Abstract
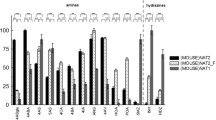
Arylamine N-acetyltransferases (NATs) catalyze a variety of biotransformation reactions, including N-acetylation of arylamines and O-acetylation of arylhydroxylamines. Chemical modification of hamster recombinant NAT2 with 2-(bromoacetylamino)fluorene (Br-AAF) and bromoacetanilide revealed that Br-AAF is an affinity label for the enzyme whereas bromoacetanilide inactivates NAT2 through a bimolecular alkylation process. Electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis of Br-AAF–treated NAT2 showed that a single molecule of 2-acetylaminofluorene had been adducted. Peptide sequencing with tandem mass spectrometry identified the catalytically essential Cys68 as the alkylated amino acid. Br-AAF exhibits similar affinity for hamster NAT1 and NAT2, but is a more effective inactivator of NAT1 because, subsequent to the formation of a reversible enzyme–Br-AAF complex, the rate of alkylation of NAT1 is greater than the rate of alkylation of NAT2. Bromoacetanilide alkylates Cys68 and, to a lesser extent, Cys237 of NAT2; it does not exhibit significant selectivity for either NAT1 or NAT2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres, H. H., Klem, A. J., Schopfer, L. M., Harrison, J. K., and Weber, W. W. (1988). J. Biol. Chem. 263: 7521–7527.
Beland, F. A., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1990). Metabolic activation and DNA adducts of aromatic amines and nitroaromatic hydrocarbons. Handbook Exp. Pharmacol. 94/I: 267–325.
Bergstrom, C. P., Wagner, C. R., Ann, D. K., and Hanna, P. E. (1995). Protein Expr. Purif. 6: 45–55.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Cheon, H. G., Boteju, L. W., and Hanna, P. E. (1992). Mol. Pharmacol. 42: 82–93.
Cheon, H. G., and Hanna, P. E. (1992). Biochem. Pharmacol. 43: 2255–2268.
Guo, Z., Vath, G. M., Wagner, C. R., and Hanna, P. E. (2003). J. Protein Chem. 22: 631–642.
Hanna, P. E. (1994). Adv. Pharmacol. 27: 401–430.
Hanna, P. E. (1996). Curr. Med. Chem. 3: 195–210.
Hein, D. W., Doll, M. A., Fretland, A. J., Gray, K., Deitz, A. C., Feng, Y., et al. (1997). Mutat. Res. 376: 101–106.
Kato, R., and Yamazoe, Y. (1995). Drug Metab. Rev. 27: 241–256.
Kitz, R., and Wilson, I. B. (1962). J. Biol. Chem. 237: 3245–3249.
Levy, G. N., and Weber, W. W. (2002). In Ionnides, c. (ed.), Enzyme Systems That Metabolize Drugs and Other Xenobiotics, John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 441–457.
Levy, H. M., Leber, P. D., and Ryan, E. M. (1963). J. Biol. Chem. 238: 3654–3659.
NIH Guidelines for the Laboratory Use of Chemical Carcinogens (1981). NIH Publication No. 81–2385, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC.
Payton, M., Mushtaq, A., Yu, T-W., Wu, L-J., Sinclair, J., and Sim, E. (2001). Microbiology 147: 1137–1147.
Sinclair, J. C., Sandy, J., Delgoda, R., Sim, E., and Noble, M. E. M. (2000). Nat. Struct. Biol. 7: 560–564.
Sticha, K. R. K., Sieg, C. A., Bergstrom, C. P., Hanna, P. E., and Wagner, C. R. (1997). Protein Expr. Purif. 10: 141–153.
Sticha, K. R. K., Bergstrom, C. P., Wagner, C. R., and Hanna, P. E. (1998). Biochem. Pharmacol. 56: 47–59.
Wagner, C. R., Bergstrom, C. P., Koning, K. R., and Hanna, P. E. (1996). Drug Metab. Disp. 24: 245–253.
Wick, M. J., Yeh, H-M., and Hanna, P. E. (1990). Biochem. Pharmacol. 40: 1389–1398.
Vatsis, K. P., Weber, W. W., Bell, D. A., Dupret, J-M., Evens, D. A. P., Grant, D. M., et al. (1995). Pharmacogenetics, 5: 1–17.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Guo, Z., Vath, G.M. et al. Chemical Modification of Hamster Arylamine N-Acetyltransferase 2 with Isozyme-Selective and Nonselective N-Arylbromoacetamido Reagents. J Protein Chem 23, 153–166 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOPC.0000020082.14480.e2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOPC.0000020082.14480.e2