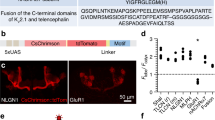
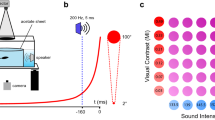
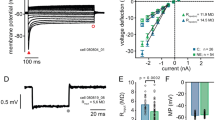
Abstract
The sea slug Hermissenda learns to associate light and hair cell stimulation, but not when the stimuli are temporally uncorrelated. Memory storage, which requires an elevation in calcium, occurs in the photoreceptors, which receive monosynaptic input from hair cells that sense acceleration stimuli such as turbulence. Both light and hair cell activity increase calcium concentration in the photoreceptor, but it is unknown whether paired calcium signals combine supralinearly to initiate memory storage. A correlate of memory storage is an enhancement of the long lasting depolarization (LLD) after light offset, which is attributed to a reduction in voltage dependent potassium currents; however, it is unclear what causes the LLD in the untrained animal.
These issues were addressed using a multi-compartmental computer model of phototransduction, calcium dynamics, and ionic currents of the Hermissenda photoreceptor. Simulations of the interaction between light and hair cell activity show that paired stimuli do not produce a greater calcium increase than unpaired stimuli. This suggests that hair cell activity is acting via some other pathway to initiate memory storage. In addition, simulations show that a potassium leak channel, which closes with an increase in calcium, is required to produce both the untrained LLD and the enhanced LLD due to the decrease in voltage dependent potassium currents. Thus, the expression of this correlate of classical conditioning may depend on a leak potassium current.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Urquidi J, Crow T (1995) Characterization of voltageactivated currents in Hermissenda type B photoreceptors. J. Neurosci. 15: 319-332.
Alkon DL, Anderson MJ, Kuzirian AJ, Rogers DF, Fass DM, Collin C, Nelson T, Kapetanovic, Matzel LD (1993) GABA-mediated synaptic interaction between the visual and vestibular pathways of Hermissenda. J. Neurochem. 61: 556-566.
Alkon DL, Farley J, Sakakibara M, Hay B (1984) Voltage-dependent calcium and calcium-activated potassium currents of a molluscan photoreceptor. Biophys. J. 46: 605-614.
Alkon DL, Naito S, Kubota M, Chen C, Bank B, Smallwood J, Gallant P, Rasmussen H (1988) Regulation of Hermissenda K+ channels by cytoplasmic and membrane-associated C-kinase. J. Neurochem. 51: 903-917.
Alkon DL, Sakakibara M (1985) Calcium activates and inactivates a photoreceptor soma potassium current. Biophys. J. 48: 983-995.
Alkon DL, Sakakibara M, Forman R, Harrigan J, Lederhendler II, Farley J (1985) Reduction of two voltage-dependant K+ currents mediates retention of a learned association. Behav. Neur. Biol. 44: 278-300.
Alkon DL, Shoukimas JJ, Heldman E (1982) Calcium-meditated decrease of a voltage-dependent potassium current. Biophys. J. 40: 245-250.
Allbritton NL, Meyer T, Stryer L (1992) Range of messenger action of calcium ion and inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate. Science 258: 1812-1815.
Berridge MJ, Galione A (1988) Cytosolic calcium oscillators. FASEB J. 2: 3074-3082.
Berthier NE, Moore JW (1986) Cerebellar Purkinje cell activity related to classically conditioned nictitating membrane response. Experim. Br. Res. 63: 341-350.
Bhatia J, Davies A, Gaudoin JB, Saibil HR (1996) Rhodopsin, Gq and phospholipase C activation in cephalopod photoreceptors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 35: 19-23.
Biddlecome GH, Berstein G, Ross EM (1996) Regulation of phospholipase C-β1, by Gq and m1 muscarinic cholinergic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 7999-8007.
Blackwell KT (2000) Evidence for a distinct light-induced calcium dependent potassium current in Hermissenda crassicornis. J. Comput. Neurosci. 9: 149-170.
Blackwell KT (2002a) Calcium waves and closure of potassium channels in response to GABA stimulation in Hermissenda type B photoreceptors. J. Neurophysiol. 87: 776-792.
Blackwell KT (2002b) The effect of intensity and duration on the light induced sodium and potassium currents in the Hermissenda type B photoreceptor. J. Neurosci. 22: 4217-4228.
Blackwell KT, Alkon DL (1999) Ryanodine receptor modulation of in vitro associative learning in Hermissenda crassicornis. Br. Res. 822: 114-125.
Blackwell KT, Hellgren-Kotaleski J (2002) Modeling the dynamics of second messenger pathways. In: Kotter R, ed. Neuroscience Databases. A Practical Guide, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp. 63-80.
