Abstract
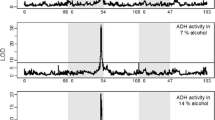
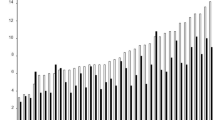
Enzyme activity variation was studied in a Drosophila melanogaster population from two villages (Tiszafüred and Tiszaszőlős) in Hungary. Two habitats (distillery and farmyard) were sampled in both villages and 8–9 isofemale lines were established from each sample with a total of 35 lines. The activities of ADH, αGPDH, IDH and 6PGDH were determined on starch gel after electrophoresis in 10 F1 females of each of the 35 isofemale lines. Three sublines were established from three selected isofemale lines of all four samples (altogether 36 sublines). Alcohol tolerance of the adult flies was assayed in these sublines. The activity of ADH was similar in the two habitats; so was the sensitivity to ethanol. Accordingly, no differences in adaptation to environmental ethanol were detected between the two habitats. The deviations between the two habitats in average activities and in the total variation of enzyme activities were not consistent in the two villages. These results suggest that founder effects and genetic drift are more pronounced in distilleries than selection. The association among enzyme activities varied greatly both between the two villages and between the two habitats. The two parameters of alcohol tolerance were not significantly different between the two habitats in any of the two villages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bokor, K. & K. Pecsenye, 1998. Comparative influence of Odhand Adhloci on alcohol tolerance in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet. Sel. Evol. 30: 503–516.
Briscoe, D. A., A. Robertson & J. Malpica, 1975. Dominance at the Adhlocus in response of adult Drosophila melanogasterto environmental alcohol. Nature 255: 148.
Crawley, M. J., 1993. GLIM for Ecologists. Blackwell Scientific Publications, London.
Dickinson, W. J. & D. T. Sullivan, 1975. Gene-enzyme Systems in Drosophila. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Francis, B., M. Green & C. Payne, 1994. GLIM 4. The Statistical System for Generalised Linear Interactive Modelling. University Press Inc., New York.
Geer, B.W., M. L. Langevin & S.W. McKechnie, 1985. Dietary ethanol and lipid synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem. Genet. 23: 607–622.
Gibson, J. B. & A. V. Wilks, 1988. The alcohol dehydrogenase polymorphism of Drosophila melanogasterin relation to environmental ethanol, ethanol tolerance and alcohol dehydrogenase activity. Heredity 60: 403–414.
Hickey, D. A. & M. D. McLean, 1980. Selection for ethanol tolerance and Adhallozymes in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetical Res., CA 36: 11–15.
Karan, D., R. Prakash & J. R. David, 1999. Microspatial differentiation for tolerance and utilization of various alcohols and acetic acid in Drosophilaspecies from India. Genetica 105: 249–258.
McCullagh P. & J. A. Nelder, 1989. Generalized Linear Models. 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, London.
McKenzie, J. A. & S. W. McKechnie, 1979. A comparative study of resource utilization in natural populations of Drosophila melanogasterand D. simulans. Oecologia 40: 299–309.
O'Brien, S. J. & MacIntyre, R. J. 1978. Genetics and biochemistry of enzymes and specific proteins of Drosophila, pp. 395–551 in The Genetics and Biology of Drosophila, Vol. 2a, edited by Ashburner, M. and T. R. F. Wright. Academic Press, London.
Oudman, L., W. van Delden, A. Kamping & R. Bijlsma, 1991. Polymorphism at the Adhand Gpdhloci in Drosophila melanogaster: effects of rearing temperature on developmental rate, body weight, and some biochemical parameters. Heredity 67: 103–115.
Pecsenye, K., 1998. Detection of individual variation in enzyme activity in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Hereditas 128: 145–151.
Pecsenye, K. & E. Meglécz, 1995. Enzyme polymorphism in Drosophila melanogasterpopulations collected in two different habitats in Hungary. Genetica 96: 257–268.
Pecsenye, K. & A. Saura, 2002. Structure of variation in enzyme activity in natural Drosophila melanogasterpopulations. Hereditas 136: 75–83.
Vouidibio, J., P. Capy, D. Defaye, E. Pla, J. Sandrin, A. Csink & J. R. David 1989. Short-range genetic structure of Drosophila melanogasterpopulations in an Afrotropical urban area and its significance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 86: 8442–8446.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pecsenye, K., Saura, A. Enzyme Activities and Alcohol Tolerance in Isofemale Lines of Drosophila melanogaster Originating from Different Habitats. Genetica 121, 277–283 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000039845.52698.f3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000039845.52698.f3