Abstract
Glutamate receptor subunit 1 (GluR1) is one of the four possible subunits of the AMPA-type glutamate receptor. The integrity of this receptor is crucial for learning processes. However, reductions of GluR1 are noticeable in the hippocampal formation of patients suffering from Alzheimer's disease. Such degradations presumably result in an impaired synaptic communication and might be causally linked to the neurodegenerative process in this cognitive disorder. The peptidergic drug Cerebrolysin counteracts cognitive deficits of patients affected by Alzheimer's disease. These findings are supported by experiments revealing neuroprotective and neurotrophic capacities of the drug.
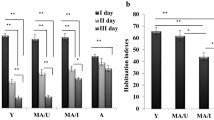
In order to examine the effect of the drug on the density of GluR1 in hippocampal formation 24-month-old rats were treated with either Cerebrolysin or its peptide fraction E021, or saline as a control. Spatial navigation of the animals was tested in the Morris water maze. Rat brain slices were stained immunohistochemically with a GluR1-specific antibody. GluR1 immunoreactivity was quantified using light microscopy and a computerised image analysis system. Cerebrolysin and E021 increased GluR1 density in most measured regions of the hippocampal formation in a highly significant way. These results correlate with the behavioural outcome, revealing an improvement in learning and memory of these rats after treatment with Cerebrolysin and E021.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Advokat C, Pellegrin AI (1992) Excitatory amino acids and memory: Evidence from research on Alzheimer's Disease and Behavioral Pharmacology. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 16: 13–24.
Akai F, Hiruma S, Sato T, Iwamoto N, Fujimoto M, Ioku M, Hashimoto S (1992) Neurotrophic factor-like effect of FPF1070 on septal cholinergic neurons after transection of fimbria-fornix in the rat brain. Histol Histopathol 7: 213–221.
Albrecht E, Hingel S, Crailsheim K, Windisch M (1993) The effects of Cerebrolysin on survival and sprouting of neurones from cerebral hemispheres and from the brainstem of chick embryos in vitro. Adv Biosci 87: 341–442.
Armstrong DM, Ikonomovic MD (1996) AMPA-selective glutamate receptor subtype immunoreactivity in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of patients with Alzheimer Disease. Mol Chem Neuropath 28: 59–64.
Bae CY, Cho CY, Cho K, Hoon OHB, Choi KG, Lee HS, Jung SP, Kim DH, Lee S, Choi GD, Cho H, Lee H (2000) A double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study of Cerebrolysin for Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc 12: 1566–1571.
Boado RJ (1996a) Molecular regulation of the blood-brain barrier GLUT1 glucose transporter reporter by brain derived peptides. J Neural Transm 47: 275.
Boado RJ (1996b) Brain derived peptides increase the expression of a blood-brain barrier GLUT1 glucose reporter gene. Neurosci Lett 220: 53–56.
Boado RJ, Wu D, Windisch M(1999) In vivo upregulation of the blood- brain barrier GLUT1 glucose transporter by brain-derived peptides. Neurosci Res 34: 217–224.
Chan SL, Griffin WS, Mattson MP (1999) Evidence for caspasemediated cleavage of AMPA receptor subunits in neuronal apoptosis and Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci Res 57: 315–323.
Clark AS, Magnusson KR, Cotman CW (1992) In vitro autoradiography of hippocampal excitatory amino acid binding in aged Fischer 344 rats: Relationship to performance on the Morris water maze. Behav Neurosci 106: 324–335.
Dewar D, Chalmers DT, Graham DI, Mcculloch J (1991) Glutamate metabotropic and AMPA binding sites are reduced in Alzheimer's disease: An autoradiographic study of the hippocampus. Brain Res 553: 58–64.
Francis-Turner L, Valouskova V (1996) Nerve growth factor and nootropic drug Cerebrolysin but not fibroblast growth factor can reduce spatial memory impairment elicited by fimbria-fornix transection: Short-term study. Neurosci Lett 202: 1–4.
Garcia-Ladona FJ, Palacios JM, Probst A, Wieser HG, Mengod G (1994) Excitatory amino acid AMPA receptor mRNA localization in several regions of normal and neurological disease affected human brain. An in situ hybridization histochemistry study. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 21: 75–84.
Greenamyre JT, Maragos WF, Albin RL, Penney JB, Young AB (1988) Glutamate transmission and toxicity in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiat 12: 421–430.
Gschanes A, Windisch M, Bures J (1993) Cerebrolysin, a peptidergic drug, increases performance of ischemic rats in the morris water maze. Eur J Neurosci 6: 543.
Gschanes A, Valouskova V, Windisch M (1997) Ameliorative influence of a nootropic drug on motor activity of rats after bilateral carotid artery occlusion. J Neural Transm 104: 1319–1327.
Gschanes A, Windisch M(1998) The influence of Cerebrolysin and E021 on spatial navigation of 24–month-old rats. J Neural Transm Suppl 53: 313–321.
Gschanes A, Windisch M (1999) Early postnatal treatment with peptide preparations influences spatial navigation of young and adult rats. Behav Brain Res 100: 161–166.
