Abstract
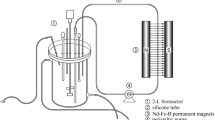
The growth of suspension cultures of Taxus chinensis var. mairei and Taxol production were promoted both by a sinusoidal alternating current magnetic field (50 Hz, 3.5 mT) and by a direct current magnetic field (3.5 mT). Taxol production increased rapidly from the 4th d with the direct current magnetic field but most slowly with the alternating current magnetic field. The maximal yield of Taxol was 490 μg l−1 with the direct current magnetic field and 425 μg l−1 with the alternating current magnetic field after 8 d of culture, which were, respectively, 1.4-fold and 1.2-fold of that without exposure to a magnetic field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fett-Neto AG, Zhang WY, DiCosmo F (1994) Kinetics of Taxol production, growth, and nutrient uptake in cell suspensions of Taxus caspidata. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 44: 205–210.
Gold S, Goodman R, Henderson AS (1994) Exposure of simian virus-40 transformed human cells to magnetic fields results in increased levels of T-antigen mRNA and protein. Bioelectromagnetics 15: 329–336.
Liburdy RP (1992) Calcium signaling in lymphocytes and ELF fields: evidence for an electric field metric and a site of interaction involving the calcium ion channel. FEBS Lett. 301: 53–59.
Lindström E, Lindström P, Berglund A, Lundgren E, Mild KH (1995) Intracellular calcium oscillations in a T-cell line after exposure to extremely-low-frequency magnetic fields with variable frequencies and flux denities. Bioelectromagnetics 16: 41–47.
Ryu DDY, Lee SO, Romani RJ (1990) Determination of growth rate for plant cell cultures: comparative studies. Biotechnol Bioeng. 35: 305–311.
Santini MT, Cametti C, Paradisi S, Straface E, Donelli G, Indovina PL, Malorni W (1995) 50 Hz sinusoidal magnetic field induces changes in the membrane electrical properties of K562 leukaemic cells. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 36: 39–45.
Yang LN, Wang J, Cheng DW (1999) Research of the biophysical mechanisms for the effects of constant magnetic field treatment of wheat seeds. J. Southwest Agr. Uni. 21: 342–344.
Yuan YJ, Wei ZJ, Wu ZL, Wu JC (2001a) Improved Taxol production in suspension cultures of Taxus cuspidata var. mairei by in situ extraction combined with feeding and additional carbon source introduction in an airlift loop reactor. Biotechnol. Lett. 23: 1659–1662.
Yuan YJ, Li C, Hu ZD, Wu C (2001b) Signal transduction pathway for oxidative burst and Taxol production in suspension cultures of Taxus chinensis var. mairei induced by oligosaccharide from Fusarium oxysprum. Enzyme Microbiol. Technol. 9: 372–379.
Yuan YJ, Li JC, Ge ZQ, Wu JC (2002) Superoxide anion burst and Taxol production induced by Ce4+ in suspension cultures of Taxus cuspidata. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 18: 251–260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, GM., Wu, JC. & Yuan, YJ. Improved cell growth and Taxol production of suspension-cultured Taxus chinensis var. mairei in alternating and direct current magnetic fields. Biotechnology Letters 26, 875–878 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:bile.0000025895.76394.ab
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:bile.0000025895.76394.ab