Abstract
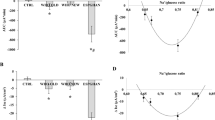
L-Glutamine is the primary metabolic fuel of theintestinal mucosa. This in vivo study compares theeffect of L-glutamine 50 mM with that of D-glucose 50 mMon water and electrolyte absorption in jejunal and ileal loops of healthy rabbits. Usingpolyethylene glycol (PEG) as a nonabsorbable marker andan incubation at 37°C, we found that absorption ofwater (P = 0.000), sodium (P = 0.002), potassium (P =0.001), and chloride (P = 0.003) from the glutamineelectrolyte solution was greater than from the glucoseelectrolyte solution in the ileum. A similar trend wasshown in the jejunum. We conclude that L-glutamine may be a useful component to be tested in oralrehydration solutions for treating diarrhealdehydration.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Souba WW, Smith RJ, Wilmore DW: Glutamine metabolism by the intestinal tract. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 9:608–617, 1985
Rhoads JM, Keku EO, Quinn J, Woosley J, Lecce JG: L-Glutamine stimulates jejunal sodium and chloride absorption in pig rotavirus enteritis. Gastroenterology 100:683–691, 1991
Nath SK, Dechelotte P, Darmaun D, Gotteland M, Rongier M, Desjeux JF: [15N] and [14C]glutamine fluxes across rabbit ileum in experimental bacterial diarrhea. Am J Physiol 262:G312–G318, 1992
Neptune EM Jr, Mitchell JG: Sodium and water transport by the everted rabbit intestine (ileum) sac. Fed Proc 23: 152, 1964 (abstract)
Gianotti L, Alexander JW, Gennari R, Pyles T, Babcock GF: Oral glutamine decreases bacterial translocation and improves survival in experimental gut-origin sepsis. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 19(1):69–74, 1995
Patra FC, Mahalanabis D, Jalan KN: Stimulation of sodium and water absorption by sucrose in the rat small intestine. Acta Paediatr Scand 71:103–107, 1982
Rolston DDK, Kelly MJ, Borodo MM, Dawson AM, Farthing MJG: Effect of bicarbonate, acetate and citrate on water and sodium movement in normal and cholera toxin-treated rat small intestine. Scand J Gastroenterol 24:1–8, 1989
Morin CL, Ling V: Effect of pentagastrin on the rat small intestine after resection. Gastroenterology 75;224–229, 1978
Hyden SA: Turbidimetric method for the determination of higher polyethylene glycols in biological materials. Kgl Lantbrunks hoegsk Ann 22:139–145, 1955
Levinson RA, Schedl HP: Absorption of sodium, chloride, water, and simple sugars in rat small intestine. Am J Physiol 211:939–942, 1966
Schultz SG: Cellular models of sodium and chloride by mammalian small and large intestine. In Secretory Diarrhoea. M Field, SJ Fordtran, SG Schultz (ed). Bethesda, Maryland, American Physiological Society, 1980; pp 1–9
Rhoads JM, Keku EO, Bennett LE, Quinn J, Lecce JG: Development of L-glutamine stimulated electroneutral sodium absorption in piglet jejunum. Am J Physiol 259:G99–G107, 1990
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, S., Mahalanabis, D., Chowdhury, A. et al. Glutamine Is Superior to Glucose in Stimulating Water and Electrolyte Absorption Across Rabbit Ileum. Dig Dis Sci 42, 420–423 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018842708454
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018842708454