Bower JM, Beeman D (1998) The Book of Genesis: Exploring Realistic Neural Models with the General Neural Simulation System. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Buckler KJ (1999) Background leak K+-currents and oxygen sensing in carotid body type 1 cells. Respir. Physiol. 115: 179-187.
Cai Y, Baxter DA, Crow T (2003) Computational study of enhanced excitability in Hermissenda: Membrane conductances modulated by 5-HT. J. Comput. Neurosci. 15: 105-121.
Connor J, Alkon DL (1984) Light-and voltage-dependant increases of calcium ion concentration in molluscan photoreceptors. J. Neurophysiol. 51: 745-751.
Crow T, Alkon DL (1980) Associative behavioral modification in Hermissenda: Cellular correlates. Science 209: 412-414.
Crow T, Forrester J (1986) Light paired with serotonin mimics the effect of conditioning on phototactic behavior of Hermissenda. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83: 7975-7978.
Crow T, Forrester J (1991) Light paired with serotonin in vivo produces both short-and long-term enhancement of generator potentials of identified B-photoreceptors in Hermissenda. J. Neurosci. 11: 608-617.
Crow T, Heldman E, Hacopian V, Enos R, Alkon DL (1979) Ultrastructure of photoreceptors in the eye of Hermissenda labelled with intracellular injections of horseradish peroxidase. J. Neurocyt. 8: 181-195.
Crow T, Tian LM (2002) Facilitation of monosynaptic and complex PSPs in type I interneurons of conditioned Hermissenda. J. Neurosci. 22: 7818-7824.
Donnelly DF (1999) K+ currents of glomus cells and chemosensory functions of carotid body. Respir. Physiol. 115: 151-160.
Dupont G, Goldbeter A (1994) Properties of intracellular Ca2+ waves generated by a model based on Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release. Biophys. J. 67: 2191-2204.
Eakin RM, Westfall JA, Dennis MJ (1967) Fine structure of the eye of a nudibranch mollusc, Hermissenda crassicornis. J. Cell. Sci. 2: 349-358.
Farley J (1987) Contingency learning and causal detection in Hermissenda: II. Cellular mechanisms. Behav. Neurosci. 101: 28-56.
Farley J (1988) Associative training results in persistent reduction in a calcium-activated potassium current in Hermissenda type B photoreceptors. Behav. Neurosci. 102: 784-802.
Farley J, Alkon DL (1982) Associative neural and behavioral change in Hermissenda: Consequences of nervous system orientation for light-and pairing-specificity. J. Neurophysiol. 48: 785-807.
Farley J, Auerbach S (1986) Protein kinase C activation induces conductance changes in Hermissenda photoreceptors like those seen in associative learning. Nature 319: 220-223.
Farley J, Han Y (1997) Ionic basis of learning-correlated excitability changes in Hermissenda type A photoreceptors. J. Neurophysiol. 77: 1861-1888.
Farley J, Richards WG, Grover LM (1990) Associative learning changes intrinsic to Hermissenda type A photoreceptors. Behav. Neurosci. 104: 135-152.
Flynn M, Cai Y, Baxter DA, Crow T (2003) A computational study of the role of spike broadening in synaptic facilitation of Hermissenda. J. Comput. Neurosci. 15: 29-41.
Fost JW, Clark GA (1996) Modeling Hermissenda: I. Differential contributions of IA and IC to type-B cell plasticity. J. Comput. Neurosci. 3: 137-153.
Frysztak RJ, Crow T (1994) Enhancement of type B and A photoreceptor inhibitory synaptic connections in conditioned Hermissenda. J. Neurosci. 14: 1245-1250.
Fujioka Y, Komeda M, Matsuoka S (2000) Stoichiometry of Na+-Ca2+ exchange in inside-out patches excised from guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J. Physiol. 523(Pt 2): 339-351.
Gall D, Gromada J, Susa I, Rorsman P, Herchuelz A, Bokvist K (1999) Significance of Na/Ca exchange for Ca2+ buffering and electrical activity in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Biophysi. J. 76: 2018-2028.
He Z, Tong Q, Quednau BD, Philipson KD, Hilgemann DW (1998) Cloning, expression, and characterization of the squid Na+-Ca2+ exchanger (NCX-SQ1). J. Gen. Physiol. 111: 857-873.
Hellgren Kotaleski J, Blackwell KT (2002) Sensitivity to interstimulus interval due to calcium interactions in the Purkinje cell spines. Neurocomput. 44-46: 13-18.
