Abstract
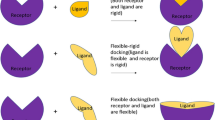
A method of structure-based ligand design – DycoBlock – has been proposed and tested by Liu et al.[1]. It was further improved by Zhu et al. and applied to design new selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase 2 [2]. In the current work, we present a new methodology – F-DycoBlock that allows for the incorporation of receptor flexibility. During the designing procedure, both the receptor and molecular building blocks are subjected to the multiple-copy stochastic molecular dynamics (MCSMD) simulation [1], while the protein moves in the mean field of all copies. It is tested for two enzymes studied previously – cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) and human immunodeficiency type 1 (HIV-1) protease. To identify the applicability of F-DycoBlock, the binding protein structure was used as starting point to explore the conformational space around the bound state. This method can be easily extended to accommodate the flexibility in different degree. Four types of treatment of the receptor flexibility – all-atom restrained, backbone restrained, intramolecular hydrogen-bond restrained and active-site flexible – were tested with or without the grid approximation. Two inhibitors, SC-558 for COX-2 and L700417 for HIV-1 protease, are used in this testing study for comparison with previous results. The accuracy of recovery, binding energy, solvent accessible surface area (SASA) and positional root-mean-square (RMS) deviation are used as criteria. The results indicate that F-DycoBlock is a robust methodology for flexible drug design. It is particularly notable that the protein flexibility has been perfectly associated with each stage of drug design – search for the binding sites, dynamic assembly and optimization of candidate compounds. When all protein atoms were restrained, F-DycoBlock yielded higher accuracy of recovery than DycoBlock (100%). If backbone atoms were restrained, the same ratio of accuracy was achieved. Moreover, with the intramolecular hydrogen bonds restrained, reasonable conformational changes were observed for HIV-1 protease during the long-time MCSMD simulation and L700417 was reassembled at the active site. It makes it possible to study the receptor motion in the binding process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, H.-Y., Duan, Z.-H., Luo, Q.-M. and Shi, Y.-Y., Proteins, 36 (1999) 462.
Zhu, J., Yu, H.B., Fan, H., Liu, H.-Y. and Shi, Y.-Y., J. Comput. Aid. Mol. Des., 15 (2001) 447.
Böhm, H.J., J. Comput. Aid. Mol. Des., 6 (1992) 61.
Eisen, M.B., Wiley, D.C., Karplus, M. and Hubbard, R.E., Proteins, 19 (1994) 199.
Pearlman, D.A. and Murcko, M.A., J. Med. Chem., 39 (1996) 1651.
Bryngelson, J.D. and Wolynes, P.G., J. Phys. Chem., 93 (1989) 6902.
Shakhnovitch, E.T. and Gutin, A.M., Protein Eng., 6 (1993) 793.
Boczko, E.M. and Brooks, C.L. III, Science, 269 (1995) 393.
Dill, K.A. and Chan, H.S., Protein Sci., 4 (1995) 561.
Karplus, M., Sali, A. and Shakhnovitch, E.T., Nature (London), 373 (1995) 664.
Onuchic, J.N., Wolynes, P.G., Luthey-Schulten, Z. and Socci, N.D., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92 (1995) 3626.
Wolynes, P.G., Onuchic, J.N. and Thirumalai, D., Science, 267 (1995) 1619.
Dill, K.A. and Chan, H.S., Nature Struct. Biol., 4 (1997) 10.
Karplus, M., Folding Des., 2 (1997) S69.
Lazaridis, T. and Karplus, M., Science, 278 (1997) 1928.
Gruebele, M. and Wolynes, P.G., Nature Struct. Biol., 5 (1998) 662.
Martinez, J.C., Pisabarro, M.T. and Serrano, L., Nature Struct. Biol., 5 (1998) 721.
Dill, K.A., Protein Sci., 6 (1999) 1166.
Tsai, C.-J., Kumar, S., Ma, B. and Nussinov, R., Protein Sci., 6 (1999) 1181.
Fischer, E., Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 27 (1894) 2985.
Koshland, D.E., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 44 (1958) 98.
Ma, B., Kumar, S., Tsai, C.-J. and Nussinov, R., Protein Eng., 12 (1999) 713.
Carlson, H.A. and McCammon, J.A., Mol. Pharmacol., 57 (2000) 213.
Gschwend, D.A., Good, A.C. and Kuntz, I.D., J. Mol. Rec., 9 (1996) 175.
Schnecke, V., Swanson, C.A., Getzoff, E.D., Tainer, J.A. and Kuhn, L.A., Proteins, 33 (1998) 74.
