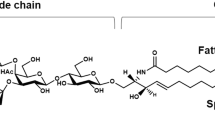
Abstract
During the course of studies on natural occurrence of sphingosine base in brain, cationic glycosphingolipids bound to carboxymethyl-Sephadex and eluted with triethylamine in organic solvents were isolated and characterized. Four classes of compounds were identified: (i) plasmalopsychosine-A and -B; (ii) glyceroplasmalopsychosine; (iii) glycosphingolipids having de-N-acetyl-hexosamine, e.g., de-N-acetyl-Lc3Cer; (iv) glycosylsphingosine, i.e., lysoglycosphingolipid. Only two kinds, galactosylsphingosine (psychosine) and lactosylsphingosine, were found to occur naturally in brain. All these compounds were isolated from extract of brain white matter. Their occurrence, quantity, and distribution pattern differ from one species to another. Their quantity is much lower than that of regular acidic and neutral glycosphingolipids. They may interact with regular glycosphingolipids in glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains to elicit signal transduction, to modify cellular phenotype, although studies along this line are highly limited at this time.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Hannun, Y. A., Loomis, C. R., Merrill, A. H. J., and Bell, R. M. 1986. Sphingosine inhibition of protein kinase C activity and of phorbol dibutyrate binding in vitro and in human platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 261:12604-12609.
Merill, A. H. J., Nimkar, S., Menaldino, D., Hannun, Y. A., Loomis, C. R., Bell, R. M., Tyagi, S. R., Lambeth, J. D., Stevens, V. L., Hunter, R., and Liotta, D. C. 1989. Structural requirements for long-chain (sphingoid) base inhibition of protein kinase C in vitro and for the cellular effects of these compounds. Biochemistry 28:3138-3145.
Igarashi, Y., Hakomori, S., Toyokuni, T., Dean, B., Fujita, S., Sugimoto, M., Ogawa, T., El-Ghendy, K., and Racker, E. 1989. Effect of chemically well-defined sphingosine and its N-methyl derivatives on protein kinase C and src kinase activities. Biochemistry 28:6796-6800.
Igarashi, Y., Kitamura, K., Toyokuni, T., Dean, B., Fenderson, B. A., Ogawa, T., and Hakomori, S. 1990. A specific enhancing effect of N,N-dimethylsphinogosine on epidermal growth factor receptor autophosphorylation: Demonstration of its endogenous occurrence (and the virtual absence of unsubstituted sphingosine) in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 265:5385-5389.
Hannun, Y. A. 1997. Sphingolipid-mediated signal transduction. Austin, TX: R. G. Landes Co.
Megidish, T., Cooper, J., Zhang, L., Fu, H., and Hakomori, S. 1998. A novel sphingosine-dependent protein kinase (SDK1) specifically phosphorylates certain isoforns of 14-3-3 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 273:21834-21845.
Megidish, T., Takio, K., Titani, K., Iwabuchi, K., Hamaguchi, A., Igarashi, Y., and Hakomori, S. 1999. Endogenous substrates of sphingosine-dependent kinases (SDKs) are chaperone proteins: Heat shock proteins, glucose-regulated proteins, protein disulfide isomerase, and calreticulin. Biochemistry 38:3369-3378.
Cuvillier, O., Edsall, L., and Spiegel, S. 2000. Involvement of sphingosine in mitochondria-dependent Fas-induced apoptosis of type II Jurkat T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 275:15691-15700.
Kannagi, R., Nudelman, B. D., Levery, S. B., and Hakomori, S. 1982. A series of human erythrocyte glycosphingolipids reacting to the monoclonal antibody directed to a developmentally regulated antigen, SSEA-1. J. Biol. Chem. 257:14865-14874.
Folch, J., Arsove, S., and Meath, J. A. 1951. Isolation of brain strandin, a new type of large molecule tissue component. J. Biol. Chem. 191:819-831.
