Abstract
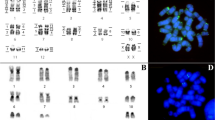
Using human probes of whole chromosomes, the homoeologies between human and Leontopithecus chrysomelas (Platyrrhini) karyotypes were established. Thirty-three conserved segments were observed between the two species. Intrachromosomal rearrangements between the two species were identified using hybridization of chromosome arm probes of human chromosomes 1 and 3. We also used chromosomal data to investigate phylogenetic relationships of Callitrichines. These data were encoded using Cebus capucinus, a species which kept fairly ancestral chromosomes, as reference. Two equi-parsimonious trees, including reversion or convergence events, were obtained. The monophyly of Callitrichines is confirmed. They share nine chromosomal rearrangements at least. The Cebuella-Callithrix group forms a clade sharing five rearrangements at least. According to the tree considered, the Tamarins, Leontopithecus and Saguinus share two chromosomal rearrangements restricted to these two taxa or none. Callimico accumulated seven chromosomal rearrangements unshared with other taxa, at least. To avoid convergence and reversion events, we propose the hypothesis of a network (or populational) evolution. Six chromosomal rearrangements would have occurred during the period of this network evolution. Finally, the karyotype of the last common ancestor to all Callitrichines has been reconstructed. It possessed 48 chromosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aniskin VM, Lavrenchenko LA, Varshavskii AA, Milishnikov AN (1998)Chromosome arrangements and cytogenetic differentiation of two species of African mice of the genus Mus (Rodentia,Muridae).Genetika 34:93 -99.
Aurias A, Dutrillaux B(1986) Apossible newtype of chromosome rearrangement:telomere -centromere translocation (tct) followed by double duplication.Hum Genet 72:25 -26.
Barros RM, Nagamachi CY, Pieczarka JC et al.(2003) Chromosomal studies in Callicebus donacophilus pallescens, with classic and molecular cytogenetic approaches:multi-colour FISH using human and Saguinus oedipus painting probes.Chromosome Res 11:327 -334.
Canavez F, Alves G, Fanning TG, Seuanez HN (1996) Comparative karyology and evolution of the Amazonian Callithrix (Platyrrhini,Primates).Chromosoma 104:348 - 357.
Chowdhary BP, Raudsepp T, Fronicke L, Scherthan H (1998) Emerging patterns of comparative genome organization in some mammalian species as revealed by Zoo-FISH.Genome Res 8:577 -589.
Consigliere S, Stanyo R, Koehler U, Agoramoorthy G, Wienberg J (1996) Chromosome painting de nes genomic rearrangements between red howler monkey subspecies. Chromosome Res 4:264 -270.
Di Berardino D, Iannuzzi L (1981) Chromosome banding homologies in Swamp and Murrah buffalo.J Hered 72:183 - 188.
Dutrillaux B (1975) Sur la nature et l’ origine des chromosomes humains.Monography of Annales de Génétique.L’ expansion Scienti que (Paris).
Dutrillaux B (1979) Very large analogy of chromosome banding between Cebus capucinus (Platyrrhini)and man. Cytogenet Cell Genet 24:84 -94.
Dutrillaux B, Couturier J (1981a) The ancestral karyotype of platyrrhine monkeys.Cytogenet Cell Genet 30:232 -242.
Dutrillaux B, Couturier J (1981b)La Pratique de l’ Analyse Chromosomique.Paris: Masson.
Dutrillaux B, Couturier J, Viegas-Pequignot E (1986a) Evolution chromosomique des Platyrhiniens.Mammalia 50: 56 -81.
Dutrillaux B, Couturier J, Sabatier L, Muleris M, Prieur M (1986b) Inversions in evolution of man and closely related species.Ann Genet 29:195 -202.
Dutrillaux B, Couturier J, Muleris M, Rumpler Y, Viegas-Pequignot E (1986c) Relations chromosomiques entre sous-ordres et infra-ordres,et schéma évolutif général des Primates.Mammalia 50:108 -121.
Dutrillaux B, Lombard M, Carroll JB, Martin RD (1988) Chromosomal af nities of Callimico goeldi (Platyrrhini)and characterization of a Y-autosome translocation in the male. Folia Primatol (Basel)50:230 -236.
Fronicke L, Wienberg J (2001) Comparative chromosome painting de nes the high rate of karyotype changes between pigs and bovids.Mamm Genome 12:442 -449.
Haig D (1999)A brief history of human autosomes.Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 354:1447 -1470.
Kay R (1990) The phyletic relationships of extant and fossil Pitheciinae (Platyrrhini,Anthropoidea).J Hum Evol 19: 175 -208.
Morescalchi MA, Schempp W, Consigliere S, Bigoni F, Wienberg J, Stanyon R (1997) Mapping chromosomal homology between humans and the black-handed spider monkey by.uorescence in situ hybridization.Chromosome Res 5:527 -536.
Mundy NI, Kelly J (2001) Phylogeny of lion tamarins (Leontopithecus spp)based on interphotoreceptor retinol binding protein intron sequences.Am J Primatol 54: 33 -40.