Leach, A.R., J. Mol. Biol., 235 (1994) 345.
Lamb, M.L. and Jorgensen, W.L., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 1 (1997) 449.
Miranker, A. and Karplus, M., Proteins, 11 (1991) 29.
Stultz, C.M. and Karplus, M., Proteins, 37 (1999) 512.
Stultz, C.M. and Karplus, M., Proteins, 40 (2000) 258.
Elber, R. and Karplus, M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 112 (1990) 9161.
Roitberg, A. and Elber, R., J. Chem. Phys., 95 (1991) 9277.
Zheng, Q., Rosenfeld, R. and Kyle. D.J., J. Chem. Phys., 99 (1993) 8892.
Zheng, W.-M. and Zheng, Q., J. Chem. Phys., 106 (1997) 1191.
Koehl, P. and Delarue, M., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 6 (1996) 222.
Zheng, Q. and Kyle, D.J., Proteins, 19 (1994) 324.
Frisch, M.J., Trucks, G.W., Schlegel, H.B., Scuseria, G.E., Robb, M.A., Cheeseman, J.R., Zakrzewski, V.G., Montgomery, J.A., Jr., Stratmann, R.E., Burant, J.C., Dapprich, S., Millam, J.M., Daniels, A.D., Kudin, K.N., Strain, M.C., Farkas, O., Tomasi, J., Barone, V., Cossi, M., Cammi, R., Mennucci, B., Pomelli, C., Adamo, C., Clifford, S., Ochterski, J., Petersson, G.A., Ayala, P.Y., Cui, Q., Morokuma, K., Malick, D.K., Rabuck, A.D., Raghavachari, K., Foresman, J.B., Cioslowski, J., Ortiz, J.V., Baboul, A.G., Stefanov, B.B., Liu, G., Liashenko, A., Piskorz, P., Komaromi, I., Gomperts, R., Martin, R.L., Fox, D.J., Keith, T., Al-Laham, M.A., Peng, C.Y., Nanayakkara, A., Gonzalez, C., Challacombe, M., Gill, P.M.W., Johnson, B., Chen, W., Wong, M.W., Andres, J.L., Gonzalez, C., Head-Gordon, M., Replogle, E.S. and Pople, J.A., Gaussian 98, Revision A.7, Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh PA, 1998.
van Gunsteren, W.F., Billeter, S.R., Eising, A.A., Hunenberger, P.H., Kruger, P., Mark, A.E., Scott, W.R.P. and Tironi, I.G., Biomolecular simulation: the GROMOS96 manual and user guide. University of Groningen, the Netherlands, ETH Zurich, Switzerland: Biomos, 1996.
Berendsen, H.J.C., Postma, J.P.M., van Gunsteren, W.F., Dinola, A. and Haak, J.R., J. Chem. Phys., 81 (1984) 3684.
Ryckaert, J.P., Ciccotti, G. and Berendsen, H.J.C., J. Comput. Phys., 23 (1977) 327.
Stouten, P.F.W., Frommel, C., NaKamura, H. and Sander, C., Mol. Simul., 10 (1993) 97.
DeWitt, D.L., El-Harith, E.A., Kraemer, S.A., Andrews, M.J., Yao, E.F., Armstrong, R.L. and Smith, W.L., J. Biol. Chem., 265 (1990) 5192.
Seibert, K., Zhang, Y., Leahy, K., Hauser, S., Masferrer, J., Perkins, W., Lee, L. and Isakson, P., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91 (1994) 12013.
Masferrer, J.L., Zweifel, B.S., Manning, P.T., Hauser, S.D., Leahy, K.M., Smith, W.G.
Isakson, P.C. and Seibert, K., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91 (1994) 3228.
Berendsen, H.J.C., Postma, J.P.M., van Gunsteren, W.F. and Hermans, J., In: Intermolecular Forces, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, pp. 331–342.
Totrov, M. and Abagyan, R., Proteins, Suppl. 1 (1997) 215.
Schaffer, L. and Verkhivker, G.M., Proteins, 33 (1998) 295.
Straub, J.E. and Karplus. M., J. Chem. Phys., 94 (1991) 6737.
Zacharias, M., Luty, B.A., Davis, M.E. and McCammon, J.A., J. Mol. Biol., 238 (1994) 455.
Huber, T., Torda, A.E. and van Gunsteren, W.F., Biopolymers, 39 (1996) 103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Fan, H., Liu, H. et al. Structure-based ligand design for flexible proteins: Application of new F-DycoBlock. J Comput Aided Mol Des 15, 979–996 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014817911249
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014817911249