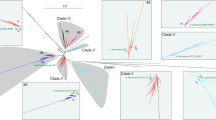
Abstract
If the diversification of microbial life can be depicted as a single tree, as inferred by comparative sequencing of ribosomal RNAs, this could provide a framework for defining the order of emergence of new metabolic pathways. However, recent recognition that lateral gene transfer has been a significant force in microbial evolution has created uncertainty about the interpretation of taxonomies based on gene sequences. In this context, the origins and evolution of sulfate respiration will be evaluated considering the evolutionary history of a central enzyme in this process, the dissimilatory sulfite reductase. These studies suggest at least two major lateral transfer events during the early diversification of sulfate respiring microorganisms. The high sequence conservation of this enzyme has also provided a mechanism to directly explore the natural diversity of sulfate-respiring organisms using molecular techniques, avoiding the bias of culture-based identification. These studies suggest that the habitat range and evolutionary diversity of this key functional group of organisms is greater than now appreciated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas, RM & Bartha R (1993) Microbial Ecology Fundamentals and Applications. 3rd Edition. The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company, Inc., Redwood City. pp. 563.
Canfield DE & Desmarais DJ (1991) Aerobic sulfate reduction in microbial mats. Science 251: 1471–1473.
Chang YJ, Peacock AD, Long PE, Stephen JR, McKinley JP, Macnaughton SJ, Hussain A, Saxton AM & White DC (2001) Diversity and characterization of sulfate-reducing bacteria in groundwater at a uranium mill tailings site. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67: 3149–3160.
Chapelle FH, Morris JT, McMahon PB & Zelibor JL (1988) Bacterial metabolism and the del-13C composition of groundwater, Floridian aquifer, South Carolina. Geology 16: 117–121.
Cottrell MT & Cary SC (1999) Diversity of dissimilatory bisulfite reductase genes of bacteria associated with the deep-sea hydrothermal vent polychaete annelid Alvinella pompejana. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 1127–1132.
Dahl C, Kredich NM, Deutzmann R & Trüper HG (1993) Dissimilatory sulphite reductase from Archaeoglobus fulgidus: physicochemical properties of the enzyme and cloning, sequencing and analysis of the reductase genes. J. Gen. Microbiol. 139: 1817–1828.
DeLong EF (1992) Archaea in coastal marine environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 5685–5689.
Fry NK, Fredrickson JK, Fishbain S, Wagner M & Stahl DA (1997) Population structure of microbial communities associated with two deep, anaerobic, alkaline aquifers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 1498–1504.
GhiorseWC & Wilson JT (1988) Microbial ecology of the terrestrial subsurface. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 33: 107–172.
Gogarten JP, Kibak H, Dittrich P, Taiz L, Bowman EJ, Bowman BJ, Manolson MF, Poole RJ, Date R, Oshima T, Konishi J, Denda K & Yoshida M (1989) Evolution of the vacuolar H+-ATPase - Implications for the origin of eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 6661–6665.
Hansen TA (1994) Metabolism of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 66: 165–185.
Hipp WM, Pott AS, ThumSchmitz N, Faath I, Dahl C & Truper HG (1997) Towards the phylogeny of APS reductases and sirohaem sulfite reductases in sulfate-reducing and sulfur-oxidizing prokaryotes. Microbiology UK 143: 2891–2902.
Iwabe N, Kuma K, Hasegawa M, Osawa S & Miyata T (1989) Evolutionary relationship of Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, and Eukaryotes inferred from phylogenetic trees of duplicated genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 9355–9359.
Karkhoff-Schweizer RR, Huber DPW & Voordouw G (1995) Conservation of the genes for dissimilatory sulfite reductase from Desulfovibrio vulgaris and Archaeoglobus fulgidus allows their detection by PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 290–296.
Klein M, Friedrich M, Roger AJ, Fishbain S, Hugenholtz P, Abicht H, Blackall LL, Stahl DA & Wagner M (2001) Multiple lateral transfer events of dissimilatory sulfite reductase genes between major lineages of bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 183: 6028–6034.