Hellgren Kotaleski J, Lester DS, Blackwell KT (2002) Subcellular interactions between parallel fibre and climbing fibre signals in Purkinje cells predict sensitivity of classical conditioning to interstimulus interval. Integr. Physiol. Behav. Sci. 37: 265-292.
Hirabayashi T, Kume K, Hirose K, Yokomizo T, Iino M, Itoh H, Shimizu T (1999) Critical duration of intracellular Ca2+ response required for continuous translocation and activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 5163-5169.
Hsiao CF, Trueblood PR, Levine MS, Chandler SH (1997) Multiple effects of serotonin on membrane properties of trigeminal motoneurons in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 77: 2910-2924.
Ito E, Oka K, Collin C, Schreurs BG, Sakakibara M, Alkon DL (1994) Intracellular calcium signals are enhanced for days after Pavlovian conditioning. J. Neurochem. 62: 1337-1344.
Jafri MS, Moore KA, Taylor GE, Weinreich D (1997) Histamine H1 receptor activation blocks two classes of potassium current, IK(rest) and IAHP, to excite ferret vagal afferents. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 503: 533-546.
Jones KA, Baughman RW (1992) Muscarinic M3 receptors inhibit a leak conductance in rat corticocallosal neurons. Neuro Report 3: 889-892.
Land PW, Crow T (1985) Serotonin immunoreactivity in the circumesophageal nervous system of Hermissenda crassicornis. Neurosci. Lett. 62: 199-205.
Lederhendler II, Alkon DL (1989) The interstimulus interval and classical conditioning in the marine snail Hermissenda crassicornis. Behav. Br. Res. 35: 75-80.
Lester DS, Collin C, Etcheberrigaray R, Alkon DL (1991) Arachidonic acid and diacyglcerol act synergistically to activate protein kinase C in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophysi. Res. Communic. 179: 1522-1528.
Levitan IB (1999) It is calmodulin after all! Mediator of the calcium modulation of multiple ion channels. Neuron. 22: 645-648.
Li Y-X, Rinzel J (1994) Equations for InsP3 receptor-mediated [Ca2+]; oscillations derived from a detailed kinetic model: A Hodgkin-Huxley like formalism. J. Theor. Biol. 166: 461-473.
Matzel LD, Muzzio IA, Rogers RF (1995) Diverse current and voltage responses to baclofen in an identified molluscan photoreceptor. J. Neurophysiol. 74: 506-518.
Matzel LD, Rogers RF (1993) Postsynaptic calcium, but not cumulative depolarization, is necessary for the induction of associative plasticity in Hermissenda. J. Neurosci. 13: 5029-5040.
Matzel LD, Schreurs BG, Lederhendler II, Alkon DL (1990) Acquisition of conditioned associations in Hermissenda: Additive effects of contiguity and the forward interstimulus interval. Behav. Neurosci. 104: 597-606.
Mayeenuddin LH, Bamsey C, Mitchell J (2001) Retinal phospholipase C from squid is a regulator of Gqα GTPase activity. J. Neurochem. 78: 1350-1358.
McPhie DL, Matzel LD, Olds JL, Lester DS, Kuzirian AM, Alkon DL (1993) Cell specificity of molecular changes during memory storage. J. Neurochem. 60: 646-651.
Mitchell J, Gutierrez J, Northup JK (1995) Purification, characterization, and partial amino acids sequence of a G protein-activated phospholipase C from squid photoreceptors. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 854-859.
Mitchell J, Mayeenuddin LH (1998) Purification, G protein activation, and partial amino acid sequence of a novel phospholipase C from squid photoreceptors. Biochem. 37: 9064-9072.
Mo JL, Blackwell KT (2003) Comparison of Hermissenda type A and type B photoreceptor's response to light as a function of intensity and duration. J. Neurosci. 23: 8020-8028.
Mukhopadhyay S, Ross EM (1999) Rapid GTP binding and hydrolysis by G(q) promoted by receptor and GTPase-activating proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 9539-9544.
Muzzio IA, Talk AC, Matzel LD (1998) Intracellular Ca2+ and adaption of voltage responses to light in Hermissenda photoreceptors. NeuroReport 9: 1625-1631.
Nicholls JG, Martin AR, Wallace BG (2000) From Neuron to Brain. Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland, MA.
Pedarzani P, Mosbacher J, Rivard A, Cingolani LA, Oliver D, Stocker M, Adelman JP, Fakler B (2001) Control of electrical activity in central neurons by modulating the gating of small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 9762-9769.
Rogers RF, Talk AC, Matzel LD (1994) Trial-spacing effects in Hermissenda suggest contributions of associative and nonassociative cellular mechanisms. Behav. Neurosci. 108: 1030-1042.
