Abstract
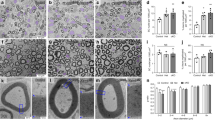
Myelin sheath formation depends on appropriate axo-glial interactions that are mediated by myelin-specific surface molecules. In this study, we have used quantitative morphological analysis to determine the roles of the prominent myelin lipids galactocerebroside (GalC) and sulfatide in both central and peripheral myelin formation, exploiting mutant mice incapable of synthesizing these lipids. Our results demonstrate a significant increase in uncompacted myelin sheaths, the frequency of multiple cytoplasmic loops, redundant myelin profiles, and Schmidt-Lanterman incisures in the CNS of these mutant mice. In contrast, PNS myelin appeared structurally normal in these animals; however, at post-natal day 10, greater than 10% of the axons withered and pulled away from their myelin sheaths. These results indicate that GalC and sulfatide are critical to the formation of CNS myelin. In contrast, PNS myelin formation is not dependent on these lipids; however, GalC and sulfatide appear to be instrumental in maintaining Schwann cell-axon contact during a specific developmental window.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbour, S., Edidin, M., Felding-Habermann, B., Taylor-Norton, J., Radin, N.S. & Fenderson, B.A. (1992) Glycolipid depletion using a ceramide analogue (PMDP) alters growth, adhesion, and membrane lipid organization in human A431 cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology 150, 610–9.
Bosio, A., Binczek, E. & Stoffel, W. (1996) Functional breakdown of the lipid bilayer of the myelin membrane in central and peripheral nervous system by disrupted galactocerebroside synthesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 93, 13280–5.
Bosio, A., Binczek, E., Haupt, F.W. & Stoffel, W. (1998a) Composition and biophysical properties of myelin lipid define the neurological defects in galactocerebroside and sulfatide-deficient mice. Journal of Neurochemistry 70, 308–15.
Bosio, A., Bussow, H., Adam, J. & Stoffel, W. (1998b) Galactosphingolipids and axono–glial interaction in myelin of the central nervous system. Cell and Tissue Research 292, 199–210.
Cestaro, B., Cervato, G., Marchesini, S., Viani, P., Pistolesi, E. & Oliva, C. (1983) Electron spin resonance studies on the dynamics of phosphatidylcholine-sulfatide model membranes. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 33, 251–62.
Coetzee, T., Fujita, N., Dupree, J., Shi, R., Blight, A., Suzuki, K., Suzuki, K. & Popko, B. (1996) Myelination in the absence of galactocerebroside and sulfatide: normal structure with abnormal function and regional instability. Cell 86, 209–19.
Coetzee, T., Suzuki, K. & Popko, B. (1998) New perspectives on the function of myelin galactolipids. Trends in Neuroscience 21, 126–30.
Cooper, N.A. & Kidman, A.D. (1984) Quantitation of the Schmidt–Lanterman incisures in juvenile, adult, remyelination and regenerated fibers of the chicken sciatic nerve. Acta Neuropathologica 64, 251–8.
Crossin, K.L. & Edelman, G.M. (1992) Specific binding of cytotactin to sulfated glycolipids. Journal of Neuroscience Research 33, 631–8.
Dupree, J. L., Coetzee, T., Blight, A., Suzuki, K. & Popko, B. (1998a) Myelin galactolipids are essential for proper node of Ranvier formation in the CNS. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 1642–9.
Dupree, J. L., Suzuki, K. & Popko, B. (1998b) Galactolipids in the formation and function of the myelin sheath. Microscopy Research and Technique 41, 431–40.
Fujita, N., Kemper, A., Dupree, J., Nakayasu, H., Bartsch, U., Schachner, M., Maeda, N., Suzuki, K., Suzuki, K. & Popko, B. (1998) The cytoplasmic domain of the large myelin-associated glycoprotein isoform is needed for the proper CNS but not peripheral nervous system myelination. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 1970–8.
Ghabriel, M.N. & Allt, G. (1980) Schmidt–Lanterman incisures II. A light and electron microscope study of remyelinating peripheral nerve fibres. Acta Neuropathologica 52, 97–104.
Gould, R.M., Byrd, A.L. & Barbarese, E. (1995) The number of Schmidt–Lanterman incisures is more than doubled in shiverer PNS myelin sheaths. Journal of Neurocytology 24, 85–98.
Griffiths, I.R. (1996) Myelin mutants: model systems for the study of normal and abnormal myelination. BioEssays 18, 189–97.
Hirano, A. & Dembitzer, H.M., (1967) A structural analysis of the myelin sheath in the central nervous system. Journal of Cell Biology 34, 555–67.