Kuznetsov SI, Ivanov MV & Lyalikova NN (1963) Introduction to Geological Microbiology. McGraw-Hill, International Series in the Earth Sciences, New York.
Larsen O, Lien T & Birkeland NK (1999) Dissimilatory sulfite reductase from Archaeoglobus profundus and Desulfotomaculum thermocisternum: phylogenetic and structural implications from gene sequences. Extremophiles 3: 63–70.
Larsen O, Lien T & Birkeland NK (2000) Characterization of the desulforubidin operons from Desulfobacter vibrioformis and Desulfobulbus rhabdoformis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 186: 41-46.
Lovley DR, Coates JD, Woodward JC & Phillips EJP (1995) Benzene oxidation coupled to sulfate reduction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 953–958.
Minz D, Green SJ, Muyzer G, Cohen Y, Rittmann BE & Stahl DA (1999) Unexpected Population distribution in a microbial mat community: sulfate-reducing bacteria localized to the highly oxic chemocline in contrast to a eukaryotic preference for anoxia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 4659–4665.
Murphy EM, Schramke JA, Fredrickson JK, Bledsoe HW, Francis AJ, Sklarew DS & Linehan JC (1992) The influence of microbial activity and sedimentary organic carbon on the isotope geochemistry of the Middendorf Aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 28: 723–740.
Pace NR, Stahl DA, Lane DJ, Olsen GJ (1986) The analysis of natural microbial populations by ribosomal RNA sequences. Adv. Microbial Ecol. 9: 1–55.
Pedersen K & Ekendahl S (1990) Distribution and activity of bacteria in deep granitic groundwaters of southeastern Sweden. Microb. Ecol. 20: 37–52.
Perez-Jimenez JR, Young LY & Kerkhof LJ (2001) Molecular characterization of sulfate-reducing bacteria in anaerobic hydrocarbon-degrading consortia and pure cultures using the dissimilatory sulfite reductase (dsr AB) genes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 35: 145–150.
Phelps CD, Kerkhof LJ & Young LY (1998) Molecular characterization of a sulfate-reducing consortium which mineralizes benzene. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 27: 269–279.
Schramm A, Santegoeds CM, Nielsen HK, Ploug M, Wagner M, Pribyl M, Wanner J, Amann R & De Beer D (1999) On the occurrence of anoxic microniches, denitrification, and sulfate reduction in aerated activated sludge. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 4189–4196.
Shen Y, Buick R & Canfield DE (2001) Isotopic evidence for microbial sulphate reduction in the early Archaean era. Nature 410: 77–81.
Stahl DA (1993) The natural history of microorganisms. ASM News 59: 609–613.
Stevens TO & McKinley JP (1995) Lithoautotrophic microbial ecosystems in deep basalt aquifers. Science 270: 450–454.
Stevens TO, McKinley JP & Fredrickson JK (1993) Bacteria associated with deep, alkaline, anaerobic groundwaters in southeast Washington. Microb. Ecol. 25: 35–50.
Thomsen TR, Finster K & Ramsing NB (2001) Biogeochemical and molecular signatures of anaerobic methane oxidation in a marine sediment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67: 1646–1656.
Wagner M, Roger AJ, Flax JL, Brusseau GA & Stahl DA (1998) Phylogeny of dissimilatory sulfite reductases supports an early origin of sulfate respiration. J. Bacteriol. 180: 2975–2982.
Wallrabenstein C, Hauschild E & Schink B (1995) Syntrophobacter pfennigii sp. nov., new syntrophically propionate-oxidizing anaerobe growing in pure culture with propionate and sulfate. Arch. Microbiol. 164: 346–352.
Weiner JM & Lovley DR (1998) Anaerobic benzene degradation in petroleum-contaminated aquifer sediments after inoculation with a benzene-oxidizing enrichment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 775–778.
Woese CR (1987) Bacterial evolution. Microbiol. Rev. 51: 221–271.
Zobell CE (1958) Ecology of sulfate reducing bacteria. Producers Monthly 22: 12–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stahl, D.A., Fishbain, S., Klein, M. et al. Origins and diversification of sulfate-respiring microorganisms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81, 189–195 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020506415921
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020506415921