Sakakibara M, Alkon DL, Kouchi T, Inoue H, Yoshioka T (1994) Induction of photoresponse by the hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositides in the Hermissenda type B photoreceptors. Biochem. Biophysi. Res. Communic. 202: 299-306.
Sakakibara M, Ikeno H, Usui S, Collin C, Alkon DL (1993) Reconstruction of ionic currents in a molluscan photoreceptor. Biophysi. J. 65: 519-527.
Sakakibara M, Inoue H, Yoshioka T (1998) Evidence for the involvement of inositol triphosphate but not cyclic nucleotides in visual transduction in Hermissenda eye. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 20795-20801.
Schachter JB, Lester DS, Alkon DL (1996) Synergistic activation of protein kinases C by arachidonic acid and diacylglycerols in vitro: Generation of stable membrane-bound, cofactor-independent state of protein kinase C activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1291: 167-176.
Schreurs BG, Gusev PA, Tomsic D, Alkon DL, Shi T (1998) Intracellular correlates of acquisition and long-term memory of classical conditioning in Purkinje cell dendrites in slices of rabbit cerebellar lobule HVI. J. Neurosci. 18: 5498-5507.
Shirai Y, Kashiwagi K, Yagi K, Sakai N, Saito N (1998) Distinct effects of fatty acids on translocation of gamma-and epsilonsubspecies of protein kinase c. J. Cell Biology 143: 511-521.
Smrcka AV, Hepler JR, Brown KO, Sternweis PC (1991) Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science 251: 804-807.
Stensaas LJ, Stensaas SS, Trujillo-Cenoz O (1969) Some morphological aspects of the visual system of Hermissenda crassicornis (Mollusca: Nudibranchia). J. Ultrastr. Res. 27: 510-532.
Suzuki T, Terakita A, Narita K, Nagai K, Tsukahara Y, Kito Y (1995) Squid photoreceptor phospholipase C is stimulated by membrane Gqα but not by soluble Gqα. FEBS 377: 333-337.
Szuts EA (1993) Concentrations of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate within the distal segment of squid photoreceptors. Vis. Neurosci. 10: 921-929.
Talk AC, Matzel LD (1996) Calcium influx and release from intracellular stores contribute differentially to activity-dependent neuronal facilitation in Hermissenda photoreceptors. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 66: 183-197.
Talk AC, Muzzio IA, Matzel LD (1997) Phospholipases and arachidonic acid contribute independently to sensory transduction and associative neuronal facilitation in Hermissenda type B photoreceptors. Br. Res. 751: 196-205.
Talley EM, Lei Q, Sirois JE, Bayliss DA (2000) TASK-1, a two-pore domain K+ channel, is modulated by multiple neurotransmitters in motoneurons. Neuron. 25: 399-410.
Tamse CT, Yamoah EN (2002) Elementary properties of axonal calcium currents in type B photoreceptors in Hermissenda crassicornis. J. Neurosci. 22: 10533-10538.
Tang Y, Othmer HG (1994) A model of calcium dynamics in cardiac myocytes based on the kinetics of ryanodine-sensitive calcium channels. Biophysi. J. 67: 2223-2235.
Trafford AW, Lipp P, O'Neill SC, Niggli E, Eisner DA (1995) Propagating calcium waves initiated by local caffeine application in rat ventricular myocytes. J. Physiol. 489: 319-326.
Wang SS, DenkW, Hausser M (2000) Coincidence detection in single dendritic spines mediated by calcium release. Nat. Neurosci. 3: 1266-1273.
West A, Barnes E, Alkon DL (1982) Primary changes of voltage responses during retention of associative learning. J. Neurophysiol. 48: 1243-1255.
Yamoah EN, Crow T (1994) Two components of calcium currents in the soma of photoreceptors of Hermissenda. J. Neurophysiol. 72: 1327-1336.
Yamoah EN, Kuzirian AM, Sanchez-Andres JV (1994) Calcium current and inactivation in identified neurons in Hermissenda crassicornis. J. Neurophysiol. 72: 2196-2208.
Yamoah EN, Matzel LD, Crow T (1998) Expression of different types of inward rectifier currents confers specificity of light and dark responses in type A and B photoreceptors of Hermissenda. J. Neurosci. 18: 6501-6511.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blackwell, K.T. Paired Turbulence and Light do not Produce a Supralinear Calcium Increase in Hermissenda . J Comput Neurosci 17, 81–99 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JCNS.0000023866.88225.03
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JCNS.0000023866.88225.03