Gschanes A, Boado R, Sametz W, Windisch M (2000) The drug Cerebrolysin and its peptide fraction E021 increase the abundance of the blood-brain barrier GLUT1 glucose transporter in brains of young and old rats. Histochem J 32: 71–77.
Hampson DR, Windisch M, Baskys A(1997) Increased binding ofBDNF to TrkB induced by the antidementia drug Cerebrolysin. Soc Neurosci 23: 1896.
Hartbauer M, Hutter-Paier B, Windisch M(2001) Effects of Cerebrolysin on the outgrowth and protection of processes of cultured brain neurons. J Neural Transm 108: 581–592.
Hollmann M, Heinemann S (1994) Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 17: 31–108.
Huang FN, Li WB, Zhang BL, Cui X, Zhang J (1998) Effects of Aβ1–40 on the functions of expressed glutamate receptors and the protective effects of brain derived peptides. Neurobiol Aging 19: 40.
Hutter-Paier B, Eggenreich U, Windisch M (1996a) Dose-dependent behavioural effects of two protein-free peptide derivatives on the passive avoidance reaction of rats. Drug Res 46(1): 242–246.
Hutter-Paier B, Eggenreich U, Windisch M (1996b) Effects of two protein-free peptide derivatives on passive avoidance behaviour of 24–month-old rats. Drug Res 46(1): 237–241.
Hutter-Paier B, Grygar E, Windisch M (1996c) Death of cultured telencephalon neurons induced by glutamate is reduced by the peptide derivative Cerebrolysin. J Neural Transm 47: 267–273.
Hutter-Paier B, Grygar E, Frühwirth M, Temmel I, Windisch M (1998a) Further evidence that Cerebrolysin protects cortical neurons from neurodegeneration in vitro. J Neural Transm Suppl 53: 363–372.
Hutter-Paier B, Steiner E, Windisch M (1998b) Cerebrolysin protects isolated cortical neurons from neurodegeneration after brief histotoxic hypoxia. J Neural Transm Suppl 53: 351–361.
Hyman BT, Penney JB, Blackstone CD, Young AB (1994) Localization of Non-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Glutamate receptors in normal and Alzheimer Hippocampal Formation. Ann Neurol 35: 31–37.
Johnston D, Amaral DG (1998) Hippocampus. In: Shepherd GM, ed. The Synaptic Organization of the Brain. 4th edn., New York/Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 417–458.
Kadar T, Silbermann M, Brandeis R, Levy A (1990) Age-related structural changes in the rat hippocampus: Correlation with working memory deficiency. Brain Res 512: 113–120.
Kadar T, Arbel I, Silbermann M, Levy A (1994) Morphological hippocampal changes during normal aging and their relation to cognitive deterioration. J Neural Transm 44: 133–143.
Krieglstein J (1997) Excitotoxicity and neuroprotection. Eur J Pharm Sci 5: 181–187.
McBain CJ, Fisahn A (2001) Interneurons unbound. Nat Rev Neurosci 2: 11–23.
Michaelis EK (1998) Molecular biology of glutamate receptors in the central nervous system and their role in excitotoxicity, oxidative stress and aging. Prog Neurobiol 54: 369–415.
Molnar E, Mcilhinney RA, Baude A, Nusser Z, Somogyi P (1994) Membrane topology of the GluR1 glutamate receptor subunit: Epitope mapping by site-directed antipeptide antibodies. J Neurochem 63: 683–693.
Narisawa-Saito M, Wakabayashi K, Tsuji S, Takahashi H, Nawa H(1996) Regional specificity of alterations in NGF, BDNF and NT-3 levels in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroreport 7: 2925–2928.
Narisawa-Saito M, Carnahan J, Araki K, Yamaguchi T, Nawa H (1999) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates the expression of AMPA receptor proteins in neocortical neurons. Neuroscience 88: 1009–1014.
Nicolle MM, Bizon JL, Gallagher M (1996) In vitro autoradiography of ionotropic glutamate receptors in hippocampus and striatum of aged Long-Evans rats: Relationship to spatial learning. Neuroscience 74: 741–756.
Nordberg AGNE (1992) Neuroreceptor changes in Alzheimer Disease. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 4: 303–328.
Pagliusi SR, Gerrard P, Abdallah M, Talabot D, Catsicas S (1994) Agerelated changes in expression of Ampa-selective glutamate receptor subunits: Is calcium-permeability altered in hippocampal neurons? Neuroscience 61: 429–433.
Pintor A, Tiburzi F, Pezzola A, Volpe MT (1998) Metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist (1S,3 R-ACPD) increased frontal cortex dopamine release in aged but not in young rats. Eur J Pharmacol 359: 139–142.
Rainer M, Windisch M, Moessler H (1998) Open-label study of Cerebrolysin in the treatment of dementia under conditions of daily clinical practice. Neurobiol Aging 19: 184.
Reinprecht I, Gschanes A, Windisch M, Fachbach G (1999) Two peptidergic drugs increase the synaptophysin immunoreactivity in brains of 24–month-old rats. Histochem J 31: 395–401.
