Abstract
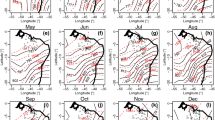
Two cases of on-ice and off-ice air flow characterizing the opposite weather situations over the ice-edge zone in the northern Baltic Sea are analysed on the basis of aircraft observations, and modelled using atwo-dimensional mesoscale model. The stable boundary layer (SBL) during theon-ice flow exhibited little thermal modification, but a low-level jet (LLJ) was generated at the 250-m high top of the SBL. In the model, the LLJ was associated with inertial oscillations in space, while the baroclinicity explained the shape of the wind profile well above the SBL. Although the observed LLJ was most pronounced over the ice, the modelling suggests that it was not generated by the ice edge but by the coastline some 400 km upwind of the ice edge, where a much more drastic change in the thermal stratification and surface roughness took place. The generation, maintenance, and strength of the LLJ were very sensitive to the parameterization of turbulent mixing in the SBL. In the case of the off-ice flow, the modification of the air mass and the development of a convective boundary layer (CBL) both over the ice and open sea were reasonably well modelled. Sensitivity runs suggested that it was essential to take into account the effects of subgrid-scale leads, a forest in the archipelago (which was crossed by the air flow), and water vapour condensationinto ice crystals. The heat flux from leads was particularly important for the heatbudget of the CBL, and the observed growth of the CBL was partly due to theeffective mixing over the rough and relatively warm forest.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alestalo, M. and Savijärvi, H.: 1985, 'Mesoscale Circulations in a Hydrostatic Model: Coastal Convergence and Orographic Lifting', Tellus 37A, 156-162.
Andersson, T. and Gustafsson, N.: 1994, 'Coast of Departure and Coast of Arrival: Two Important Concepts for the Formation and Structure of Convective Snowbands over Seas and Lakes', Mon. Wea. Rev. 122, 1036-1049.
Andersson, T. and Michelson, D. B.: 1999, 'The December 1998 Snowfall over Sweden as Seen by Weather Radars', Polarfront, Swedish Meteorological Society, Norrköping, No. 100-101, pp. 26-33.
Andreas, E. L., Claffey, K. J., and Makshtas, A. P.: 2000, 'Low-Level Atmospheric Jets and Inversions over the Weddell Sea', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 97, 459-486.
Andreas, E. L., Tucker III, W. B., and Ackley, S. F.: 1984, 'Atmospheric Boundary-Layer Modification, Drag Coefficient, and Surface Heat Flux in the Antarctic Marginal Ice Zone', J. Geophys. Res. 89, 649-661.
Bennett, Jr., T. J. and Hunkins, K.: 1986, 'Atmospheric Boundary LayerModification in the Marginal Ice Zone', J. Geophys. Res. 91, 13033-13044.
Buck, A. L.: 1981, 'New Equations for Computing Vapour Pressure and Enhancement Factor', J. Appl. Meteorol. 20, 1527-1532.
Brümmer, B.: 1997, 'Boundary Layer Mass, Water, and Heat Budgets in Wintertime Cold-Air Outbreaks from the Arctic Sea Ice', Mon. Wea. Rev. 125, 1824-1837.
Brümmer, B. and Latif M.: 1985, 'Some Studies on Inflection Point Instability', Contr. Atmos. Phys. 58, 117-126.
Brümmer, B. and Müller, G.: 1999, 'Boundary Layer Measurements with Research Aircraft Falcon', in J. Launiainen (ed.), BALTEX-BASIS Data Report 1998, Int. BALTEX Secretariat Publ., Vol. 1, Geesthacht, Germany, pp. 26-38.
Brümmer, B., Busack, B., Hoeber, H., and Kruspe, G.: 1994, 'Boundary-Layer Observations over Water and Arctic Sea Ice During On-Ice Air Flow', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 68, 75-108.
Cheng, B., Launiainen, J., Vihma, T., and Uotila, J.: 2001, 'Modelling Sea Ice Thermodynamics in BALTEX-BASIS', Ann. Glaciol., in press.
