Abstract
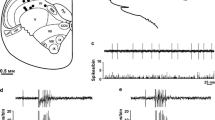
The direct and indirect effects of nitrous oxide (N2O) on the nociceptive responses of lumbar dorsal horn neurons, and the indirect effects on midbrain reticular formation (MRF) neurons and thalamic neurons were determined in goats anaesthetized with isoflurane. The technique used enabled the differential delivery of N2O to either the torso or the cerebral circulation, thus allowing assessment of the direct spinal and indirect brain effects of N2O. Systemic delivery of N2O appeared to have divergent effects, facilitating (4/11) or depressing (7/11) the responses of dorsal horn neurons. Such divergent effects were also observed when N2O was differentially delivered to the circulation in the torso (i.e. the spinal cord). Likewise, MRF and thalamic responses to noxious stimulation were variably affected by administration of N2O to the torso, with some cells facilitated (7/13 MRF neurons, 3/8 thalamic neurons) and others depressed (6/13 MRF neurons, 5/8 thalamic neurons). It appears that N2O has variable effects on the caprine CNS. The facilitatory action of N2O might partially explain why it is a relatively weak anaesthetic.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Antognini, J.F. and Kien, N.D., 1994. A method for preferential delivery of volatile anesthetics to the in situ goat brain. Anesthesiology, 80, 1148-1154
Antognini, J.F. and Schwartz, K., 1993. Exaggerated anesthetic requirements in the preferentially anesthetized brain. Anesthesiology, 79, 1244-1249
Antognini, J.F., Lewis, B.K. and Reitan, J.A., 1994. Hypothermia minimally decreases nitrous oxide anesthetic requirements. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 79, 980-982
Antognini, J.F., Carstens, E., Sudo, M. and Sudo, S., 2000a. Isoflurane depresses electroencephalographic and medial thalamic responses to noxious stimulation via an indirect spinal action. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 91, 1282-1288
Antognini, J.F., Wang, X.W. and Carstens, E., 2000b. Isoflurane action in the spinal cord blunts electroencephalographic and thalamic-reticular formation responses to noxious stimulation in goats. Anesthesiology, 92, 559-566
Antognini, J.F., Wang, X.W., Piercy, M. and Carstens, E., 2000c. Propofol directly depresses lumbar dorsal horn neuronal responses to noxious stimulation in goats. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia, 47, 273-279
Antognini, J.F., Saadi, J., Wang, X.W., Carstens, E. and Piercy, M., 2001. Propofol action in both spinal cord and brain blunts electroencephalographic responses to noxious stimulation in goats. Sleep, (in press).
Barr, G., Jakobsson, I.G., Öwall, A. and Anderson, R.E., 1999. Nitrous oxide does not alter bispectral index: study with nitrous oxide as sole agent and as an adjunct to i.v. anaesthesia. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 82, 827-830
Deady, J.E., Koblin, D.D., Eger, E.I., Heavner, J.E. and D'Aoust, B., 1981. Anesthetic potencies and the unitary theory of narcosis. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 60, 380-384
de Jong, R.H. and Wagman, I.H., 1968. Block of afferent impulses in the dorsal horn of monkey: a possible mechanism of anesthesia. Experimental Neurology, 20, 352-358
de Jong, R.H., Robles, R. and Morikawa, K.-I., 1969. Actions of halothane and nitrous oxide on dorsal horn neurons (“The Spinal Gate”). Anesthesiology, 31, 205-212
Forster, C. and Handwerker, H.O., 1990. Automatic classification and analysis of microneurographic spike data using a PC/AT. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 31, 109-118
Friedman, Y., King, B.S. and Rampil, I.J., 1996. Nitrous oxide depresses spinal F waves in rats. Anesthesiology, 85, 135-141
Guo, T.Z., Poree, L., Golden, W., Stein, J., Fujinaga, M. and Maze, M., 1996. Antinociceptive response to nitrous oxide is mediated by supraspinal opiate and spinal alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in rats. Anesthesiology, 85, 846-852
Gyulai, F.E., Firestone, L.L., Mintun, M.A. and Winter, P.M., 1996. In vivo imaging of human limbic responses to nitrous oxide inhalation. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 83, 291-298
Hagihira, S., Taenaka, N. and Yoshiya, I., 1997. Inhalation anesthetics suppress the expression of c-Fos protein evoked by noxious somatic stimulation in the deeper layer of the spinal cord in the rat. Brain Research, 751, 124-130
Hoffman, W.E., Charbel, F.T., Edelman, G., Albrecht, R.F. and Ausman, J.I., 1995. Nitrous oxide added to isoflurane increases brain artery blood flow and low frequency brain electrical activity. Journal of Neurosurgical Anesthesiology, 7, 82-88