Riedel G, Micheau J, Lam AG, Roloff E, Martin SJ, Bridge H, Hoz L, Poeschel B, Mcculloch J, Morris RG (1999) Reversible neural inactivation reveals hippocampal participation in several memory processes. Nat Neurosci 2: 898–905.
Rüther E, Ritter R, Apecechea M, Freytag S, Windisch M (1994) Effi-cacy of the peptidergic nootropic drug Cerebrolysin in patients with senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (SDAT). Pharmacopsychiatry 27: 32–40.
Satou T, Itoh T, Tamai Y, Ohde H, Anderson A, Hashimoto S (2000) Neurotrophic effects of FPF-1070 (Cerebrolysin) on cultured neurons from chicken embryo dorsal root ganglia, ciliary ganglia and sympathetic trunks. J Neural Transm 107: 1253–1262.
Schwab M, Bauer R, Zwiener U (1995) Effects of CERE on ECoG during moderate forebrain ischemia under normothermic and hypothermic conditions. In: Eiselt M, Zwiener U, Witte H, eds. Quantitative and Topological EEG and MEG Analysis. Jena: Universitätsverlag, pp. 243–247
Schwab M, Bauer R, Zwiener U (1997) Physiological effects and brain protection by hypothermia and Cerebrolysin after moderate forebrain ischemia in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 49: 105–116.
Sugita Y, Kondo T, Kanazawa A, Itou T, Mizuno Y (1993) Protective effect of FPF (Cerebrolysin) on delayed neuronal death in the gerbildetection of hydroxyl radicals with salicylic acid. Brain and Nerve 45: 325–331.
Swanson LW (1998) Brain Maps: Structure of the Rat Brain. 2nd edn., Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier Science.
Tamaru M, Yoneda Y, Ogita K, Shimizu J, Nagata Y (1991) Age-related decreases of theN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor complex in the rat cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Brain Res 542: 83–90.
Terry RD, Masliah E, Hansen LA (1999) The neuropathology of Alzheimer Disease and the structural basis of its cognitive alterations. In: Terry RD, Katzman R, Bick KL, Sisodia SS, eds. Alzheimer Disease. 2nd edn., Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, pp. 187–206.
Ueki A, Miwa C, Shinjo H, Kokai M, Morita Y(1997) Synapse alteration in hippocampal CA3 field following entorhinal cortex lesion. J Neurol Sci 151: 1–5.
Vereschagin N, Nekrasova Y, Lebedova N, Suslina Z, Soloviev O, Priadov M, Altunina M (1991) Mild forms of multi-infarct dementia: Efficacy of cerebrolysin. Sovjetskaja Medicina 11: 1–6.
Verkhratsky A, Toescu EC (1998) Calcium and neuronal ageing. Trends Neurosci 21: 2–7.
Wakabayashi K, Narisawa-Saito M, Iwakura Y, Arai T, Ikeda K, Takahashi H, Nawa H (1999) Phenotypic down-regulation of glutamate receptor subunit GluR1 in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 20: 287–295.
Wang Y, Tesfaye E, Yasuda RP, Mash DC, Armstrong DM, Wolfe BB (2000) Effects of post-mortem delay on subunits of ionotropic glutamate receptors in human brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 80: 123–131.
Wenzel J, Stender G, Duwe G (1981) DeZur Entwicklung der Neuronenstruktur der Fascia dentata bei der Ratte. Neurohistologischmorphometrische, ultrastrukturelle und experimentelle Untersuchungen. DeJ Hirnforsch 22: 629–683.
Windholz E, Gschanes A, Windisch M, Fachbach G (2000) Two peptidergic drugs increase the synaptophysin immunoreactivity in brains of 6–week-old rats. Histochem J 32: 79–84.
Windisch M, Gschanes A, Valouskova V (1993) The effects of different growth factors in rats after lesions of the somato sensory cortex. Eur J Neurosci 6: 542.
Windisch M, Gschanes A, Hutter-Paier B(1998a) Neurotrophic activities and therapeutic experience with a brain derived peptide preparation. J Neural Transm Suppl 53: 289–298.
Windisch M, Grygar E, Hutter-Paier B (1998b) Cerebrolysin enhances the protective effects of MK-801 against neuronal degeneration in vitro. Neurobiol Aging 19: 260.
Wronski R, Hutter-Paier B, Crailsheim K, Windisch M (1998) The peptide derivative Cerebrolysin inhibits the calcium dependent protease Calpain II. Neurobiol Aging 19: 185.
Yasuda RP, Ikonomovic MD, Sheffield R, Rubin RT, Wolfe BB, Armstrong DM(1995) Reduction ofAMPA-selective glutamate receptor subunits in the entorhinal cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease pathology: A biochemical study. Brain Res 678: 161–167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eder, P., Reinprecht, I., Schreiner, E. et al. Increased Density of Glutamate Receptor Subunit 1 Due to Cerebrolysin Treatment: An Immunohistochemical Study on Aged Rats. Histochem J 33, 605–612 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016394031947
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016394031947