Abstract
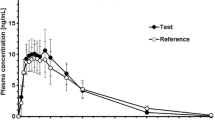
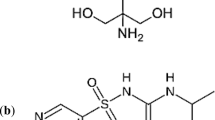
Ketorolac tromethamine (KT), a potent analgesic with cyclooxygenase inhibitory activity, was administered in an open, randomized, single-dose study of Latin-square design to 12 healthy male volunteers. Doses of 30 mg oral (po) and 30, 60, and 90 mg intramuscular (im) KT were administered in solution. Plasma samples were analyzed for ketorolac (K) and its inactive metabolite, p-hydroxyketorolac (PHK), by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The 30-mg im dose was found to be similar to the 30-mg po dose with respect to total AUC values for both K and PHK. The amount of PHK circulating in plasma was very low as judged by AUC ratios (PHK/K × 100) of 1.9 and 1.5% for the 30-mg po and im doses, respectively. The rate of absorption of K and formation of PHK, as determined by C max and T max values, was significantly slower following the im doses. Total AUC and C max for K and PHK increased linearly with dose after im administration of 30, 60, and 90 mg of KT. The mean plasma half-life of K was remarkably consistent between po and im administration and was independent of dose, ranging from 5.21 to 5.56 hr. The plasma metabolic profile was similar following both routes of administration and graded im doses.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
K. Hillier. Drugs Future. 6:669–670 (1981).
J. M. Muchowski, S. H. Unger, J. Ackrell, et al. J. Med. Chem. 28:1037–1049 (1982).
W. H. Rooks, A. J. Tomolonis, P. J. Maloney, M. B. Wallach, and M. E. Schuler. Agents Actions 12:684–690 (1982).
W. H. Rooks, P. J. Maloney, L. D. Shott, M. E. Schuler, H. Sevelius, A. H. Strosberg, L. Tannenbaum, A. J. Tomolonis, M. B. Wallach, D. Waterburg, and J. P. Yee. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 11:479–482 (1985).
S. S. Bloomfield, J. Mitchell, G. Cissell, and T. P. Barden. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 35:228 (1984).
J. Yee, C. R. Brown, H. Sevelius, and V. Wild. Curr. Ther. Res. 35:284 (1984).
J. Yee, C. Allison, J. Koshiver, and C. R. Brown. Pharmacotherapy 6:253–261 (1986).
C. R. Brown, V. M. Wild, and L. Bynum. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 43:142 (1988).
M. Staquet, J. Lloyd, and R. Bullingham. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 43:159 (1988).
A. T. Wu and I. J. Massey. Am. Pharm. Assoc. Abstr. 16:145 (1986).
SAS Institute Inc. SAS User's Guide: Statistics, Version 5 Edition, SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, N.C., 1985.
R. J. Miller. Simultaneous Statistical Inference, 2nd ed., Springer-Verlag, New York, 1981.
D. Jung, E. Mroszczak, and L. Bynum. Submitted for publication.
E. J. Mroszczak, T. Ling, J. Yee, I. Massey, and H. Sevelius. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 37:215 (1985).
E. Mroszczak, F. W. Lee, D. Combs, F. H. Sarnquist, B.-L. Huang, A. T. Wu, L. G. Tokes, M. L. Maddox, and D. K. Cho. Drug Metab. Disp. 15:618–626 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, D., Mroszczak, E.J., Wu, A. et al. Pharmacokinetics of Ketorolac and p-Hydroxyketorolac Following Oral and Intramuscular Administration of Ketorolac Tromethamine. Pharm Res 6, 62–65 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015803803650
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015803803650