Abstract
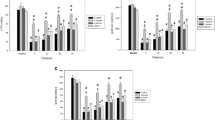
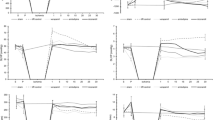
Myocardial contractile function after coronary artery bypass graft surgery is often depressed and may require inotropic support, particularly in patients on treatment with beta-adrenergic and Ca2+ blockers. In view of the increase in cytosolic Ca2+ during early reperfusion, use of Ca2+ sensitizing agents may be preferable to adrenergic agonists for enhancement of contractile function after cardioplegic arrest. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy of the Ca2+ sensitizer, levosimendan, as an inotrope on the mechanical recovery of hearts after normothermic and hypothermic cardioplegic arrest in the absence and presence of Ca2+ and beta-blockers. Isolated perfused working guinea pig hearts were perfused in the absence or presence of propranolol (10−6 M) and/or nifedipine (10−8 M), subjected to 45 minutes of normothermic or 180 minutes of hypothermic cardioplegic arrest, reperfused, and exposed to increasing concentrations of levosimendan (10−9 to 10−6 M). Levosimendan (10−7 to 10−6 M) has positive inotropic, chronotropic, and vasodilatory effects on normoxic perfused control hearts, as well as during reperfusion after 45 minutes of normothermic cardioplegic arrest. Similar effects were elicited in the presence of the blockers. Levosimendan had no stimulatory effect during reperfusion of hearts subjected to prior hypothermic arrest. Except for the increase in heart rate, the effects of levosimendan on functional performance during reperfusion were comparable with those of adrenaline. Levosimendan elicits a positive inotropic and chronotropic response during reperfusion of hearts after normothermic cardioplegic arrest, both in the absence and presence of Ca2+ and beta-adrenergic blockers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robson RH, Vishwanath MC. Nifedipine and β-blockade as a cause of cardiac failure. Br Med J 1982;284:104.
Packer MP, Meller J, Medina N, et al. Hemodynamic consequences of combined beta-adrenergic and slow calcium channel blockade in man. Circulation 1982;65:660-668.
Packer MP. Combined beta-adrenergic and calcium-entry blockade in angina pectoris. N Engl J Med 1989;320:709-718.
Marban E, Koretsune Y, Corretti M. Calcium and its role in myocardial injury during ischaemia and reperfusion. Circulation 1989;80(Suppl. VI):VI17-VI22.
Du Toit EF, Opie LH. Modulation of the severity of reperfusion stunning in the isolated rat heart by agents altering calcium flux at the onset of reperfusion. Circ Res 1992;70: 960-967.
Haikala H, Kaivola J, Nissinen E, Wall P, Levijoki J, Linden I-B. Cardiac troponin-C as a target protein for a novel calcium sensitizing drug, levosimendan. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1995;27:1859-1866.
Haikala H, Nissinen E, Etemadzadek E, Levijoki J, Linden I-B. Troponin C-mediated calcium sensitization induced by levosimendan does not impair relaxation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1995;25:794-801.
Edes I, Kiss E, Kitada Y, et al. Effect of levosimendan, a cardiotonic agent targeted to troponin C, on cardiac function and on phosphorylation and calcium sensitivity of cardiac myofibrils and sarcoplasmic reticulum in guinea pig heart. Circ Res 1995;77:107-113.
Lancaster MK, Cook SJ. The effects of levosimendan on (Ca2+)i in guinea pig isolated ventricular myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 1997;339:97-100.
Yokoshiki H, Katsube Y, Sunagawa M, Sperelakis N. The novel calcium sensitizer levosimendan activates the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in rat ventricular cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997;283:375-383.
Gruhn N, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, Theilgaard S, Bang L, Olesen SP, Aldershvile J. Coronary vasorelaxant effect of levosimendan, a new inodilator with calcium-sensitizing properties. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1998;31:741-749.