Murphy WJ, Stanyon R, O'Brien SJ (2001) Evolution of mammalian genome organization inferred from comparative gene mapping.Genome Biol 2:REVIEWS0005.
Nagamachi CY, Pieczarka JC, Schwarz M, Barros RM, Mattevi MS (1997) Chromosomal similarities and differ-ences between tamarins,Leontopithecus and Saguinus (Platyrrhini,Primates).Am J Primatol 43:265 -276.
Nagamachi CY, Pieczarka JC, Muniz JA, Barros RM, Mattevi MS (1999) Proposed chromosomal phylogeny for the South American primates of the Callitrichidae family (Platyrrhini). Am J Primatol 49:133 -152.
Napier JR, Napier PH (1967)A Handbook of Living Primates. London: Academic Press.
Neusser M, Stanyon R, Bigoni F, Wienberg J, Muller S (2001) Molecular cytotaxonomy of New World monkeys (Pla-tyrrhini)-comparative analysis of ve species by multi-color chromosome painting gives evidence for a classi cation of Callimico goeldii within the family of Callitrichidae. Cytogenet Cell Genet 94:206 -215.
Olert J, Schmid M (1978) Comparative analysis of karyotypes in European shrew species.I.The sibling species Sorex araneus and S.gemellus:Q-bands,G-bands,and position of NORs.Cytogenet Cell Genet 20:308 -322.
Pastorini J, Forstner MR, Martin RD, Melnick DJ (1998) A reexamination of the phylogenetic position of Callimico (primates)incorporating new mitochondrial DNA sequence data.J Mol Evol 47:32 -41.
Perrotez C (1974) Etude du caryotype du marmouset (Cal-lithrixjacchus )avec les bandes R.Exp Animale 7:173 -180.
Popescu P, Hayes H, Dutrillaux B (1998)Techniques de Cytogénétique Animale.Paris: INRA.
Richard F, Lombard M, Dutrillaux B (1996) Zoo-FISH suggests a complete homology between human and capuchin monkey (Platyrrhini)euchromatin.Genomics 36:417 -423.
Richard F, Lombard M, Dutrillaux B (2000) Phylogenetic origin of human chromosomes 7,16,and 19 and their homologs in placental mammals.Genome Res 10:644 -651.
Richard F, Lombard M, Dutrillaux B (2003) Reconstruction of the ancestral karyotype of eutherian mammals.Chro-mosome Res 11:605 -618.
Schneider H, Canavez FC, Sampaio I, Moreira MA, Tagliaro CH, Seuanez HN (2001) Can molecular data place each neotropical monkey in its own branch?Chromosoma 109: 515 -523.
Sena L, Vallinoto M, Sampaio I, Schneider H, Ferrari SF, Schneider MP (2002) Mitochondrial COII gene sequences provide new insights into the phylogeny of marmoset species groups (Callitrichidae,Primates).Folia Primatol (Basel)73: 240 -251.
Seuanez HN, Forman L, Alves G (1988) Comparative chromosomemorphologyinthreeCallitrichidgenera:Cebuella, Callithrix,and Leontopithecus.J Hered 79:418 -424.
Sherlock JK, Grifin DK, Delhanty JD, Parrington JM (1996) Homologies between human and marmoset (Callithrix jacchus )chromosomes revealed by comparative chromosome painting.Genomics 33:214 -219.
Singer SS, Schmitz J, Schwiegk C, Zischler H (2003) Molecular cladistic markers in New World monkey phylogeny (Platyrrhini,Primates).Mol Phylogenet Evol 26: 490 -501.
Stanyon R, Consigliere S, Muller S, Morescalchi A, Neusser M, Wienberg J (2000) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)maps chromosomal homologies between the dusky titi and squirrel monkey.Am J Primatol 50:95 -107.
Stanyon R, Consigliere S, Bigoni F, Ferguson-Smith M, O'Brien PC, Wienberg J (2001). Reciprocal chromosome painting between a New World primate,the woolly monkey, and humans.Chromosome Res 9:97 -106.
Stanyon R, Bonvicino CR, Svartman M, Seuanez HN (2003) Chromosome painting in Callicebus lugens,the species with the lowest diploid number (2n=16)known in primates. Chromosoma,112:201 -206.
Steiper ME, Ruvolo M (2002) New World monkey phylogeny based on X-linked G6PD DNA sequences.Mol Phylogenet Evol 27:121 -130.
Tanaka K, Matsuda Y, Masangkay JS, Solis CD, Anunciado RV, Namikawa T.(1999). Characterization and chromo-somal distribution of satellite DNA sequences of the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis ).J Hered 90:418 -422.
Thomsen PD, Hoyheim B, Christensen K (1996) Recent fusion events during evolution of pig chromosomes 3 and 6 identi ed by comparison with the babirusa karyotype. Cytogenet Cell Genet 73:203 -208.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerbault-Serreau, M., Bonnet-Garnier, A., Richard, F. et al. Chromosome painting comparison of Leontopithecus chrysomelas (Callitrichine, Platyrrhini) with man and its phylogenetic position. Chromosome Res 12, 691–701 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CHRO.0000045754.43803.db
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CHRO.0000045754.43803.db