Nudelman, E. D., Levery, S. B., Igarashi, Y., and Hakomori, S. 1992. Plasmalopsychosine, a novel plasmal (fatty aldehyde) conjugate of psychosine with cyclic acetal linkage: Isolation and characterization from human brain white matter. J. Biol. Chem. 267:11007-11016.
Levery, S. B., Nudelman, E. D., and Hakomori, S. 1992. Novel modification of glycosphingolipids by long-chain cyclic acetals: Isolation and characterization of plasmalocerebroside from human brain. Biochemistry 31:5335-5340.
Taketomi, T., Hara, A., Uemura, K., and Sugiyama, E. 1998. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometric analysis of glycosphingolipids including gangliosides. Acta Biochim. Polon. 45:987-999.
Yachida, Y., Kashiwaga, M., Mikami, T., Tsuchihashi, K., Daino, T., Akino, T., and Gasa, S. 1998. Stereochemical structures of synthesized and natural plasmalogalactosylceramides from equine brain. J. Lipid Res. 39:1039-1045.
Sadozai, K. K., Levery, S. B., Anand, J. K., and Hakomori, S. 1996. Model compounds for plasmaloglycolipids: Preparation of long chain cyclic acetals of methyl β-D-galactopyranoside and determination of their regio-and stereochemistry by proton NMR. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 15:715-725.
Yachida, Y., Kashiwagi, M., Mikami, T., Tsuchihashi, K., Daino, T., Akino, T., and Gasa, S. 1999. Novel plasmalogalactosylalkylglycerol from equine brain. J. Lipid Res. 40:2271-2278.
Hamasaki, H., Aoyagi, M., Kasama, T., Handa, S., Hirakawa, K., and Taki, T. 1999. GT1b in human metastatic brain tumors: GT1b as a brain metastasis-associated ganglioside. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1437:93-99.
Hikita, T., Tadano-Aritomi, K., Iida-Tanaka, N., Anand, J. K., Ishizuka, I., and Hakomori, S. 2001.A novel plasmal conjugate to glycerol and psychosine (“glyceroplasmalopsychosine”): Isolation and characterization from bovine brain white matter. J. Biol. Chem. 276:23084-23091.
Domon, B. and Costello, C. E. 1988. A systematic nomenclature for carbohydrate fragmentations in FAB-MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconj. J. 5:397-409.
Vanier, M. T. and Svennerholm, L. 1975. Chemical pathology of Krabbe's disease. III. Ceramide-hexosides and gangliosides of brain. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 64:641-648.
Igisu, H. and Suzuki, K. 1984. Analysis of galactosylsphingosine (psychosine) in the brain. J. Lipid Res. 25:1000-1006.
Lambeth, J. D. and Ryu, S. H. 1996. Glycerolipids in signal transduction. In Biochemistry of lipids, lipoproteins and membranes, ed. D. E. Vance and J. Vance, pp. 237-255. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Sakakura, C., Igarashi, Y., Anand, J. K., Sadozai, K. K., and Hakomori, S. 1996. Plasmalopsychosine of human brain mimics the effect of nerve growth factor by activating its receptor kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase in PC12 cells: Induction of neurite outgrowth and prevention of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 271:946-952.
Prinetti, A., Iwabuchi, K., and Hakomori, S. 1999. Glycosphingolipid-enriched signaling domain in mouse neuroblastoma Neuro2a cells: Mechanism of ganglioside-dependent neuritogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 274:20916-20924.
Megidish, T., White, T., Takio, K., Titani, K., Igarashi, Y., and Hakomori, S. 1995. The signal modulator protein 14-3-3 is a target of sphingosine-or N,N-dimethylsphingosine-dependent kinase in 3T3(A31) cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 216: 739-747.
Mano, N., Oda, Y., Yamada, K., Asakawa, N., and Katayama, K. 1997. Simultaneous quantitative determination method for sphingolipid metabolites by liquid chromatography/ionspray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 244:291-300.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hikita, T., Tadano-Aritomi, K., Iida-Tanaka, N. et al. Cationic Glycosphingolipids in Neuronal Tissues and Their Possible Biological Significance. Neurochem Res 27, 575–581 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020259630034
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020259630034