Abstract
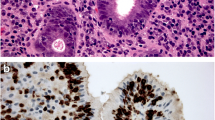
Our purpose was to evaluate the relationshipbetween the clinical and histological features in acohort of patients who had gastroesophagealreflux-related lesions diagnosed after upper digestiveendoscopy. In all, 589 patients scheduled for electiveendoscopy in a multicentric prospective study wereevaluated. Multiple biopsies from the distal esophagusshowing aspects of esophagitis or metaplastic epithelium were taken. Esophagitis was histologicallydetected in 25.6%, gastric-type Barrett's esophagus in36.2%, and specialized columnar epithelium in 33.1%. Thefrequency of esophagitis was constant across age decades. Patients with specialized columnarepithelium were significantly older (P = 0.01) and hada greater extent of metaplastic epithelium (P <0.0001). Specialized columnar epithelium was observed in 15% of patients with only distalesophagitis. In conclusion, endoscopic esophagitis wasconstant across age strata. The presence of specializedcolumnar epithelium was associated with older age andwith longer segments of Barrett's esophagus. Shortareas of esophagitis should be biopsied in view of theirpotential for holding areas of specialized columnarepithelium.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Monnier P, Fontolliet C, Savary M, Ollyo JB: Barrett's esophagus or columnar epithelium of the lower esophagus. Bailliere's Clin Gastroenterol 1:769–789, 1987
Spechler SJ, Goyal R: Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med 315:362–371, 1986
Winters C Jr, Spurling TJ, Chobanian SJ, Curtis DJ, Esposito RL, Hacke r JF III, Johnson DA, et al: Barrett's esophagus. A prevalent occult complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 92:118–124, 1987
Cameron AJ, Ott BJ, Payne WS: The incidence of adenocarcinoma in a columnar lined Barrett' s esophagus. N Engl J Med 313:857–859, 1985
Rbertson CS, Mayberry JF, Nickolson DA, James PD, Atkinson M: Value of endoscopic surve illance in the detection of neoplastic changes in Barrett' s esophagus. Br J Surg 75:760–763, 1988
Hameeteman W, Tytgat GNJ, Houthof HJ, Vander T weel JG: Barrett's esophagus: Development of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 96:1249–1256, 1989
Iftikhar SY, James PD, Steele RJC, Hardcastle JD, Atkinson M: Length of Barrett's esophagus: An important factor in the development of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma. Gut 33:1155–1158, 1992
Ferraris R, Bonelli L, Conio M, Fracchia M, Lapertosa G, Aste H, Gospe: Incidence of adenocarcinoma in an Italian population: An endoscopic surveillance programme. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:881–885, 1997
Drewitz DJ, Sampliner RE, Garewal HS: The incidence of adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus: A prospective study of170 patients followed 4.8 years. Am J Gastroenterol 92:212–215, 1997
GOSPE: Barre tt's esophagus: Epidemiological and clinical results of a multicentric survey. Int J Cancer 48:364–368, 1991
Savary M, Miller G: L' oesophage. Manuel et at las d'endoscopie. Soleure, Gassmann, 1977
Carson FL, Martin JH, Lyn JA: Formalin fixation for electron microscopy: Are-evaluation. Am J Clin Pathol 49:365–373,1973
Whitehead R: Mucosal biopsy of the gastrointestinal tract. In Gastroesophage al Reflux and Esophagitis. R Whitehead (ed). Philadelphia, Saunders, 1985
Paull A, Trier JS, Dalton MD, Camp RC, Loeb P, Goyal RK: The histologic spectrum of Barrett' s esophagus. N Engl J Med 295:476–480, 1976
Schmidt HG, Riddel RH, Walter B, Skinner DB, Riedmann JF: Dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol110:145–152, 1985
Armitage P, Berry G: Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 3rd ed. Oxford, Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1994
Schlesselman JJ: Case-Control Studies. Design, Conduct, Analysis. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1982
Dixon WJ: BMDP Statistical Software Manual. Berkeley, University of California Press, 1992
Bremner CG, Lynch VP, Ellis FH: Barrett's esophagus: congenital or acquired? An experimental study of esophageal mucosal regeneration in the dog. Surgery 68:209–226, 1970
Gillen P, Keeling P, Byrne PJ, Nest AB, Hennessy TP: Experimental columnar metaplasia in the canine esophagus. Br J Surg 75:113–115, 1988
Cameron AJ, Lombay CT: Barre tt's esophagus: Age, prevalence and extent of columnar epithelium. Gastroenterology 103:1241–1245, 1992
Thompson JJ, Zensser KR, Enterline HT: Barrett' s metaplasia and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastroe sophageal junction. Hum Pathol 14:42–61, 1983
Conio M, Aste H, Bonelli L: "Short" Barrett's esophagus: A condition not to be undere stimated. Gastrointest Endosc 40:111, 1994
Spechler SJ, Zeroogian JM, Wang HH, Goyal RK: Prevalence of me taplasia at the gastro-oe sophage al junction. Lancet 344:1533–1536, 1994
Hamilton SR, Smith RRL, Cameron JL: Prevalence and characteristics of Barrett' s esophagus in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus or esophagogastric junction. Hum Pathol 19:942–948, 1988
Schnell TG, Sontag SJ, Chejfec G: Adenocarcinoma arising in tongues of short segme nts of Barrett' s esophagus. Dig Dis Sci 37:133–134, 1992
Berstod A, Weberg R, Froyshow Larsen I, Hoel B, Hauer-Jensen M: Re lationship of hiatus hernia to refluxesophagitis.A prospective study of coincidence using endoscopy. Scand J Gastroenterol 21:35–58, 1986
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aste, H., Bonelli, L., Ferraris, R. et al. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Relationship Between Clinical and Histological Features). Dig Dis Sci 44, 2412–2418 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026666417658
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026666417658