Hornbein, T.F., Eger, E.I., Winter, P.M., Smith, G., Wetstone, D. and Smith, K.H., 1982. The minimum alveolar concentration of nitrous oxide in man. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 61, 553-556
Jevtovic-Todorovic, V., Todorovic, S.M., Mennerick, S., Powell, S., Dikranian, K., Benshoff, N., Zorumski, C.F. and Olney, J.W., 1998. Nitrous oxide (laughing gas) is an NMDA antagonist, neuroprotectant and neurotoxin. Nature Medicine, 4, 460-463
Jinks, S., Antognini, J.F., Carstens, E., Buzin, V. and Simons, C., 1999. Isoflurane can indirectly depress lumbar dorsal horn activity in the goat via action within the brain. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 82, 244-249
Miyazaki, Y., Adachi, T., Utsumi, J., Shichino, T. and Segawa, H., 1999. Xenon has greater inhibitory effects on spinal dorsal horn neurons than nitrous oxide in spinal cord transected cats. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 88, 893-897
Quock, R.M., Curtis, B.A., Reynolds, B.J. and Mueller, J.L., 1993. Dose-dependent antagonism and potentiation of nitrous oxide antinociception by naloxone in mice. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 267, 117-122
Rampil, I.J., 1994. Anesthetic potency is not altered after hypothermic spinal cord transection in rats. Anesthesiology, 80, 606-610
Rampil, I.J., Kim, J.S., Lenhardt, R., Negishi, C. and Sessler, D.I., 1998. Bispectral EEG index during nitrous oxide administration. Anesthesiology, 89, 671-677
Shimoji, K. and Bickford, R.G., 1971a. Differential effects of anesthetics on mesencephalic reticular neurons, I. Spontaneous firing patterns. Anesthesiology, 35, 68-75
Shimoji, K. and Bickford, R.G., 1971b. Differential effects of anesthetics on mesencephalic reticular neurons, II. Responses to repetitive somatosensory electrical stimulation. Anesthesiology, 35, 76-80
Smith, R.A., Wilson, M. and Miller, K.W., 1978. Naloxone has no effect on nitrous oxide anesthesia. Anesthesiology, 49, 6-8
Steffey, E.P., Gillespie, J.R., Berry, J.D., Eger, E.I. and Munson, E.S., 1974. Anesthetic potency (MAC) of nitrous oxide in the dog, cat, and stump-tail monkey. Journal of Applied Physiology, 36, 530-532
Sun, W.Z., Shyu, B.C. and Shieh, J.Y., 1996. Nitrous oxide or halothane, or both, fail to suppress c-fos expression in rat spinal cord dorsal horn neurones after subcutaneous formalin. British Journal of Anaesthetics, 76, 99-105
Taub, A., Hoffert, M. and Kitahata, L.M., 1974. Lamina-specific suppression and acceleration of dorsal-horn unit activity by nitrous oxide: a statistical analysis. Anesthesiology, 40, 24-31
Tindal, J.S., Knaggs, G.S. and Turvey, A., 1968. The forebrain of the goat in stereotaxic coordinates. Journal of Anatomy, 103, 457-469
Utsumi, J., Adachi, T., Miyazaki, Y., Kurata, J., Shibata, M., Murakawa, M., Arai, T. and Mori, K., 1997. The effect of xenon on spinal dorsal horn neurons: a comparison with nitrous oxide. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 84, 1372-1376
Utsumi, J., Adachi, T., Kurata, J., Miyazaki, Y., Shibata, M., Murakawa, M., Arai, T. and Mori, K., 1998. Effect of xenon on central nervous system electrical activity during sevoflurane anesthesia in cats: comparison with nitrous oxide. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 80, 628-633
Willer, J.C., Bergeret, S., Gaudy, J.H. and Dauthier, C., 1985. Failure of naloxone to reverse the nitrous oxide-induced depression of a brain stem reflex: an electrophysiologic and double-blind study in humans. Anesthesiology, 63, 467-472
Yang, J.C., Clark, W.C. and Ngai, S.H., 1980. Antagonism of nitrous oxide analgesia by naloxone in man. Anesthesiology, 52, 414-417
Yli-Hankala, A., Lindgren, L., Porkkala, T. and Jantti, V., 1993. Nitrous oxide-mediated activation of the EEG during isoflurane anaesthesia in patients. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 70, 54-57
Zar, J.H., 1999. Biostatistical Analysis, 4th edn, (Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ), 136-139
Zhang, C., Davies, M.F., Guo, T.Z. and Maze, M., 1999. The analgesic action of nitrous oxide is dependent on the release of norepinephrine in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Anesthesiology, 91, 1401-1407
Zhou, H.H., Mehta, M. and Leis, A.A., 1997. Spinal cord motoneuron excitability during isoflurane and nitrous oxide anesthesia. Anesthesiology, 86, 302-307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antognini, J., Chen, X., Sudo, M. et al. Variable Effects of Nitrous Oxide at Multiple Levels of the Central Nervous System in Goats. Vet Res Commun 25, 523–538 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017961631371
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017961631371