ERK pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276, 36632–36638.
TAKEKOSHI, K., ISHII, K., NANMOKU, T., SHIBUYA, S., KAWAKAMI, Y., ISOBE, K. & NAKAI, T. (2001) Leptin stimulates catecholamine synthesis in a PKC-dependent manner in cultured porcine adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. Endocrinology 142, 4861–4871.
THANNICKAL, V. J. & FANBURG, B. L. (2000) Reactive oxygen species in cell signaling. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 279, L1005–L1028.
TOESCU, E. C. (1999) Activity of voltage-operated calcium channels in rat cerebellar granule neurons and neuronal survival. Neuroscience 94, 561–570.
TOKUMITSU, H., CHIJIWA, T., HAGIWARA, M., MIZUTANI, A., TERASAWA, M. & HIDAKA, H. (1990) KN-62, 1-[N,O-bis(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-N-methyl-L-tyrosyl]-4-phenylpiperazine, a specific inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Journal of Biological Chemistry 265, 4315–4320.
XIE, C., MARKESBERY, W. R. & LOVELL, M. A. (2000) Survival of hippocampal and cortical neurons in a mixture of MEM+ and B27-supplemented neurobasal medium.Free Radical Biology & Medicine 28, 665– 672.
YOSHIZUMI, M., ABE, J., HAENDELER, J., HUANG, Q. & BERK, B. C. (2000) Src and Cas mediate JNK activation but not ERK1/2 and p38 kinases by reactive oxygen species. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, 11706–11712.
YOSHIZUMI, M., KOGAME, T., SUZAKI, Y., FUJITA, Y., KYAW, M., KIRIMA, K., ISHIZAWA, K., TSUCHIYA, K., KAGAMI, S. & TAMAKI, T. (2002) Ebselen attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via the inhibition of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase and activator protein-1 signalling pathway in PC12 cells. British Journal of Pharmacology 136, 1023–1032.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Hou, XY., Gao, C. et al. Regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation in hydrogen peroxide induced neurotoxicity. J Neurocytol 32, 143–151 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEUR.0000005599.10952.33
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEUR.0000005599.10952.33