Hirano, A., Zimmerman, H.M. & Levine, S. Electron microscopic observations of peripheral myelin in a central nervous system lesion. Acta Neuropathologica 12, 348–65.
Klugmann, M., Schwab, M.H., Puhlhofer, A., Schneider, A., Zimmerman, F., Griffiths, I.R. & Nave, K.-A. (1997) Assembly of CNS myelin in the absence of proteolipid protein. Neuron 18, 59–70.
Knobler, R.L., Stempak, J. G. & Laurencin, M. (1974) Oligodendroglial ensheathment of axons during myelination in the developing rat central nervous system. Aserial section electron microscopical study. Journal of Ultrastructure Research 49, 34–49.
Kunishita, T., Uemura, K., Ohano, A. & Taketomi, T. (1979) Isolation of basic protein–acidic lipid complex. Japanese Journal of Experimental Medicine 49, 391–6.
Li, C., Tropak, M.B., Gerlai R., Clapoff, S., Abramow-Newerly, W., Trapp, B., Peterson, A. & Roder, J. (1994) Myelination in the absence of myelin-associated glycoprotein. Nature 369, 747–50.
Maggio, B. (1997) Molecular interactions of the major myelin glycosphingolipids and myelin basic protein in model membranes. Neurochemical Research 22, 475–81.
Maggio, B. & Yu, R.K. (1989) Interaction and fusion of unilamellar vesicles containing cerebrosides and sulfatides induced by myelin basic protein. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 51, 127–36.
Montag, D., Giese, K.P., Bartsch, U., Martini, R., Lang, Y., Bluthmann, H., Karthigasan, J., Kirschner, D. A., Wintergerst, E. S., Nave, K., Zielasek, J., Toyka, K.V., Lipp, H. & Schachner, M. (1994) Mice deficient for the myelin-associated glycoprotein show subtle abnormalities in myelin. Neuron 13, 229–46.
Morell, P. & Radin, N. S. (1969) Synthesis of cerebroside by brain from uridine diphosphate galactose and ceramide containing hydroxy fatty acid. Biochemistry 8, 506–12.
Pesheva, P., Gloor, S., Schachner, M. & Probtmeier, R. (1997) Tenascin-R is an intrinsic autocrine factor for oligodendrocyte differentiation and promotes cell adhesion by a sulfatide-mediated mechanism. Journal of Neuroscience 17, 4642–51.
Peters, A., Palay, S. L. & Webster, H. DeF. (1991) The Fine Structure of the Nervous System: Neurons and Their Supporting Cells, 3rd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Raff, M.C., Mirsky, R., Fields, K.L., Lisak, R. P., Dorfman, S.H., Silberberg, D.H., Gregson, N.A., Leibowitz, S. & Kennedy, M. C. (1978) Galactocerebroside is a specific cell-surface antigenic marker for oligodendrocytes in culture. Nature 274, 813–6.
Readhead, C., Popko, B., Takahashi, N. Shine, H. D., Saavedra, R. A., Sidman, R. L. & Hood, R.L. (1987) Expression of a myelin basic protein gene in transgenic shiverer mice: correction of the dysmyelinating phenotype. Cell 48, 703–12.
Roberts, D. & Ginsburg, V. (1988) Sulfated glycolipids and cell adhesion. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 267, 405–15.
Schaeren-Wiemers, N., Vander Bijl, P. & Schwab, M. D. (1995) The UDP-galactose:ceramide galactosyltransferase: expression pattern in oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells during myelination and substrate preference for hydroxyceramide. Journal of Neurochemistry 65, 2267–78.
Schulte, S. & Stoffel, W. (1993) Ceramide UDP galactosyltransferase from myelinating rat brain: purification, cloning and expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 90, 10265–9.
Stahl, N., Jurevics, H., Morell, P., Suzuki, K. & Popko, B. (1994) Isolation, characterization, and expression of cDNA clones that encode rat UDP-galactose: ceramide galactosyltransferase. Journal of Neuroscience Research 38, 234–42.
Stoffel, W. & Bosio, A. (1997) Myelin glycolipids and their functions. Current Opinions in Neurobiology 7, 654–61.
Vos, J.P., Lopes-Cardozo, M. & Gadella, B.M. (1994) Metabolic and functional aspects of sulfogalactolipids. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1211, 125–49.
Wintergerst, E. S., Fuss, B. & Bartsch, U. (1993) Localization of janusin mRNA in the central nervous system of the developing and adult mouse. European Journal of Neuroscience 5, 299–309.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dupree, J.L., Coetzee, T., Suzuki, K. et al. Myelin abnormalities in mice deficient in galactocerebroside and sulfatide. J Neurocytol 27, 649–659 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006908013972
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006908013972