Abstract
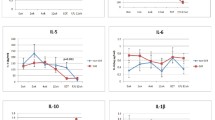
Virological response to interferon (IFN) is poor in patients with plasma levels of HCV RNA higher than 1 Meq/ml and genotype 1b hepatitis C viral infection. In 60 patients, a randomized control study was conducted to compare 3 MU of IFN-β twice daily for four weeks (group A) and 6 MU once a day for four weeks (group B) followed by a four-week administration of 6 MU once a day. The plasma levels of HCV RNA, determined by an amplicore-monitor method, for patients in group A were significantly lower than those for group B at the fourth and eighth day of IFN administration, and complete virological responses were noted in two patients from group A but none in group B. It is concluded that twice daily administration of 3 MU IFN-β is more effective than once a day 6 MU in the early phase of IFN therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFRENCES
Tsubota A, Chayama K, Ikeda, K, Yasuji A, Koida I, Saitoh S, Hashimoto H, Iwasaki S, Kobayashi M, Kumada H: Factors predictive of response to interferon-alfa therapy in hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 19:1088–1094, 1994
Yoshioka K, Kakumu S, Wakita T, Ishikawa T, Itoh Y, Takayanagi M, Higashi Y, Shibata M, Morishima T: Detection of hepatitis C virus by polymerase chain reaction and response to interferon-a therapy: Relationship to genotypes of hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 16:293–299, 1992
Martinot-Peignoux M, Marcellin P, Pouteau M, Castelnau C, Boyer N, Poliquin M, Degott C, Descombes I, LeBreton V, Milotova V: Pretreatment serum hepatitis C virus levels and hepatitis C virus genotypes are the main and independent prognostic factors of sustained interferon alpha therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 22:1050–1056, 1995
Matsumoto A, Tanaka E, Suzuki, Ogata H, Kiyosawa K: Viral and host factors that contribute to efficacy of interferon-alpha therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci 39:1273–1280, 1994
Okushin K, Morii K, Kishi F, Yuasa S: Efficacy of the combination therapy using twice-a-day IFN-b followed by IFN-a-2b in treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Kanzou 38:11–18, 1997
Okamoto H, Sugiyama Y, Okada S, Kurai K, Akahane Y, Sugai Y, Tanaka T, Sato K, Tsuda F, Miyakaw Y, Matumi T: Typing hepatitis C virus by polymerase chain reaction with type specific primers-application to clinical surveys and tracing infectious sources. J Gen Virol 73:673–679, 1992
Tsukiyama-Kohara K, Kohara M, Yamaguchi K, Maki N, Toyoshima A, Miki M, Tanaka S, Hattori N, Nomoto A: A second group of hepatitis C viruses. Virus Genes 5:243–254, 1991
Desmet VJ, Gerber M, Hoofnagle JH, Manns M, Scheuer PJ: Classification of chronic hepatitis- diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology 19:1513–1520, 1994
Enomoto N, Sakuma I, Asahina Y, Kurosaki M, Murakami T, Yamamoto C, Ogura Y, Izumi N, Marumo F, Sato C: Mutations in the nonstructural protein 5A gene and response to interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus 1b infection. N Engl J Med 334:77–81, 1996
Chayama K, Tsubota A, Kobayashi M, Okamoto K, Hashimoto M, Miyano Y, Koike H, Kobayashi M, Koida I, Arase Y, Saitoh S, Suzuki Y, Murashima N, Ikeda K, Kumada H: Pretreatment virus load and multiple amino acid substitutions in the interferon sensitivity-determining region predict the outcome of interferon treatment in patients with chronic genotype 1b hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 25:745–749, 1997
Iino S: Multi-center cooperative study for the response to interferon in chronic hepatitis C patients in Japan. Official report of Japanese Health and Welfare Ministry 1995, pp 72–73
Bellobuono A, Monddazzi L, Tempini S, Chiodo F, Magliano E, Mondini C, Ideo G: Should patients with early loss of serum HCVRNA during alpha interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C be treated for 6 or 12 months? J Hepatol 30:8–13, 1999
Ikeda K, Saitoh S, Arase Y, Chayama K, Suzuki Y, Kobayashi M, Tsubota A, Nakamura I, Murashima N, Kumada H, Kawanishi M: Effect of interferon therapy on hepatocellular carcinogenesis in patients with chronic hepatitis type C: A longterm observation study of 1,643 patients using statistical bias correlation with proportinal hazard analysis. Hepatology 29:1124–1130, 1999
Zeuzem S, Schmidt JM, Lee JH, Ruster B, Roth WK: Effect of interferon alfa on the dynamics of hepatitis C virus turnover in vivo. Hepatology 23:366–371, 1996
Neumann AU, Lam NP, Dahari H, Gretch DR, Wiley TE, Layden TJ, Pereison AS: Hepatitis C viral dynamics in vivo and the antiviral efficacy of interferon-alpha therapy. Science 282:103–107, 1998
Yasui K, Okanoue T, Murakami Y, Itoh Y, Minami M, Sakamoto S, Sakamoto M, Nishioji K: Dynamics of hepatitis C viremia following interferon-alpha administration. J Infect Dis 177:1475–1479, 1998
Zeuzem S, Schmidt JM, Lee JH, von Wagner M, Teuber G, Roth WK: Hepatitis C virus dynamics in vivo: Effect of ribavirin interferon alfa on viral turnover. Hepatology 28:245–252, 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Izumi, N., Kumada, H., Hashimoto, N. et al. Rapid Decrease of Plasma HCV RNA in Early Phase of Twice Daily Administration of 3 MU Doses Interferon-β in Patients with Genotype 1b Hepatitis C Infection. Dig Dis Sci 46, 516–523 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005686829416
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005686829416