Abstract
1. Studies have shown that adenosine transport and adenosine A1 receptors in rat brain are subjected to regulation by thyroid hormone levels. Since the ectonucleotidase pathway is an important source of adenosine extracellular, in the present study the in vitro action of T3 and T4 hormones on ectonucleotidase activities in hippocampal synaptosomes was evaluated.
2. T3 (Triiodo-l-thyronine) significantly inhibited, in an uncompetitive manner, the ATP and ADP hydrolysis promoted by ATP diphosphohydrolase activity in hippocampal synaptosomes of adult rats.
3. In contrast, T4 (Thyroxine) only inhibited ATP hydrolysis in an uncompetitive mechanism, at the concentrations tested (100–500 μM), but at the same time did not affect ADP hydrolysis.
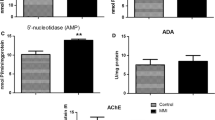
4. In the present study, we also investigate the in vitro effect of T3 and T4 on 5′-nucleotidase activity. However, there are no changes in the activity of this enzyme in the presence of T3 and T4 in the hippocampal synaptosomes of rats.
5. These results suggest that thyroid hormones could be involved in the regulation of ectonucleotidase activities, such as ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase and ecto-ATPase, possibly exerting a modulatory role in extracellular adenosine levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Balazs, R., Lewis, P. D., and Patel, A. J. (1975). Effects of metabolic factors on brain development. In Brazier, M. A. B. (ed.), Growth and Development of the Brain, Raven Press, New York, pp. 83–115.
Battasttini, A. M.O., Rocha, J.B.T., Barcellos, C. K., Dias, R.D., and Sarkis, J. J. F. (1991). Characterization of an ATP diphosphohydrolase (EC 3.6.1.5.) in synaptosomes from cerebral cortex of adult rats. Neurochem. Res. 16:1303–1310.
Bernal, J., and Nunez, J. (1995). Thyroid hormones and brain development. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 133:390–398.
Bernstein, H. G., Weib, J., and Luppa, H. (1978). Cytochemical investigation on the localization of 50-nucleotidase in rat hippocampus with special reference to synaptic regions. Histochemistry 55:261–267.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quntification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:218–254.
Brundege, J. M., and Dunwiddie, T. V. (1997). Role of adenosine as a modulator of synaptic activity in the central nervous system. Adv. Pharmacol. 39:353–391.
Chan, K., Delfert, D., and Junger, K. D. (1986). A direct colorimetric assay for CaC2-ATPase activity. Anal. Biochem. 157:375–380.
Cunha, R. A., Vizi, E. S., Ribeiro, J. A., and Sebastião, A. M. (1996). Preferential release of ATP and its extracellular catabolism as a source of adenosine upon high-but not low-frequency stimulation of rat hippocampal slices. J. Neurochem. 67:2180–2187.
Davis, P. J., and Davis, F. B. (1996). Nongenomic actions of thyroid hormone. Thyroid 6:497–504.
Di Iorio, P., Ballerini, P., Caciagli, F., and Cicarelli, R. (1998). Purinoceptor-mediated modulation of purine and neurotransmitter release from nervous tissue. Pharmacol. Res. 37:169–178.
Dragunow, M. (1988). Purinergic mechanisms in epilepsy. Prog. Neurobiol. 31:85–108.
Dratman, M. B., and Gordon, J. T. (1996). Thyroid hormones as neurotransmitters. Thyroid 6:639–647.
Dunwiddie, T. V., and Masino, S. A. (2001). The role and regulation of adenosine in the central nervous system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24:31–55.
Fideu, M.D., Arce, A., Esquifino, A., and Miras-Portugal, M. T. (1994). Thyroid hormones modulate both transport and A1 receptors in rat brain. Am. J. Physiol. 256:1651–1656.
Fideu, M. D., and Miras-Portugal, M. T. (1992). Long-term regulation of nucleoside transport by thyroid hormone (T3) in cultured chromaffin cells. Neurochem. Res. 17:1099–1104.
Heymann, D., Reddington, M., and Kreutzberg, G. W. (1984). Subcellular localization of 50-nucleotidase in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 43:971–978.
Kegel, B., Braun, N., Maliszewski, C. R., Heine, P., and Zimmermann, H. (1997). An ecto-ATPase and ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase are expressed in rat brain. Neuropharmacology 36:1189–1200.
Leonard, J. L., and Farwell, A.P. (1997).Thyroid hormone-regulated actin polymerization in brain. Thyroid 7:147–151.
Mazurkiewicz,D., and Saggerson,D. (1989). Changes in the activities of adenosine-metabolizing enzymes in six regions of the rat brain on chemical induction of hypothyroidism. Biochem. J. 261:667–672.
Nagy, A. K., and Delgado-Escueta, A. V. (1984). Rapid preparation of synaptosomes from mammalian brain using a non toxic isoosmotic gradient (Percoll). J. Neurochem. 43:1114–1123.
Phillips, J. W., and Wu, P. H. (1981). The role of adenosine and its nucleotides in central synaptic transmission. Prog. Neurobiol. 16:187–239.
Sarkar, P. K., and Ray, A.K. (1993). Synaptosomal Action ofThyroid Hrmone changes inNaC-KC-ATPase activity in adult rat cerebral cortese. Houm. Metab. Res. 25:1–3.
Sarkis, J. J. F., and Salto, C. (1991). Characterization of synaptosomal ATP diphosphohidrolase from the eletric organ of Torpedo marmorata. Brain Res. Bull. 26:871–876.
Schoen, S. W., and Kreutzberg, G. W. (1994). Synaptic 50-nucleotidase activity reflects lesion-induced sprouting within the adult rat dentate gyrus. Exp. Neurol. 127:106–118.
Schwartz, H. L., Lazar, M. A., and Oppenheimer, J.H. (1994).Widespread distribution of immunoreactive thyroid hormone beta 2 receptor (TR beta 2) in the nuclei of extrapituitary rat tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 269:24777–24782.
Slotkin, T. A., and Slepetis, R. J. (1984). Obligatory role of thyroid hormones in development of peripheral sympathetic and central nervous system catecholaminergic neurons: Effects of propylthiouracilinduced hypothyroidism on transmitter levels, turnover and release. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 230:53–61.
Zimmermann, H. (1996). Biochemistry, localization and functional roles of ecto-nucleotidases in the nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 49:589–618.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Aguiar Matos, J.A., Bruno, A.N., Oses, J.P. et al. In Vitro Effects of Thyroid Hormones on Ectonucleotidase Activities in Synaptosomes from Hippocampus of Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 22, 345–352 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020776119612
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020776119612