Yokoshiki H, Katsube Y, Sunagawa M, Sperelakis N. Levosimendan, a novel Ca2+-sensitizer, activates the glibenclamide-sensitiveK+ channel in rat arterial myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 1997;333:249-259.
Jamali IN, Kersten JR, Pagel PS, Hettrick DA, Warltier DC. Intracoronary levosimendan enhances contractile function of stunned myocardium. Anesth Analg 1997;85:23-29.
Kannengieser GJ, Opie LH, Van der Werff TJ. Impaired cardiac work and oxygen uptake after reperfusion of regionally ischaemic myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1979;11:197-207.
Hattingh P, Coetzee A, Harper I, Genade S, Lochner A. Effects of beta-blockers and Ca2+-antagonists on the response of the isolated working rat heart to adrenergic stimulants after cardioplegic arrest. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 1993;7:851-861.
Boknik P, Neumann J, Kaspareit G, et al. Mechanisms of the contractile effects of levosimendan in the mammalian heart. J Pharmacol Exp Therap 1997;280:277-283.
Sato S, Talukder MA, Sugawara H, Sawada H, Endoh M. Effects of levosimendan on myocardial contractility and Ca2+ transients in aequorin-loaded right-ventricular papillary muscles and Indo-1-loaded single ventricular cardiomyocytes of the rabbit. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1998;30:1115-1128.
DiFrancesco D, Mangoni M. Modulation of single hyperpolarization-activated channels (if) by cAMP in rabbit sino-atrial node. J Physiol 1994;474:473-482.
Harkin CP, Pagel PS, Tessmer JP, Warltier DC. Systemic and coronary hemodynamic actions and left ventricular functional effects of levosimendan in conscious dogs. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1995;26:179-188.
Pagel PS, Harkin CP, Hettrick DA, Warltier DC. Zatebradine, a specific bradycardic agent, alters the hemodynamic and left ventricular mechanical actions of levosimendan, a new myofilament calcium sensitizer, in conscious dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1995;275:127-135.
Bowman P, Haikala H, Paul RJ. Levosimendan, a calcium sensitizer in cardiac muscle, induces relaxation in coronary smooth muscle through calcium desensitization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1999;288:316-325.
Soei LK, Sassen LMA, Fan DS. Myofibrillar Ca2+ sensitization predominantly enhances function and mechanical efficiency of stunned myocardium. Circulation 1994;90:959-969.
Lilleberg J, Nieminen MS, Akkila J, et al. Effects of a new calcium sensitizer, levosimendan, on haemodynamics, coronary blood flow and myocardial substrate utilization early after coronary artery bypass grafting. Eur Heart J 1998;19:660-668.
Slogoff S, Keats AS. Randomized trial of primary anesthetic agents on outcome of coronary artery bypass operations. Anesthesiology 1989;70:179-188.
Nayler WG, Ferrari R, Williams A. Protective effect of pretreatment with verapamil, nifedipine and propranolol on myocardial function in the ischaemic and reperfused myocardium. Am J Cardiol 1980;46:242-248.
Mak IT, Weglicki WB. Protection by β-blocking agents against free radical-mediated sarcolemmal lipid peroxidation. Circ Res 1988;63:262-266.
Mak IT, Weglicki WB. Comparative anti-oxidant activities of propranolol, nifedipine, verapamil and diltiazem against sarcolemmal membrane lipid peroxidation. Circ Res 1990;66:1449-1452.
Du Toit EF, Muller CA, McCarthy J, Opie LH. Levosimendan: Effects of a calcium sensitizer on function and cyclic nucleotide levels during ischemia/reperfusion in the Langendorff perfused guinea pig heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1999;290:505-514.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lochner, A., Colesky, F. & Genade, S. Effect of a Calcium-Sensitizing Agent, Levosimendan, on the Postcardioplegic Inotropic Response of the Myocardium. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 14, 271–281 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007878523663
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007878523663