Chrobok, G., Raasch, S., and Etling, D.: 1992, 'A Comparison of Local and Non-Local Turbulence Closure Methods for the Case of a Cold Air Outbreak', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 58, 69-90.
Gustafsson, N., Nyberg, L., and Omstedt, A.: 1998, 'Coupling of a High-Resolution Atmospheric Model and an Ocean Model for the Baltic Sea', Mon. Wea. Rev. 126, 2822-2846.
Gryning, S.-E. and Batchvarova, E.: 2002, 'Marine Boundary Layer and Turbulent Fluxes over the Baltic Sea: Measurements and Modelling', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 103, 29-47.
Gryning, S.-E., Batchvarova, E., and De Bruin, H. A. R.: 2001, 'Energy Balance of a Sparse Coniferous High-Latitude Forest under Winter Conditions', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 99, 465-488.
Häggmark, L., Ivarsson, K. I., Gollvik, S., and Olofsson, P. O.: 2000, 'Mesan, an Operational Mesoscale Analysis System', Tellus 52A, 2-20.
Hartmann, J., Kottmeier, C., and Raasch, S.: 1997, 'Roll Vortices and Boundary-Layer Development During a Cold Air Outbreak', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 84, 45-65.
Högström, U.: 1988, 'Non-Dimensional Wind and Temperature Profiles in the Atmospheric Surface Layer: A Re-Evaluation', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 42, 55-78.
Högström, U. and Smedman, A.-S.: 1984, 'The Wind Regime in Coastal Areas with Special Reference to Results Obtained from Swedish Wind Energy Program', Boundary Layer Meteorol. 30, 351-373.
Holtslag, A. A. M. and de Bruin, H. A. R.: 1988, 'Applied Modeling of the Nighttime Surface Energy Balance over Land', J. Appl. Meteorol. 37, 689-704.
Holtslag, A. A. M. and Moeng, C.-H.: 1991, 'Eddy Diffusivity and Countergradient Transport in the Convective Atmospheric Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 48, 1690-1698.
Joffre, S. M.: 1982, 'Momentum and Heat Transfers in the Surface Layer over a Frozen Sea', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 24, 211-229.
Joffre, S. M.: 1983, 'Determining the Form Drag Contribution to the Total Stress of the Atmospheric Flow over Ridged Sea Ice', J. Geophys. Res. 88, 4524-4530.
Källstrand, B.: 1998, 'Low Level Jets in a Marine Boundary Layer during Spring', Contr. Atmos. Phys. 71, 359-373.
King, J. C. and Turner, J.: 1997, Antarctic Meteorology and Climatology, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., 409 pp.
Langland, R. H., Tag, P. M., and Fett, R. W.: 1989, 'An Ice Breeze Mechanism for Boundary-Layer Jets', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 48, 177-195.
Launiainen, J. (ed.): 1999, BALTEX-BASIS Data Report 1998, Int. BALTEX Secretariat Publ., Vol. 14, Geesthacht, Germany, 94 pp.
Launiainen, J. and Cheng, B.: 1998, 'Modelling of Ice Thermodynamics in Natural Water Bodies', Cold Reg. Sci. Tech. 27, 153-178.
Launiainen, J. and Laurila, T.: 1984, 'Marine Wind Characteristics in the Northern Baltic Sea', Finnish Marine Res. 250, 52-86.
Launiainen, J., Cheng, B., Uotila, J., and Vihma, T.: 2001, 'Turbulent Surface Fluxes and Air-Ice Coupling in BASIS', Ann. Glaciol. in press.
Lenschow, D. H.: 1973, 'Two Examples of Planetary Boundary Layer Modification over the Great Lakes', J. Atmos. Sci. 30, 568-581.
Lüpkes, C. and Schlünzen, K. H.: 1996, 'Modelling the Arctic Convective Boundary-Layer with Different Turbulence Parameterizations', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 79, 107-130.
