Abstract
Using cDNA from a CRFK cell line as a template, PCR amplification was performed with the Ub1S and poly(dT) primers to isolate feline ubiquitin genes. Sequencing of the 495 bp PCR fragment revealed that the putative amino acids induced by this fragment gave a fusion protein consisting of a ubiquitin polypeptide (76 amino acids) and an extension protein of ribosomal proteins L40 (52 amino acids). The putative amino acid sequence of ubiquitin was identical to those of humans, rats and pigs.
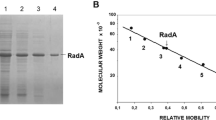
The recombinant glutathione S-transferase (GST)–feline ubiquitin fusion proteins were produced in Escherichia coli and purified. The fusion proteins had a molecular weight of about 42 kDa and were detected by immunoblot assay with rabbit anti-ubiquitin antiserum.
The mRNAs from heat-shocked and non-heat-shocked cells were subjected to RT-PCR (Ub1S and poly(dT) primers) analysis. The molecular weights of the ubiquitinated proteins in heat-shocked CFRK cells were between 18 kDa and 24 kDa by immunoblot assay.
These results suggested that there were more ubiquinated proteins in the heat-shocked CRFK cells than in the pre-heat-shocked cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bond, U. and Schlesinger, M.J., 1985. Ubiquitin is a heat shock protein in chicken embryo fibroblast. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 5, 949-956
Chan, Y.-L., Suzuki, K. and Wool, I.G., 1995. The carboxyl extensions of two rat ubiquitin fusion proteins are ribosomal proteins S27a and L40. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 215, 682-690
Chwetzoff, S. and d'Andrea, S., 1997. Ubiquitin is physiologically induced by interferons in luminal epithelium of porcine uterine endometrium in early pregnancy: global RT-PCR cDNA in place of RNA for differential display screening. FEBS Letters, 405, 148-152
Epstein, F.H., 1996. Mechanisms of muscle wasting. New England Journal of Medicine, 335, 1897-1905
Hass, A.L., Baboshina, O., Williams, B. and Schwartzn, L.M., 1995. Coordinated induction of the ubiquitin conjugation pathway accompanies the developmentally programmed death of insect skeletal muscle. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 270, 9407-9412
Hershko, A., Heller, H., Elias, S. and Ciechanover, A., 1983. Components of ubiquitin-protein ligase system. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 258, 8206-8214
Hershko, A. and Ciechanover, A., 1992. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 61, 760-807
Ibrahim, P., 1998. Production of anti-polyubiquitin and anti-ubiquitin carboxyl terminal hydrolase antibodies and immunohistochemical assessment of Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body disease. International Journal of Neuroscience, 95, 33-42
Piedimonte, G., Crinell, R., Salda, D.S., Corsi, D., Pennisi, M.G., Kramer, L., Casabianca, A., Sarli, G., Bendinelli, M., Marcato, P.S. and Magnani, M., 1999. Protein degradation and apoptotic death in lymphocytes during FIV infection: activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic system. Experimental Cell Research, 248, 381-390
Schwartz, A.L. and Ciechanover, A., 1999. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and pathogenesis of human diseases. Annual Review of Medicine, 50, 57-74
Varshavsky, A., 1992. The n-end rule. Cell, 69, 752-735
Yamao, F., 1999. Ubiquitin system: selectivity and timing of protein destruction. Journal of Biochemistry, 125, 223-229
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kano, R., Kubota, A., Nakamura, Y. et al. Feline Ubiquitin Fusion Protein Genes. Vet Res Commun 25, 615–622 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012735028363
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012735028363