Mahrt, L.: 1981, 'Modelling the Depth of the Stable Boundary Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 21, 3-19.
Mai, S., Wamser, C., and Kottmeier, C.: 1996, 'Geometric and Aerodynamic Roughness of Sea Ice', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 77, 233-248.
Ni, W. and Woodcock, C. E.: 2000, 'Effect of Canopy Structure and the Presence of Snow on the Albedo of Boreal Conifer Forests', J. Geophys. Res. 105, 11879-11888.
Olsson, P. Q. and Harrington, J. Y.: 2000, 'Dynamics and Energetics of the Cloudy Boundary Layer in Simulations of Off-Ice Flow in the Marginal Ice Zone', J. Geophys. Res. 105, 11889-11899.
Raasch, S.: 1990, 'Numerical Simulation of the Development of the Convective Boundary Layer during a Cold Air Outbreak', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 52, 349-375.
Renfrew, I. A. and Moore, G. W. K.: 1999, 'An Extreme Cold Air Outbreak over the Labrador Sea: Roll Vortices and Air-Sea Interaction', Mon. Wea. Rev. 127, 2379-2394.
Savijärvi, H.: 1991, 'The United States Great Plains Diurnal ABL Variation and the Nocturnal Lowlevel Jet', Mon. Wea. Rev. 119, 833-840.
Savijärvi, H.: 1997, 'Diurnal Winds around Lake Tanganyika', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 123, 901-918.
Savijärvi, H. and Alestalo, M.: 1988, 'Sea Breeze over a Lake or Gulf as the Function of the Prevailing Flow', Contr. Atmos. Phys. 61, 98-104.
Smedman, A.-S., Tjernstróm, M., and Högström, U.: 1993, 'Analysis of the Turbulence Structure of a Marine Low-Level Jet', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 66, 105-126.
Smith, S. D.: 1988, 'Coefficients for Sea Surface Wind Stress, Heat Flux, and Wind Profiles as a Function of Wind Speed and Temperature', J. Geophys. Res. 93, 15,467-15,472.
Thorpe, A. J. and Guymer, T. H.: 1977, 'The Nocturnal Jet', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 103, 633-653.
Uotila, J., Vihma, T., and Launiainen, J.: 1997, Marine Meteorological Radiosoundings in the Northern Baltic Sea from R/V Aranda in 1994-95, Meri, Report Series of The Finnish Institute of Marine Research, Vol. 30, 57 pp.
Vihma, T.: 1995, 'Subgrid Parameterization of Surface Heat and Momentum Fluxes over Polar Oceans', J. Geophys. Res. 100, 22,625-22,646.
Vihma, T. and Kottmeier, C.: 2000, 'A Modelling Approach for Optimizing Flight Patterns in Airborne Meteorological Measurements', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 95, 211-230.
Vihma, T. and Savijärvi, H.: 1991, 'On the Effective Roughness Length for Heterogeneous Terrain', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 117, 399-407.
Vihma, T., Uotila, J., Cheng, B., Purokoski, T., Kosloff, P., Launiainen, J., and Schrum, C.: 1999, 'Marine Meteorological, Sea Ice and Oceanographic Observations by the Finnish Institute of Marine Research', in J. Launiainen (ed.), BALTEX-BASIS Data Report 1998, Int. BALTEX Secretariat Publ., Vol. 14, Geesthacht, Germany, pp. 14-25.
Vihma, T., Uotila, J., and Launiainen, J.: 1998, 'Air-sea Interaction over a Thermal Marine front in the Denmark Strait', J. Geophys. Res. 103, 27,665-27,678.
Wu, J.: 1980, 'Wind Stress Coefficients over Sea Surface, a Revisit', J. Phys. Oceanog. 10, 727-740.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vihma, T., Brümmer, B. Observations And Modelling Of The On-Ice And Off-Ice Air Flow Over The Northern Baltic Sea. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 103, 1–27 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014566530774
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014566530774